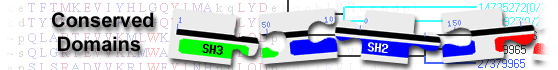epidermal growth factor-like protein 8 precursor [Mus musculus]
EMI and EGF_CA domain-containing protein( domain architecture ID 10540656)
EMI and EGF_CA domain-containing protein
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| EMI | pfam07546 | EMI domain; The Pfam alignment is truncated at the C-terminus and does not include the final ... |
37-102 | 2.27e-19 | ||
EMI domain; The Pfam alignment is truncated at the C-terminus and does not include the final cysteine defined in Callebaut et al. This is to stop the family overlapping with other domains. : Pssm-ID: 462204 Cd Length: 69 Bit Score: 80.16 E-value: 2.27e-19
|
||||||
| EGF_CA | smart00179 | Calcium-binding EGF-like domain; |
144-183 | 2.38e-05 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF-like domain; : Pssm-ID: 214542 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 39 Bit Score: 40.69 E-value: 2.38e-05
|
||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| EMI | pfam07546 | EMI domain; The Pfam alignment is truncated at the C-terminus and does not include the final ... |
37-102 | 2.27e-19 | ||
EMI domain; The Pfam alignment is truncated at the C-terminus and does not include the final cysteine defined in Callebaut et al. This is to stop the family overlapping with other domains. Pssm-ID: 462204 Cd Length: 69 Bit Score: 80.16 E-value: 2.27e-19
|
||||||
| EGF_CA | smart00179 | Calcium-binding EGF-like domain; |
144-183 | 2.38e-05 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF-like domain; Pssm-ID: 214542 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 39 Bit Score: 40.69 E-value: 2.38e-05
|
||||||
| EGF_CA | cd00054 | Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular ... |
144-183 | 1.26e-04 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular (mostly animal) proteins. Many of these proteins require calcium for their biological function and calcium-binding sites have been found to be located at the N-terminus of particular EGF-like domains; calcium-binding may be crucial for numerous protein-protein interactions. Six conserved core cysteines form three disulfide bridges as in non calcium-binding EGF domains, whose structures are very similar. EGF_CA can be found in tandem repeat arrangements. Pssm-ID: 238011 Cd Length: 38 Bit Score: 38.77 E-value: 1.26e-04
|
||||||
| EGF_CA | pfam07645 | Calcium-binding EGF domain; |
144-172 | 2.73e-03 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF domain; Pssm-ID: 429571 Cd Length: 32 Bit Score: 34.91 E-value: 2.73e-03
|
||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| EMI | pfam07546 | EMI domain; The Pfam alignment is truncated at the C-terminus and does not include the final ... |
37-102 | 2.27e-19 | ||
EMI domain; The Pfam alignment is truncated at the C-terminus and does not include the final cysteine defined in Callebaut et al. This is to stop the family overlapping with other domains. Pssm-ID: 462204 Cd Length: 69 Bit Score: 80.16 E-value: 2.27e-19
|
||||||
| EGF_CA | smart00179 | Calcium-binding EGF-like domain; |
144-183 | 2.38e-05 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF-like domain; Pssm-ID: 214542 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 39 Bit Score: 40.69 E-value: 2.38e-05
|
||||||
| EGF_CA | cd00054 | Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular ... |
144-183 | 1.26e-04 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular (mostly animal) proteins. Many of these proteins require calcium for their biological function and calcium-binding sites have been found to be located at the N-terminus of particular EGF-like domains; calcium-binding may be crucial for numerous protein-protein interactions. Six conserved core cysteines form three disulfide bridges as in non calcium-binding EGF domains, whose structures are very similar. EGF_CA can be found in tandem repeat arrangements. Pssm-ID: 238011 Cd Length: 38 Bit Score: 38.77 E-value: 1.26e-04
|
||||||
| vWA_Matrilin | cd01475 | VWA_Matrilin: In cartilaginous plate, extracellular matrix molecules mediate cell-matrix and ... |
119-182 | 5.94e-04 | ||
VWA_Matrilin: In cartilaginous plate, extracellular matrix molecules mediate cell-matrix and matrix-matrix interactions thereby providing tissue integrity. Some members of the matrilin family are expressed specifically in developing cartilage rudiments. The matrilin family consists of at least four members. All the members of the matrilin family contain VWA domains, EGF-like domains and a heptad repeat coiled-coiled domain at the carboxy terminus which is responsible for the oligomerization of the matrilins. The VWA domains have been shown to be essential for matrilin network formation by interacting with matrix ligands. Pssm-ID: 238752 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 224 Bit Score: 40.45 E-value: 5.94e-04
|
||||||
| EGF_CA | pfam07645 | Calcium-binding EGF domain; |
144-172 | 2.73e-03 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF domain; Pssm-ID: 429571 Cd Length: 32 Bit Score: 34.91 E-value: 2.73e-03
|
||||||
| FXa_inhibition | pfam14670 | Coagulation Factor Xa inhibitory site; This short domain on coagulation enzyme factor Xa is ... |
155-183 | 3.08e-03 | ||
Coagulation Factor Xa inhibitory site; This short domain on coagulation enzyme factor Xa is found to be the target for a potent inhibitor of coagulation, TAK-442. Pssm-ID: 464251 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 36 Bit Score: 34.53 E-value: 3.08e-03
|
||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|