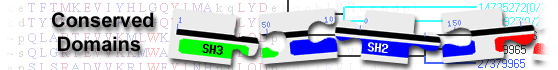high-molecular-weight protein 2, partial [Lelliottia amnigena]
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||||
| C_NRPS-like super family | cl40425 | Condensation domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); Condensation (C) domains of ... |
114-317 | 4.85e-97 | ||||
Condensation domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); Condensation (C) domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long, with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression. There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; mutations in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. The actual alignment was detected with superfamily member cd19535: Pssm-ID: 394795 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 423 Bit Score: 292.85 E-value: 4.85e-97
|
||||||||
| AcpA | COG3433 | Acyl carrier protein/domain [Lipid transport and metabolism, Secondary metabolites ... |
5-95 | 2.10e-16 | ||||
Acyl carrier protein/domain [Lipid transport and metabolism, Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism]; : Pssm-ID: 442659 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 295 Bit Score: 77.87 E-value: 2.10e-16
|
||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||||||
| Cyc_NRPS | cd19535 | Cyc (heterocyclization) domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); belongs to the ... |
114-317 | 4.85e-97 | ||||||
Cyc (heterocyclization) domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); belongs to the Condensation-domain family; Cyc (heterocyclization) domains catalyze two separate reactions in the creation of heterocyclized peptide products in nonribosomal peptide synthesis: amide bond formation followed by intramolecular cyclodehydration between a Cys, Ser, or Thr side chain and a carbonyl carbon on the peptide backbone to form a thiazoline, oxazoline, or methyloxazoline ring. Cyc-domains are homologous to standard NRPS Condensation (C) domains. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; Cyc-domains have an alternative, conserved DxxxxD active site motif, mutation of the aspartate residues in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and Cyc-domains. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. Pssm-ID: 380458 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 423 Bit Score: 292.85 E-value: 4.85e-97
|
||||||||||
| AcpA | COG3433 | Acyl carrier protein/domain [Lipid transport and metabolism, Secondary metabolites ... |
5-95 | 2.10e-16 | ||||||
Acyl carrier protein/domain [Lipid transport and metabolism, Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism]; Pssm-ID: 442659 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 295 Bit Score: 77.87 E-value: 2.10e-16
|
||||||||||
| COG4908 | COG4908 | Uncharacterized conserved protein, contains a NRPS condensation (elongation) domain [General ... |
144-316 | 6.95e-15 | ||||||
Uncharacterized conserved protein, contains a NRPS condensation (elongation) domain [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 443936 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 243 Bit Score: 72.76 E-value: 6.95e-15
|
||||||||||
| Condensation | pfam00668 | Condensation domain; This domain is found in many multi-domain enzymes which synthesize ... |
155-316 | 7.77e-10 | ||||||
Condensation domain; This domain is found in many multi-domain enzymes which synthesize peptide antibiotics. This domain catalyzes a condensation reaction to form peptide bonds in non- ribosomal peptide biosynthesis. It is usually found to the carboxy side of a phosphopantetheine binding domain (pfam00550). It has been shown that mutations in the HHXXXDG motif abolish activity suggesting this is part of the active site. Pssm-ID: 395541 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 454 Bit Score: 59.65 E-value: 7.77e-10
|
||||||||||
| PRK12316 | PRK12316 | peptide synthase; Provisional |
6-317 | 1.21e-09 | ||||||
peptide synthase; Provisional Pssm-ID: 237054 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 5163 Bit Score: 59.59 E-value: 1.21e-09
|
||||||||||
| PP-binding | pfam00550 | Phosphopantetheine attachment site; A 4'-phosphopantetheine prosthetic group is attached ... |
22-82 | 1.05e-08 | ||||||
Phosphopantetheine attachment site; A 4'-phosphopantetheine prosthetic group is attached through a serine. This prosthetic group acts as a a 'swinging arm' for the attachment of activated fatty acid and amino-acid groups. This domain forms a four helix bundle. This family includes members not included in Prosite. The inclusion of these members is supported by sequence analysis and functional evidence. The related domain of Swiss:P19828 has the attachment serine replaced by an alanine. Pssm-ID: 425746 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 62 Bit Score: 51.02 E-value: 1.05e-08
|
||||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||||||
| Cyc_NRPS | cd19535 | Cyc (heterocyclization) domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); belongs to the ... |
114-317 | 4.85e-97 | ||||||
Cyc (heterocyclization) domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); belongs to the Condensation-domain family; Cyc (heterocyclization) domains catalyze two separate reactions in the creation of heterocyclized peptide products in nonribosomal peptide synthesis: amide bond formation followed by intramolecular cyclodehydration between a Cys, Ser, or Thr side chain and a carbonyl carbon on the peptide backbone to form a thiazoline, oxazoline, or methyloxazoline ring. Cyc-domains are homologous to standard NRPS Condensation (C) domains. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; Cyc-domains have an alternative, conserved DxxxxD active site motif, mutation of the aspartate residues in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and Cyc-domains. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. Pssm-ID: 380458 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 423 Bit Score: 292.85 E-value: 4.85e-97
|
||||||||||
| ArgR-Cyc_NRPS-like | cd20480 | Cyc (heterocyclization)-like domain of Vibrio anguillarum AngR and similar proteins; belongs ... |
116-317 | 3.03e-18 | ||||||
Cyc (heterocyclization)-like domain of Vibrio anguillarum AngR and similar proteins; belongs to the Condensation-domain family; Vibrio anguillarum AngR plays a role in regulating the expression of iron transport genes as well as in the production of the siderophore anguibactin. Cyc-domains are a type of Condensation (C) domain. Cyc-domains catalyze two separate reactions in the creation of heterocyclized peptide products in nonribosomal peptide synthesis: amide bond formation followed by intramolecular cyclodehydration between a Cys, Ser, or Thr side chain and a carbonyl carbon on the peptide backbone to form a thiazoline, oxazoline, or methyloxazoline ring. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; Cyc-domains have a alternative, conserved DxxxxD active site motif, mutation of the aspartate residues in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. Members of this subfamily have an SxxxD motif at the active site. C-domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). In addition to Cyc-domains there are various other subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. Pssm-ID: 380470 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 406 Bit Score: 84.48 E-value: 3.03e-18
|
||||||||||
| AcpA | COG3433 | Acyl carrier protein/domain [Lipid transport and metabolism, Secondary metabolites ... |
5-95 | 2.10e-16 | ||||||
Acyl carrier protein/domain [Lipid transport and metabolism, Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism]; Pssm-ID: 442659 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 295 Bit Score: 77.87 E-value: 2.10e-16
|
||||||||||
| COG4908 | COG4908 | Uncharacterized conserved protein, contains a NRPS condensation (elongation) domain [General ... |
144-316 | 6.95e-15 | ||||||
Uncharacterized conserved protein, contains a NRPS condensation (elongation) domain [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 443936 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 243 Bit Score: 72.76 E-value: 6.95e-15
|
||||||||||
| C_PKS-NRPS | cd20483 | Condensation domain of hybrid polyketide synthetase/nonribosomal peptide synthetases (PKS ... |
155-317 | 4.52e-14 | ||||||
Condensation domain of hybrid polyketide synthetase/nonribosomal peptide synthetases (PKS/NRPSs); Condensation (C) domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. Hybrid PKS/NRPS create polymers containing both polyketide and amide linkages. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; mutations in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. Most members of this subfamily have the typical C-domain HHXXXD motif. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. Pssm-ID: 380471 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 430 Bit Score: 72.29 E-value: 4.52e-14
|
||||||||||
| C_PKS-NRPS | cd19532 | Condensation domain of hybrid polyketide synthetase/nonribosomal peptide synthetases (PKS ... |
144-317 | 4.66e-13 | ||||||
Condensation domain of hybrid polyketide synthetase/nonribosomal peptide synthetases (PKS/NRPSs); Condensation (C) domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. Hybrid PKS/NRPS create polymers containing both polyketide and amide linkages. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; mutations in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. Most members of this subfamily have the typical C-domain HHxxxD motif, a few such as Monascus pilosus lovastatin nonaketide synthase MokA have a non-canonical HRxxxD motif in the C-domain and are unable to catalyze amide-bond formation. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. Pssm-ID: 380455 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 421 Bit Score: 69.02 E-value: 4.66e-13
|
||||||||||
| Condensation | pfam00668 | Condensation domain; This domain is found in many multi-domain enzymes which synthesize ... |
155-316 | 7.77e-10 | ||||||
Condensation domain; This domain is found in many multi-domain enzymes which synthesize peptide antibiotics. This domain catalyzes a condensation reaction to form peptide bonds in non- ribosomal peptide biosynthesis. It is usually found to the carboxy side of a phosphopantetheine binding domain (pfam00550). It has been shown that mutations in the HHXXXDG motif abolish activity suggesting this is part of the active site. Pssm-ID: 395541 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 454 Bit Score: 59.65 E-value: 7.77e-10
|
||||||||||
| PRK12316 | PRK12316 | peptide synthase; Provisional |
6-317 | 1.21e-09 | ||||||
peptide synthase; Provisional Pssm-ID: 237054 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 5163 Bit Score: 59.59 E-value: 1.21e-09
|
||||||||||
| EntF | COG1020 | EntF, seryl-AMP synthase component of non-ribosomal peptide synthetase [Secondary metabolites ... |
95-317 | 5.46e-09 | ||||||
EntF, seryl-AMP synthase component of non-ribosomal peptide synthetase [Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism]; Pssm-ID: 440643 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 1329 Bit Score: 57.56 E-value: 5.46e-09
|
||||||||||
| LCL_NRPS-like | cd19531 | LCL-type Condensation (C) domain of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases(NRPSs) and similar ... |
155-316 | 9.77e-09 | ||||||
LCL-type Condensation (C) domain of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases(NRPSs) and similar domains including the C-domain of SgcC5, a free-standing NRPS with both ester- and amide- bond forming activity; LCL-type Condensation (C) domains catalyze peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, ((L)C(L)). C-domains of NRPSs catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). In addition to the LCL-type, there are various subtypes of C-domains such as the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. Streptomyces globisporus SgcC5 is a free-standing NRPS condensation enzyme (rather than a modular NRPS), which catalyzes the condensation between the SgcC2-tethered (S)-3-chloro-5-hydroxy-beta-tyrosine and (R)-1phenyl-1,2-ethanediol, forming an ester bond, during the synthesis of the chromoprotein enediyne antitumor antibiotic C-1027. It has some acceptor substrate promiscuity as it has been shown to also catalyze the formation of an amide bond between SgcC2-tethered (S)-3-chloro-5-hydroxy-beta-tyrosine and a mimic of the enediyne core acceptor substrate having an amine at its C-2 position. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; mutations in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. An HHxx[SAG]DGxSx(6)[ED] motif is characteristic of LCL-type C-domains. Pssm-ID: 380454 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 427 Bit Score: 56.21 E-value: 9.77e-09
|
||||||||||
| PP-binding | pfam00550 | Phosphopantetheine attachment site; A 4'-phosphopantetheine prosthetic group is attached ... |
22-82 | 1.05e-08 | ||||||
Phosphopantetheine attachment site; A 4'-phosphopantetheine prosthetic group is attached through a serine. This prosthetic group acts as a a 'swinging arm' for the attachment of activated fatty acid and amino-acid groups. This domain forms a four helix bundle. This family includes members not included in Prosite. The inclusion of these members is supported by sequence analysis and functional evidence. The related domain of Swiss:P19828 has the attachment serine replaced by an alanine. Pssm-ID: 425746 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 62 Bit Score: 51.02 E-value: 1.05e-08
|
||||||||||
| E_NRPS | cd19534 | Epimerization domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); belongs to the ... |
114-314 | 1.41e-08 | ||||||
Epimerization domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); belongs to the Condensation-domain family; Epimerization (E) domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) flip the chirality of the end amino acid of a peptide being manufactured by the NRPS. E-domains are homologous to the Condensation (C) domains. NRPSs catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. Specialized tailoring NRPS domains such as E-domains greatly increase the range of possible peptide products created by the NRPS machinery. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the E-domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; mutations in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. Pssm-ID: 380457 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 428 Bit Score: 55.72 E-value: 1.41e-08
|
||||||||||
| DCL_NRPS | cd19543 | DCL-type Condensation domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs), which catalyzes the ... |
155-302 | 2.95e-07 | ||||||
DCL-type Condensation domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs), which catalyzes the condensation between a D-aminoacyl/peptidyl-PCP donor and a L-aminoacyl-PCP acceptor; The DCL-type Condensation (C) domain catalyzes the condensation between a D-aminoacyl/peptidyl-PCP donor and a L-aminoacyl-PCP acceptor. This domain is D-specific for the peptidyl donor and L-specific for the aminoacyl acceptor ((D)C(L)); this is in contrast with the standard LCL domains which catalyze peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, and the restriction of ribosomes to use only L-amino acids. C domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains in addition to the LCL- and DCL-types such as starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; mutations in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. Pssm-ID: 380465 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 423 Bit Score: 51.43 E-value: 2.95e-07
|
||||||||||
| CT_NRPS-like | cd19542 | Terminal Condensation (CT)-like domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); Unlike ... |
115-311 | 8.58e-07 | ||||||
Terminal Condensation (CT)-like domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); Unlike bacterial NRPS, which typically have specialized terminal thioesterase (TE) domains to cyclize peptide products, many fungal NRPSs employ a terminal condensation-like (CT) domain to produce macrocyclic peptidyl products (e.g. cyclosporine and echinocandin). Domains in this subfamily (which includes both terminal and non-terminal domains) typically have a non-canonical conserved [SN]HxxxDx(14)Y motif at their active site compared to the standard Condensation (C) domain active site motif (HHxxxD). C-domains of NRPSs catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. Pssm-ID: 380464 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 401 Bit Score: 50.00 E-value: 8.58e-07
|
||||||||||
| PRK05691 | PRK05691 | peptide synthase; Validated |
66-317 | 3.05e-06 | ||||||
peptide synthase; Validated Pssm-ID: 235564 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 4334 Bit Score: 49.01 E-value: 3.05e-06
|
||||||||||
| DCL_NRPS-like | cd19536 | DCL-type Condensation domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs), such as terminal ... |
115-311 | 3.29e-06 | ||||||
DCL-type Condensation domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs), such as terminal fungal CT domains and Dual Epimerization/Condensation (E/C) domains; Condensation (C) domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type [D-specific for the peptidyl donor and L-specific for the aminoacyl acceptor ((D)C(L))], which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; mutations in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. Pssm-ID: 380459 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 419 Bit Score: 48.21 E-value: 3.29e-06
|
||||||||||
| entF | PRK10252 | enterobactin non-ribosomal peptide synthetase EntF; |
150-311 | 5.35e-05 | ||||||
enterobactin non-ribosomal peptide synthetase EntF; Pssm-ID: 236668 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 1296 Bit Score: 45.04 E-value: 5.35e-05
|
||||||||||
| PRK12316 | PRK12316 | peptide synthase; Provisional |
44-310 | 7.09e-05 | ||||||
peptide synthase; Provisional Pssm-ID: 237054 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 5163 Bit Score: 44.56 E-value: 7.09e-05
|
||||||||||
| PRK12316 | PRK12316 | peptide synthase; Provisional |
42-310 | 1.82e-04 | ||||||
peptide synthase; Provisional Pssm-ID: 237054 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 5163 Bit Score: 43.41 E-value: 1.82e-04
|
||||||||||
| starter-C_NRPS | cd19533 | Starter Condensation domains, found in the first module of nonribosomal peptide synthetases ... |
116-311 | 1.56e-03 | ||||||
Starter Condensation domains, found in the first module of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs); Condensation (C) domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) catalyze peptide bond formation within (usually) large multi-modular enzymatic complexes. While standard C-domains catalyze peptide bond formation between two amino acids, an initial, ('starter') C-domain may instead acylate an amino acid with a fatty acid. NRPS can use a large variety of acyl monomers (approximately 500 different possible monomer substrates as opposed to the 20 standard amino acids in ribosomal protein synthesis) to construct bioactive secondary metabolites of 2 to 18 units long (with various activities such as antibiotic, antifungal, antitumor and immunosuppression). There are various subtypes of C-domains such as the LCL-type which catalyzes peptide bond formation between two L-amino acids, the DCL-type which links an L-amino acid to the D-amino acid at the end of a growing peptide, starter C-domains which acylate the first amino acid with a beta-hydroxy carboxylic acid, and heterocyclization (Cyc) domains which catalyze both peptide bond formation and cyclization of Cys, Ser, or Thr residues. Typically, an NRPS module consists of an adenylation domain, a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain (also known as thiolation (T) domain) and a C-domain. NRPS modules may also include specialized domains such as the terminal-module thioesterase (Te) domain that releases the product via hydrolysis or macrocyclization and any of various C-domain family members such as the epimerization (E) domain, the ester-bond forming C-domain, dual E/C (epimerization and condensation) domains, and the X-domain. C-domains typically have a conserved HHxxxD motif at the active site; mutations in this motif can abolish or diminish condensation activity. Pssm-ID: 380456 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 419 Bit Score: 40.05 E-value: 1.56e-03
|
||||||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|