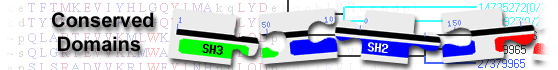chloride intracellular channel, isoform A [Drosophila melanogaster]
GST_N_CLIC and GST_C_CLIC domain-containing protein( domain architecture ID 10122793)
GST_N_CLIC and GST_C_CLIC domain-containing protein
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| GST_C_CLIC | cd03198 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channels; Glutathione S-transferase ... |
118-232 | 8.52e-58 | |||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channels; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLICs (CLIC1-6 in vertebrates), p64, parchorin, and similar proteins. They are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. Biochemical studies of the Caenorhabditis elegans homolog, EXC-4, show that the membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. CLICs display structural plasticity, with CLIC1 adopting two soluble conformations. The structure of soluble human CLIC1 reveals that it is monomeric and adopts a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. Upon oxidation, the N-terminal domain of CLIC1 undergoes a structural change to form a non-covalent dimer stabilized by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between two cysteines that are far apart in the reduced form. The CLIC1 dimer bears no similarity to GST dimers. The redox-controlled structural rearrangement exposes a large hydrophobic surface, which is masked by dimerization in vitro. In vivo, this surface may represent the docking interface of CLIC1 in its membrane-bound state. The two cysteines in CLIC1 that form the disulfide bond in oxidizing conditions are essential for dimerization and chloride channel activity, however, in other subfamily members, the second cysteine is not conserved. : Pssm-ID: 198307 Cd Length: 119 Bit Score: 180.11 E-value: 8.52e-58
|
|||||||
| GST_N_CLIC | cd03061 | GST_N family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLIC1-5, p64, ... |
18-112 | 1.53e-40 | |||
GST_N family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLIC1-5, p64, parchorin and similar proteins. They are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states, and are found in various vesicles and membranes. Biochemical studies of the C. elegans homolog, EXC-4, show that the membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. The structure of soluble human CLIC1 reveals that it is monomeric and it adopts a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a TRX fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. Upon oxidation, the N-terminal domain of CLIC1 undergoes a structural change to form a non-covalent dimer stabilized by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between two cysteines that are far apart in the reduced form. The CLIC1 dimer bears no similarity to GST dimers. The redox-controlled structural rearrangement exposes a large hydrophobic surface, which is masked by dimerization in vitro. In vivo, this surface may represent the docking interface of CLIC1 in its membrane-bound state. The two cysteines in CLIC1 that form the disulfide bond in oxidizing conditions are essential for dimerization and chloride channel activity, however, in other subfamily members, the second cysteine is not conserved. : Pssm-ID: 239359 Cd Length: 91 Bit Score: 134.81 E-value: 1.53e-40
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||||
| GST_C_CLIC | cd03198 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channels; Glutathione S-transferase ... |
118-232 | 8.52e-58 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channels; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLICs (CLIC1-6 in vertebrates), p64, parchorin, and similar proteins. They are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. Biochemical studies of the Caenorhabditis elegans homolog, EXC-4, show that the membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. CLICs display structural plasticity, with CLIC1 adopting two soluble conformations. The structure of soluble human CLIC1 reveals that it is monomeric and adopts a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. Upon oxidation, the N-terminal domain of CLIC1 undergoes a structural change to form a non-covalent dimer stabilized by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between two cysteines that are far apart in the reduced form. The CLIC1 dimer bears no similarity to GST dimers. The redox-controlled structural rearrangement exposes a large hydrophobic surface, which is masked by dimerization in vitro. In vivo, this surface may represent the docking interface of CLIC1 in its membrane-bound state. The two cysteines in CLIC1 that form the disulfide bond in oxidizing conditions are essential for dimerization and chloride channel activity, however, in other subfamily members, the second cysteine is not conserved. Pssm-ID: 198307 Cd Length: 119 Bit Score: 180.11 E-value: 8.52e-58
|
||||||||
| GST_N_CLIC | cd03061 | GST_N family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLIC1-5, p64, ... |
18-112 | 1.53e-40 | ||||
GST_N family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLIC1-5, p64, parchorin and similar proteins. They are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states, and are found in various vesicles and membranes. Biochemical studies of the C. elegans homolog, EXC-4, show that the membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. The structure of soluble human CLIC1 reveals that it is monomeric and it adopts a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a TRX fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. Upon oxidation, the N-terminal domain of CLIC1 undergoes a structural change to form a non-covalent dimer stabilized by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between two cysteines that are far apart in the reduced form. The CLIC1 dimer bears no similarity to GST dimers. The redox-controlled structural rearrangement exposes a large hydrophobic surface, which is masked by dimerization in vitro. In vivo, this surface may represent the docking interface of CLIC1 in its membrane-bound state. The two cysteines in CLIC1 that form the disulfide bond in oxidizing conditions are essential for dimerization and chloride channel activity, however, in other subfamily members, the second cysteine is not conserved. Pssm-ID: 239359 Cd Length: 91 Bit Score: 134.81 E-value: 1.53e-40
|
||||||||
| O-ClC | TIGR00862 | intracellular chloride channel protein; The Organellar Chloride Channel (O-ClC) Family (TC 1.A. ... |
21-231 | 2.03e-33 | ||||
intracellular chloride channel protein; The Organellar Chloride Channel (O-ClC) Family (TC 1.A.12) Proteins of the O-ClC family are voltage-sensitive chloride channels found in intracellular membranes but not the plasma membranes of animal cells. They are found in human nuclear membranes, and the bovine protein targets to the microsomes, but not the plasma membrane, when expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. These proteins are thought to function in the regulation of the membrane potential and in transepithelial ion absorption and secretion in the kidney. [Transport and binding proteins, Anions] Pssm-ID: 129941 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 236 Bit Score: 121.12 E-value: 2.03e-33
|
||||||||
| PLN02817 | PLN02817 | glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) |
23-228 | 1.00e-12 | ||||
glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) Pssm-ID: 166458 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 265 Bit Score: 66.17 E-value: 1.00e-12
|
||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||||
| GST_C_CLIC | cd03198 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channels; Glutathione S-transferase ... |
118-232 | 8.52e-58 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channels; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLICs (CLIC1-6 in vertebrates), p64, parchorin, and similar proteins. They are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. Biochemical studies of the Caenorhabditis elegans homolog, EXC-4, show that the membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. CLICs display structural plasticity, with CLIC1 adopting two soluble conformations. The structure of soluble human CLIC1 reveals that it is monomeric and adopts a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. Upon oxidation, the N-terminal domain of CLIC1 undergoes a structural change to form a non-covalent dimer stabilized by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between two cysteines that are far apart in the reduced form. The CLIC1 dimer bears no similarity to GST dimers. The redox-controlled structural rearrangement exposes a large hydrophobic surface, which is masked by dimerization in vitro. In vivo, this surface may represent the docking interface of CLIC1 in its membrane-bound state. The two cysteines in CLIC1 that form the disulfide bond in oxidizing conditions are essential for dimerization and chloride channel activity, however, in other subfamily members, the second cysteine is not conserved. Pssm-ID: 198307 Cd Length: 119 Bit Score: 180.11 E-value: 8.52e-58
|
||||||||
| GST_N_CLIC | cd03061 | GST_N family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLIC1-5, p64, ... |
18-112 | 1.53e-40 | ||||
GST_N family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) subfamily; composed of CLIC1-5, p64, parchorin and similar proteins. They are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states, and are found in various vesicles and membranes. Biochemical studies of the C. elegans homolog, EXC-4, show that the membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. The structure of soluble human CLIC1 reveals that it is monomeric and it adopts a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a TRX fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. Upon oxidation, the N-terminal domain of CLIC1 undergoes a structural change to form a non-covalent dimer stabilized by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between two cysteines that are far apart in the reduced form. The CLIC1 dimer bears no similarity to GST dimers. The redox-controlled structural rearrangement exposes a large hydrophobic surface, which is masked by dimerization in vitro. In vivo, this surface may represent the docking interface of CLIC1 in its membrane-bound state. The two cysteines in CLIC1 that form the disulfide bond in oxidizing conditions are essential for dimerization and chloride channel activity, however, in other subfamily members, the second cysteine is not conserved. Pssm-ID: 239359 Cd Length: 91 Bit Score: 134.81 E-value: 1.53e-40
|
||||||||
| O-ClC | TIGR00862 | intracellular chloride channel protein; The Organellar Chloride Channel (O-ClC) Family (TC 1.A. ... |
21-231 | 2.03e-33 | ||||
intracellular chloride channel protein; The Organellar Chloride Channel (O-ClC) Family (TC 1.A.12) Proteins of the O-ClC family are voltage-sensitive chloride channels found in intracellular membranes but not the plasma membranes of animal cells. They are found in human nuclear membranes, and the bovine protein targets to the microsomes, but not the plasma membrane, when expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. These proteins are thought to function in the regulation of the membrane potential and in transepithelial ion absorption and secretion in the kidney. [Transport and binding proteins, Anions] Pssm-ID: 129941 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 236 Bit Score: 121.12 E-value: 2.03e-33
|
||||||||
| GST_C_CLIC6 | cd10301 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 6; Glutathione ... |
138-231 | 4.21e-21 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 6; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) 6 subfamily; CLICs are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. The membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. Structures of soluble CLICs reveal that they adopt a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. CLIC6 is expressed predominantly in the stomach, pituitary, and brain. It interacts with D2-like dopamine receptors directly and through scaffolding proteins. CLIC6 may be involved in the regulation of secretion, possibly through chloride ion transport regulation. Pssm-ID: 198334 Cd Length: 140 Bit Score: 86.22 E-value: 4.21e-21
|
||||||||
| GST_C_CLIC4 | cd10296 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 4; Glutathione ... |
140-227 | 6.56e-20 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 4; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) 4 subfamily; CLICs are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. The membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. Structures of soluble CLICs reveal that they adopt a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. CLIC4, also known as p64H1, is expressed ubiquitously and its localization varies depending on the nature of the cells and tissues, from the plasma membrane to subcellular compartments including the nucleus, mitochondria, ER, and the trans-Golgi network, among others. In response to cellular stress such as DNA damage and senescence, cytoplasmic CLIC4 translocates to the nucleus, where it acts on the TGF-beta pathway. Studies on knockout mice suggest that CLIC4 also plays an important role in angiogenesis, specifically in network formation, capillary sprouting, and lumen formation. CLIC4 has been found to induce apoptosis in several cell types and to retard the growth of grafted tumors in vivo. Pssm-ID: 198329 Cd Length: 141 Bit Score: 83.15 E-value: 6.56e-20
|
||||||||
| GST_C_CLIC2 | cd10298 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 2; Glutathione ... |
156-231 | 1.78e-19 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 2; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) 2 subfamily; CLICs are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. The membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. Structures of soluble CLICs reveal that they adopt a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. CLIC2 contains an intramolecular disulfide bond and exists as a monomer regardless of redox conditions, in contrast to CLIC1 which forms a dimer under oxidizing conditions. It is expressed in most tissues except the brain, and is highly expressed in the lung, spleen, and in cardiac and skeletal muscles. CLIC2 interacts with ryanodine receptors (cardiac RyR2 and skeletal RyR1) and modulates their activity, suggesting that CLIC2 may function in the regulation of calcium release and signaling in cardiac and skeletal muscles. Pssm-ID: 198331 Cd Length: 138 Bit Score: 81.85 E-value: 1.78e-19
|
||||||||
| GST_C_CLIC5 | cd10297 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 5; Glutathione ... |
137-231 | 1.07e-17 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 5; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) 5 subfamily; CLICs are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. The membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. Structures of soluble CLICs reveal that they adopt a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. CLIC5 exists in two alternatively-spliced isoforms, CLIC5A or CLIC5B (also called p64). It is expressed at high levels in hair cell stereocilia and is associated with the actin cytoskeleton and ezrin. A recessive mutation in the CLIC5 gene in mice led to the lack of coordination and deafness, due to a defect in the basal region of the hair bundle causing stereocilia to degrade. CLIC5 is therefore essential for normal inner ear function. CLIC5 is also highly expressed in podocytes where it is colocalized with the ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) complex. It is essential for foot process integrity, and for podocyte morphology and function. Pssm-ID: 198330 Cd Length: 141 Bit Score: 77.31 E-value: 1.07e-17
|
||||||||
| GST_C_CLIC3 | cd10299 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 3; Glutathione ... |
121-232 | 1.53e-16 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 3; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) 3 subfamily; CLICs are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. The membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. Structures of soluble CLICs reveal that they adopt a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. CLIC3 is highly expressed in placental tissues, and may play a role in fetal development. Pssm-ID: 198332 Cd Length: 133 Bit Score: 74.04 E-value: 1.53e-16
|
||||||||
| GST_C_CLIC1 | cd10300 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 1; Glutathione ... |
145-233 | 1.57e-13 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Chloride Intracellular Channel 1; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC) 1 subfamily; CLICs are auto-inserting, self-assembling intracellular anion channels involved in a wide variety of functions including regulated secretion, cell division, and apoptosis. They can exist in both water-soluble and membrane-bound states and are found in various vesicles and membranes, and they may play roles in the maintenance of these intracellular membranes. The membrane localization domain is present in the N-terminal part of the protein. Soluble CLIC1 is monomeric and adopts a fold similar to GSTs, containing an N-terminal domain with a thioredoxin fold and a C-terminal alpha helical domain. Upon oxidation, the N-terminal domain of CLIC1 undergoes a structural change to form a non-covalent dimer stabilized by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between two cysteines that are far apart in the reduced form. The CLIC1 dimer bears no similarity to GST dimers. The redox-controlled structural rearrangement exposes a large hydrophobic surface, which is masked by dimerization in vitro. In vivo, this surface may represent the docking interface of CLIC1 in its membrane-bound state. The two cysteines in CLIC1 that form the disulfide bond in oxidizing conditions are essential for dimerization and chloride channel activity. CLIC1 is widely expressed in many tissues and its subcellular localization is dependent on cell type and cell cycle phase. It acts as a sensor of cell oxidation and appears to have a role in diseases that involve oxidative stress including tumorigenic and neurodegenerative diseases. Pssm-ID: 198333 Cd Length: 139 Bit Score: 66.12 E-value: 1.57e-13
|
||||||||
| PLN02817 | PLN02817 | glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) |
23-228 | 1.00e-12 | ||||
glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) Pssm-ID: 166458 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 265 Bit Score: 66.17 E-value: 1.00e-12
|
||||||||
| GST_C_DHAR | cd03201 | C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Dehydroascorbate Reductase; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) ... |
146-228 | 1.38e-12 | ||||
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Dehydroascorbate Reductase; Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Dehydroascorbate Reductase (DHAR) subfamily; composed of plant-specific DHARs, which are monomeric enzymes catalyzing the reduction of DHA into ascorbic acid (AsA) using glutathione as the reductant. DHAR allows plants to recycle oxidized AsA before it is lost. AsA serves as a cofactor of violaxanthin de-epoxidase in the xanthophyll cycle and as an antioxidant in the detoxification of reactive oxygen species. Because AsA is the major reductant in plants, DHAR serves to regulate their redox state. It has been suggested that a significant portion of DHAR activity is plastidic, acting to reduce the large amounts of ascorbate oxidized during hydrogen peroxide scavenging by ascorbate peroxidase. DHAR contains a conserved cysteine in its active site and in addition to its reductase activity, shows thiol transferase activity similar to glutaredoxins. Pssm-ID: 198310 Cd Length: 121 Bit Score: 62.82 E-value: 1.38e-12
|
||||||||
| PLN02378 | PLN02378 | glutathione S-transferase DHAR1 |
23-231 | 6.21e-12 | ||||
glutathione S-transferase DHAR1 Pssm-ID: 166019 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 213 Bit Score: 63.19 E-value: 6.21e-12
|
||||||||
| GST_N_family | cd00570 | Glutathione S-transferase (GST) family, N-terminal domain; a large, diverse group of cytosolic ... |
52-104 | 6.98e-03 | ||||
Glutathione S-transferase (GST) family, N-terminal domain; a large, diverse group of cytosolic dimeric proteins involved in cellular detoxification by catalyzing the conjugation of glutathione (GSH) with a wide range of endogenous and xenobiotic alkylating agents, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins and products of oxidative stress. In addition, GSTs also show GSH peroxidase activity and are involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. This family, also referred to as soluble GSTs, is the largest family of GSH transferases and is only distantly related to the mitochondrial GSTs (GSTK subfamily, a member of the DsbA family). Soluble GSTs bear no structural similarity to microsomal GSTs (MAPEG family) and display additional activities unique to their group, such as catalyzing thiolysis, reduction and isomerization of certain compounds. The GST fold contains an N-terminal TRX-fold domain and a C-terminal alpha helical domain, with an active site located in a cleft between the two domains. Based on sequence similarity, different classes of GSTs have been identified, which display varying tissue distribution, substrate specificities and additional specific activities. In humans, GSTs display polymorphisms which may influence individual susceptibility to diseases such as cancer, arthritis, allergy and sclerosis. Some GST family members with non-GST functions include glutaredoxin 2, the CLIC subfamily of anion channels, prion protein Ure2p, crystallins, metaxin 2 and stringent starvation protein A. Pssm-ID: 238319 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 71 Bit Score: 34.47 E-value: 6.98e-03
|
||||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|