NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.

LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Biperiden is an oral anticholinergic agent used predominantly in the symptomatic therapy of Parkinson disease and movement disorders. Biperiden has not been associated with serum enzyme elevations during treatment and must be a very rare cause of clinically apparent acute liver injury, if it occurs at all.
Background
Biperiden (bye per' i den) is an anticholinergic agent that blocks the central cholinergic receptors, helping to balance cholinergic transmission in the basal ganglia. Biperiden may also block dopamine reuptake and storage in central sites thus increasing dopaminergic activity. The exact mechanism(s) by which the anticholinergic agents are beneficial for symptoms of Parkinson disease is unknown. They are used largely in early Parkinsonism and as adjunctive therapy with levodopa or more potent antiParkinson disease agents. Biperiden was approved for use in the United States in 1959 and has been in use since. Current indications include therapy of symptomatic Parkinson disease as well as spastic disorders and extrapyramidal disorders due to medications. Biperiden is available in tablets of 2 mg in generic forms and under the brand name of Akineton. The recommended dose is 2 mg three to four times daily. Common side effects are due to its anticholinergic activity and include nervousness, drowsiness, confusion, tachycardia, blurred vision, constipation, dry mouth, nausea and urinary retention.
Hepatotoxicity
Biperiden has not been reported to cause serum aminotransferase elevations, but it has not been evaluated for effects on serum enzyme levels in a prospective manner. Despite its use for more than 50 years, there have been no reports of biperiden liver injury in the literature and it must be a very rare cause of liver injury, if it occurs at all.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Drug Class: Antiparkinson Agents
Other Drugs in the Subclass, Anticholinergic Agents: Benztropine, Trihexyphenidyl
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Biperiden – Akineton®
DRUG CLASS
Antiparkinson Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
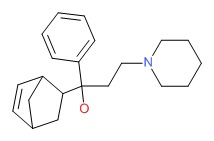
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biperiden | 514-65-8 | C21-H29-N-O |
 |
REFERENCES
References updated: 20 July 2017
- Zimmerman HJ. Antiparkinsonism drugs. In, Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1999, pp. 715-7.(Expert review of hepatotoxicity published in 1999; among anticholinergic agents, "only trihexyphenidyl has been incriminated in hepatic injury"; other antiparkinsonism drugs discussed include levodopa, lergotrile [no longer available], pergolide and bromocriptine).
- Larrey D, Ripault MP. Hepatotoxicity of psychotropic drugs and drugs of abuse. In, Kaplowitz N, DeLeve LD, eds. Drug-induced liver disease. 3rd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc, 2013, pp. 443-62.(Review of hepatotoxicity of agents acting on the central nervous system).
- Standaert DG, Roberson ED. Treatment of central nervous system degenerative disorders. In, Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 12th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2011, pp. 609-28.(Textbook of pharmacology and therapeutics).
- McDowell F. Symposium on levodopa in Parkinson's disease. Clinical and pharmacological aspects. Clinical laboratory abnormalities. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1971; 12: 335-9. [PubMed: 4102803](Retrospective analysis of laboratory abnormalities arising in 974 patients with Parkinson disease treated with levodopa; AST elevations occurred in 9% of 5427 determinations, but were usually mild and transient returning to normal in 1-2 months without dose adjustment; AST levels rose to 1600 U/L in one patient who later died of complications of diabetes).
- Lambert D, Waters CH. Comparative tolerability of the newer generation antiparkinsonian agents. Drugs Aging 2000; 16: 55-65. [PubMed: 10733264](Review of mechanism of action, tolerability and safety of selegiline, pramipexole, ropinirole, tolcapone and entacapone in Parkinson disease).
- Reuben A, Koch DG, Lee WM; Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Drug-induced acute liver failure: results of a U.S. multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology 2010; 52: 2065-76. [PMC free article: PMC3992250] [PubMed: 20949552](Among 1198 patients with acute liver failure enrolled in a US prospective study between 1998 and 2007, 133 were attributed to drug induced liver injury, but none were attributed to agents used for Parkinson disease).
- Björnsson ES, Bergmann OM, Björnsson HK, Kvaran RB, Olafsson S. Incidence, presentation, and outcomes in patients with drug-induced liver injury in the general population of Iceland. Gastroenterology 2013; 144: 1419-25,1425. [PubMed: 23419359](In a population based study of drug induced liver injury from Iceland, 96 cases were identified over a 2 year period, but none of the 96 were attributed to an agent used to treat Parkinson disease).
- Drugs for Parkinson's disease. Treat Guidel Med Lett 2013; 11 (135): 101-6. [PubMed: 24165688](Concise review of recommendations for therapy of Parkinson disease with description of mechanisms of action, efficacy and adverse events).
- Hernández N, Bessone F, Sánchez A, di Pace M, Brahm J, Zapata R, A Chirino R, et al. Profile of idiosyncratic drug induced liver injury in Latin America: an analysis of published reports. Ann Hepatol 2014; 13: 231-9. [PubMed: 24552865](Among 176 reports of drug induced liver injury from Latin America published between 1996 and 2012, none were attributed to an agent to treat Parkinson disease).
- Chalasani N, Bonkovsky HL, Fontana R, Lee W, Stolz A, Talwalkar J, Reddy KR, et al.; United States Drug Induced Liver Injury Network. Features and outcomes of 899 patients with drug-induced liver injury: The DILIN Prospective Study. Gastroenterology 2015; 148: 1340-52. [PMC free article: PMC4446235] [PubMed: 25754159](Among 899 cases of drug induced liver injury from the US enrolled in a prospective database between 2004 and 2012, none were attributed to an agent used to treat Parkinson disease).
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Benztropine.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Benztropine.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Trihexyphenidyl.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Trihexyphenidyl.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- [Delirium syndrome in biperiden poisoning].[Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 1988][Delirium syndrome in biperiden poisoning].Hewer W, Biedert S. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 1988 Apr; 56(4):133-6.
- The movement pattern of oral tardive dyskinesia in relation to anticholinergic and antidopaminergic treatment.[Int Pharmacopsychiatry. 1976]The movement pattern of oral tardive dyskinesia in relation to anticholinergic and antidopaminergic treatment.Gerlach J, Thorsen K. Int Pharmacopsychiatry. 1976; 11(1):1-7.
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome Improved with Intramuscular Administration of the Anticholinergic Agent, Biperiden.[Int Med Case Rep J. 2023]Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome Improved with Intramuscular Administration of the Anticholinergic Agent, Biperiden.Nisijima K. Int Med Case Rep J. 2023; 16:281-286. Epub 2023 May 12.
- Biperiden - LiverToxBiperiden - LiverTox
- The Effects of Tobacco Use on Health - Public Health Implications of Raising the...The Effects of Tobacco Use on Health - Public Health Implications of Raising the Minimum Age of Legal Access to Tobacco Products
- Innovation and the Orphan Drug Act, 1983-2009: Regulatory and Clinical Character...Innovation and the Orphan Drug Act, 1983-2009: Regulatory and Clinical Characteristics of Approved Orphan Drugs - Rare Diseases and Orphan Products
- alcohol dehydrogenase [Candida albicans]alcohol dehydrogenase [Candida albicans]gi|576627|gb|AAA53300.1|Protein
- LINC02752 long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2752 [Homo sapiens]LINC02752 long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2752 [Homo sapiens]Gene ID:105376550Gene
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...