NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.

LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
The natural or "first generation" penicillins are bactericidal antibiotics naturally derived from the mold, Penicillium chrysogenum. Their basic structure includes a thiazolidine ring connected to a beta-lactam ring with a variable side chain. Penicillins bind to bacterial proteins and inhibit synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, causing cell lysis particularly in rapidly growing organisms. Bacterial resistance to penicillin is usually mediated by beta-lactamase, an enzyme which destroys the beta-lactam ring of penicillin, rendering it inactive. Penicillin was introduced into medicine in the 1940’s and ushered in the modern era of antibiotic therapy, ending the dominance of many diseases that had been major causes of morbidity and mortality. At present, several first generation penicillins are available in the United States: the benzathine, potassium, procaine and sodium salts of penicillin G and the orally available penicillin V potassium. These agents are discussed together as they are rare causes of hepatotoxicity and can be considered similar enough to be grouped together.
Drug Class: Antiinfective Agents
The following are links to each drug record:
CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND STRUCTURES
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NO | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillin G (Benzylpenicillin) | 61-33-6 | C16-H18-N2-O4-S |
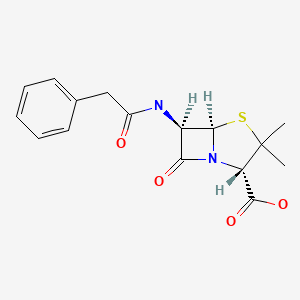
|
| Penicillin G Sodium | 69-57-8 | C16-H18-N2-O4-S |
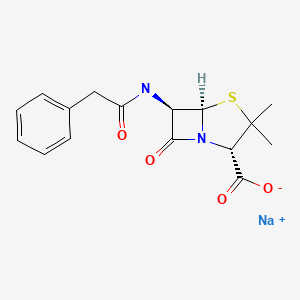
|
| Penicillin G Potassium | 113-98-4 | C16-H18-N2-O4-S.K |
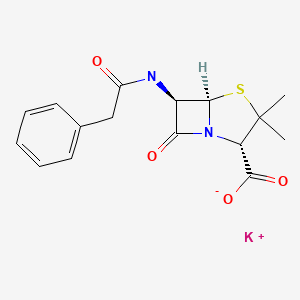
|
| Penicillin V | 87-08-1 | C16-H18-N2-O5-S |
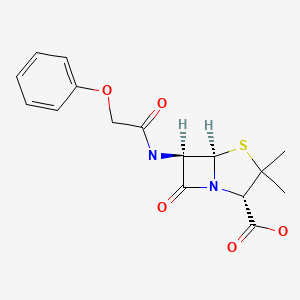
|
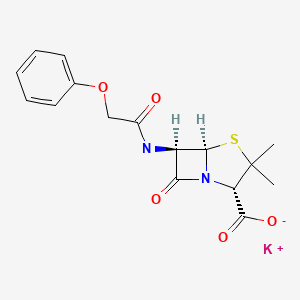
| Penicillin V Potassium | 132-98-9 | C16-H17-K-N2-O5-S C16-H17-N2-O5-S.K C16-H18-N2-O5-S.K |
|
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- Review Penicillins (4th Generation).[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Penicillins (4th Generation).. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Penicillins (3rd Generation).[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Penicillins (3rd Generation).. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Cephalosporins.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Cephalosporins.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Production of beta-lactam antibiotics and its regulation.[Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub Chin...]Review Production of beta-lactam antibiotics and its regulation.Demain AL. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1991 Oct; 15(4):251-65.
- Specificity of penicillin acylase of Fusarium and of Penicillium chrysogenum.[Appl Microbiol. 1968]Specificity of penicillin acylase of Fusarium and of Penicillium chrysogenum.Vanderhaeghe H, Claesen M, Vlietinck A, Parmentier G. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct; 16(10):1557-63.
- Penicillins (1st Generation) - LiverToxPenicillins (1st Generation) - LiverTox
- Isotretinoin - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Isotretinoin - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
- Anabolic Steroids - StatPearlsAnabolic Steroids - StatPearls
- Loeys-Dietz Syndrome, Type 1bLoeys-Dietz Syndrome, Type 1bMedGen
- C2674876[conceptid] (1)MedGen
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...