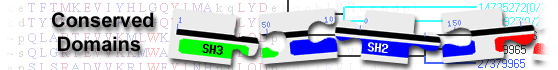differentially expressed in FDCP 8 homolog isoform 2 [Homo sapiens]
C1 domain-containing protein( domain architecture ID 3571)
C1 (protein kinase C conserved region 1) domain-containing protein similar to Homo sapiens differentially expressed in FDCP 8 homolog isoform 2
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| C1 super family | cl00040 | protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1 domain) superfamily; The C1 domain is a cysteine-rich ... |
134-172 | 1.65e-15 | ||
protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1 domain) superfamily; The C1 domain is a cysteine-rich zinc binding domain that does not bind DNA nor possess structural similarity to conventional zinc finger domains. It contains the motif HX12CX2CXnCX2CX4HX2CX7C, where C and H are cysteine and histidine, respectively; X represents other residues; and n is either 13 or 14. C1 has a globular fold with two separate Zn(2+)-binding sites. It was originally discovered as lipid-binding modules in protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms. C1 domains that bind and respond to phorbol esters (PE) and diacylglycerol (DAG) are referred to as typical, and those that do not respond to PE and DAG are deemed atypical. A C1 domain may also be referred to as PKC or non-PKC C1, based on the parent protein's activity. Most C1 domain-containing non-PKC proteins act as lipid kinases and scaffolds, except PKD which acts as a protein kinase. PKC C1 domains play roles in membrane translocation and activation of the enzyme. The actual alignment was detected with superfamily member cd20819: Pssm-ID: 412127 Cd Length: 62 Bit Score: 67.69 E-value: 1.65e-15
|
||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| C1_DEF8 | cd20819 | protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1 domain) found in differentially expressed in FDCP 8 ... |
134-172 | 1.65e-15 | ||
protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1 domain) found in differentially expressed in FDCP 8 (DEF-8) and similar proteins; DEF-8 positively regulates lysosome peripheral distribution and ruffled border formation in osteoclasts. It is involved in bone resorption. DEF-8 contains a protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1) domain followed by a putative zinc-RING and/or ribbon. This model corresponds to the C1 domain. The C1 domain is a cysteine-rich zinc binding domain that does not bind DNA nor possess structural similarity to conventional zinc finger domains; it contains two separate Zn(2+)-binding sites. Pssm-ID: 410369 Cd Length: 62 Bit Score: 67.69 E-value: 1.65e-15
|
||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| C1_DEF8 | cd20819 | protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1 domain) found in differentially expressed in FDCP 8 ... |
134-172 | 1.65e-15 | ||
protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1 domain) found in differentially expressed in FDCP 8 (DEF-8) and similar proteins; DEF-8 positively regulates lysosome peripheral distribution and ruffled border formation in osteoclasts. It is involved in bone resorption. DEF-8 contains a protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1) domain followed by a putative zinc-RING and/or ribbon. This model corresponds to the C1 domain. The C1 domain is a cysteine-rich zinc binding domain that does not bind DNA nor possess structural similarity to conventional zinc finger domains; it contains two separate Zn(2+)-binding sites. Pssm-ID: 410369 Cd Length: 62 Bit Score: 67.69 E-value: 1.65e-15
|
||||||
| C1 | cd00029 | protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1 domain) superfamily; The C1 domain is a cysteine-rich ... |
139-171 | 4.15e-03 | ||
protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1 domain) superfamily; The C1 domain is a cysteine-rich zinc binding domain that does not bind DNA nor possess structural similarity to conventional zinc finger domains. It contains the motif HX12CX2CXnCX2CX4HX2CX7C, where C and H are cysteine and histidine, respectively; X represents other residues; and n is either 13 or 14. C1 has a globular fold with two separate Zn(2+)-binding sites. It was originally discovered as lipid-binding modules in protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms. C1 domains that bind and respond to phorbol esters (PE) and diacylglycerol (DAG) are referred to as typical, and those that do not respond to PE and DAG are deemed atypical. A C1 domain may also be referred to as PKC or non-PKC C1, based on the parent protein's activity. Most C1 domain-containing non-PKC proteins act as lipid kinases and scaffolds, except PKD which acts as a protein kinase. PKC C1 domains play roles in membrane translocation and activation of the enzyme. Pssm-ID: 410341 Cd Length: 50 Bit Score: 34.03 E-value: 4.15e-03
|
||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|