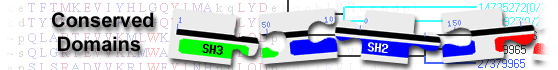telomerase regulation-associated protein [Homo sapiens]
SCY1-like family protein( domain architecture ID 10195806)
SCY1-like family protein belonging to the protein kinase superfamily is a catalytically inactive protein with similarity to yeast Scy1, and may be involved in membrane trafficking
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||
| PK_SCY1_like | cd14011 | Pseudokinase domain of Scy1-like proteins; The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to protein ... |
37-296 | 1.61e-78 | |||||
Pseudokinase domain of Scy1-like proteins; The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to protein kinases but lacks crucial residues for catalytic activity. This subfamily is composed of the catalytically inactive kinases with similarity to yeast Scy1. It includes four mammalian proteins called SCY1-like protein 1 (SCYL1), SCYL2, SCYL3, as well as Testis-EXpressed protein 14 (TEX14). SCYL1 binds to and co-localizes with the membrane trafficking coatomer I (COPI) complex, and regulates COPI-mediated vesicle trafficking. Null mutations in the SCYL1 gene are responsible for the pathology in mdf (muscle-deficient) mice which display progressive motor neuropathy. SCYL2, also called coated vesicle-associated kinase of 104 kDa (CVAK104), is involved in the trafficking of clathrin-coated vesicles. It also binds the HIV-1 accessory protein Vpu and acts as a regulatory factor that promotes the dephosphorylation of Vpu, facilitating the restriction of HIV-1 release. SCYL3, also called ezrin-binding protein PACE-1, may be involved in regulating cell adhesion and migration. TEX14 is required for spermatogenesis and male fertility. It localizes to kinetochores (KT) during mitosis and is a target of the mitotic kinase PLK1. It regulates the maturation of the outer KT and the KT-microtubule attachment. The SCY1-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein serine/threonine kinases, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. : Pssm-ID: 270913 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 287 Bit Score: 254.55 E-value: 1.61e-78
|
|||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||
| PK_SCY1_like | cd14011 | Pseudokinase domain of Scy1-like proteins; The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to protein ... |
37-296 | 1.61e-78 | |||||
Pseudokinase domain of Scy1-like proteins; The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to protein kinases but lacks crucial residues for catalytic activity. This subfamily is composed of the catalytically inactive kinases with similarity to yeast Scy1. It includes four mammalian proteins called SCY1-like protein 1 (SCYL1), SCYL2, SCYL3, as well as Testis-EXpressed protein 14 (TEX14). SCYL1 binds to and co-localizes with the membrane trafficking coatomer I (COPI) complex, and regulates COPI-mediated vesicle trafficking. Null mutations in the SCYL1 gene are responsible for the pathology in mdf (muscle-deficient) mice which display progressive motor neuropathy. SCYL2, also called coated vesicle-associated kinase of 104 kDa (CVAK104), is involved in the trafficking of clathrin-coated vesicles. It also binds the HIV-1 accessory protein Vpu and acts as a regulatory factor that promotes the dephosphorylation of Vpu, facilitating the restriction of HIV-1 release. SCYL3, also called ezrin-binding protein PACE-1, may be involved in regulating cell adhesion and migration. TEX14 is required for spermatogenesis and male fertility. It localizes to kinetochores (KT) during mitosis and is a target of the mitotic kinase PLK1. It regulates the maturation of the outer KT and the KT-microtubule attachment. The SCY1-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein serine/threonine kinases, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270913 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 287 Bit Score: 254.55 E-value: 1.61e-78
|
|||||||||
| S_TKc | smart00220 | Serine/Threonine protein kinases, catalytic domain; Phosphotransferases. Serine or ... |
69-259 | 1.16e-09 | |||||
Serine/Threonine protein kinases, catalytic domain; Phosphotransferases. Serine or threonine-specific kinase subfamily. Pssm-ID: 214567 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 254 Bit Score: 59.85 E-value: 1.16e-09
|
|||||||||
| PTZ00267 | PTZ00267 | NIMA-related protein kinase; Provisional |
27-305 | 2.05e-07 | |||||
NIMA-related protein kinase; Provisional Pssm-ID: 140293 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 478 Bit Score: 54.25 E-value: 2.05e-07
|
|||||||||
| PK_Tyr_Ser-Thr | pfam07714 | Protein tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase; Protein phosphorylation, which plays a key role ... |
50-221 | 7.79e-05 | |||||
Protein tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase; Protein phosphorylation, which plays a key role in most cellular activities, is a reversible process mediated by protein kinases and phosphoprotein phosphatases. Protein kinases catalyze the transfer of the gamma phosphate from nucleotide triphosphates (often ATP) to one or more amino acid residues in a protein substrate side chain, resulting in a conformational change affecting protein function. Phosphoprotein phosphatases catalyze the reverse process. Protein kinases fall into three broad classes, characterized with respect to substrate specificity; Serine/threonine-protein kinases, tyrosine-protein kinases, and dual specificity protein kinases (e.g. MEK - phosphorylates both Thr and Tyr on target proteins). This entry represents the catalytic domain found in a number of serine/threonine- and tyrosine-protein kinases. It does not include the catalytic domain of dual specificity kinases. Pssm-ID: 462242 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 258 Bit Score: 45.18 E-value: 7.79e-05
|
|||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||
| PK_SCY1_like | cd14011 | Pseudokinase domain of Scy1-like proteins; The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to protein ... |
37-296 | 1.61e-78 | |||||
Pseudokinase domain of Scy1-like proteins; The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to protein kinases but lacks crucial residues for catalytic activity. This subfamily is composed of the catalytically inactive kinases with similarity to yeast Scy1. It includes four mammalian proteins called SCY1-like protein 1 (SCYL1), SCYL2, SCYL3, as well as Testis-EXpressed protein 14 (TEX14). SCYL1 binds to and co-localizes with the membrane trafficking coatomer I (COPI) complex, and regulates COPI-mediated vesicle trafficking. Null mutations in the SCYL1 gene are responsible for the pathology in mdf (muscle-deficient) mice which display progressive motor neuropathy. SCYL2, also called coated vesicle-associated kinase of 104 kDa (CVAK104), is involved in the trafficking of clathrin-coated vesicles. It also binds the HIV-1 accessory protein Vpu and acts as a regulatory factor that promotes the dephosphorylation of Vpu, facilitating the restriction of HIV-1 release. SCYL3, also called ezrin-binding protein PACE-1, may be involved in regulating cell adhesion and migration. TEX14 is required for spermatogenesis and male fertility. It localizes to kinetochores (KT) during mitosis and is a target of the mitotic kinase PLK1. It regulates the maturation of the outer KT and the KT-microtubule attachment. The SCY1-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein serine/threonine kinases, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270913 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 287 Bit Score: 254.55 E-value: 1.61e-78
|
|||||||||
| PKc | cd00180 | Catalytic domain of Protein Kinases; PKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group ... |
34-260 | 3.33e-14 | |||||
Catalytic domain of Protein Kinases; PKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine or tyrosine residues on protein substrates. PKs make up a large family of serine/threonine kinases (STKs), protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs), and dual-specificity PKs that phosphorylate both serine/threonine and tyrosine residues of target proteins. Majority of protein phosphorylation occurs on serine residues while only 1% occurs on tyrosine residues. Protein phosphorylation is a mechanism by which a wide variety of cellular proteins, such as enzymes and membrane channels, are reversibly regulated in response to certain stimuli. PKs often function as components of signal transduction pathways in which one kinase activates a second kinase, which in turn, may act on other kinases; this sequential action transmits a signal from the cell surface to target proteins, which results in cellular responses. The PK family is one of the largest known protein families with more than 100 homologous yeast enzymes and more than 500 human proteins. A fraction of PK family members are pseudokinases that lack crucial residues for catalytic activity. The mutiplicity of kinases allows for specific regulation according to substrate, tissue distribution, and cellular localization. PKs regulate many cellular processes including proliferation, division, differentiation, motility, survival, metabolism, cell-cycle progression, cytoskeletal rearrangement, immunity, and neuronal functions. Many kinases are implicated in the development of various human diseases including different types of cancer. The PK family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and actin-fragmin kinase. Pssm-ID: 270622 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 215 Bit Score: 72.30 E-value: 3.33e-14
|
|||||||||
| S_TKc | smart00220 | Serine/Threonine protein kinases, catalytic domain; Phosphotransferases. Serine or ... |
69-259 | 1.16e-09 | |||||
Serine/Threonine protein kinases, catalytic domain; Phosphotransferases. Serine or threonine-specific kinase subfamily. Pssm-ID: 214567 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 254 Bit Score: 59.85 E-value: 1.16e-09
|
|||||||||
| STKc_MARK | cd14072 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinases; ... |
39-233 | 5.50e-09 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. MARKs, also called Partitioning-defective 1 (Par1) proteins, function as regulators of diverse cellular processes in nematodes, Drosophila, yeast, and vertebrates. They are involved in embryogenesis, epithelial cell polarization, cell signaling, and neuronal differentiation. MARKs phosphorylate tau and related microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs), and regulates microtubule-based intracellular transport. Vertebrates contain four isoforms, namely MARK1 (or Par1c), MARK2 (or Par1b), MARK3 (Par1a), and MARK4 (or MARKL1). Known substrates of MARKs include the cell cycle-regulating phosphatase Cdc25, tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1, MAPK scaffolding protein KSR1, class IIa histone deacetylases, and plakophilin 2. The MARK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270974 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 253 Bit Score: 57.53 E-value: 5.50e-09
|
|||||||||
| PK_eIF2AK_GCN2_rpt1 | cd14012 | Pseudokinase domain, repeat 1, of eukaryotic translation Initiation Factor 2-Alpha Kinase 4 or ... |
56-261 | 7.68e-09 | |||||
Pseudokinase domain, repeat 1, of eukaryotic translation Initiation Factor 2-Alpha Kinase 4 or General Control Non-derepressible-2; The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to protein kinases but lacks crucial residues for catalytic activity. EIF2AKs phosphorylate the alpha subunit of eIF-2, resulting in the overall downregulation of protein synthesis. eIF-2 phosphorylation is induced in response to cellular stresses including virus infection, heat shock, nutrient deficiency, and the accummulation of unfolded proteins, among others. There are four distinct kinases that phosphorylate eIF-2 and control protein synthesis under different stress conditions: GCN2, protein kinase regulated by RNA (PKR), heme-regulated inhibitor kinase (HRI), and PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). GCN2 is activated by amino acid or serum starvation and UV irradiation. It induces GCN4, a transcriptional activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes, leading to increased production of amino acids under amino acid-deficient conditions. In serum-starved cells, GCN2 activation induces translation of the stress-responsive transcription factor ATF4, while under UV stress, GCN2 triggers transcriptional rescue via NF-kappaB signaling. GCN2 contains an N-terminal RWD, a degenerate kinase-like (repeat 1), the catalytic kinase (repeat 2), a histidyl-tRNA synthetase (HisRS)-like, and a C-terminal ribosome-binding and dimerization (RB/DD) domains. The degenerate pseudokinase domain of GCN2 may function as a regulatory domain. The GCN2 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of serine/threonine kinases, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270914 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 254 Bit Score: 57.37 E-value: 7.68e-09
|
|||||||||
| STKc_MEKK1_plant | cd06632 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Plant Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) ... |
71-258 | 8.55e-09 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Plant Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP)/Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) Kinase Kinase 1; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. This subfamily is composed of plant MAPK kinase kinases (MAPKKKs) including Arabidopsis thaliana MEKK1 and MAPKKK3. Arabidopsis thaliana MEKK1 activates MPK4, a MAPK that regulates systemic acquired resistance. MEKK1 also participates in the regulation of temperature-sensitive and tissue-specific cell death. MAPKKKs phosphorylate and activate MAPK kinases, which in turn phosphorylate and activate MAPKs during signaling cascades that are important in mediating cellular responses to extracellular signals. The plant MEKK1 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270802 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 259 Bit Score: 57.03 E-value: 8.55e-09
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek6_7 | cd08224 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related ... |
69-229 | 3.21e-08 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase 6 and 7; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Nek6 and Nek7 are the shortest Neks, consisting only of the catalytic domain and a very short N-terminal extension. They show distinct expression patterns and both appear to be downstream substrates of Nek9. They are required for mitotic spindle formation and cytokinesis. They may also be regulators of the p70 ribosomal S6 kinase. Nek6/7 is part of a family of 11 different Neks (Nek1-11) that are involved in cell cycle control. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270863 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 262 Bit Score: 55.35 E-value: 3.21e-08
|
|||||||||
| STKc_CDKL | cd07833 | Catalytic domain of Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase Like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs ... |
36-220 | 3.57e-08 | |||||
Catalytic domain of Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase Like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. This subfamily is composed of CDKL1-5 and similar proteins. Some CDKLs, like CDKL1 and CDKL3, may be implicated in transformation and others, like CDKL3 and CDKL5, are associated with mental retardation when impaired. CDKL2 plays a role in learning and memory. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. The CDKL subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270827 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 288 Bit Score: 55.79 E-value: 3.57e-08
|
|||||||||
| STKc_PLK | cd14099 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Polo-like kinases; STKs catalyze the ... |
69-212 | 1.75e-07 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Polo-like kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. PLKs play important roles in cell cycle progression and in DNA damage responses. They regulate mitotic entry, mitotic exit, and cytokinesis. In general PLKs contain an N-terminal catalytic kinase domain and a C-terminal regulatory polo box domain (PBD), which is comprised by two bipartite polo-box motifs (or polo boxes) and is involved in protein interactions. PLKs derive their names from homology to polo, a kinase first identified in Drosophila. There are five mammalian PLKs (PLK1-5) from distinct genes. There is good evidence that PLK1 may function as an oncogene while PLK2-5 have tumor suppressive properties. PLK1 functions as a positive regulator of mitosis, meiosis, and cytokinesis. PLK2 functions in G1 progression, S-phase arrest, and centriole duplication. PLK3 regulates angiogenesis and responses to DNA damage. PLK4 is required for late mitotic progression, cell survival, and embryonic development. PLK5 was first identified as a pseudogene containing a stop codon within the kinase domain, however, both murine and human genes encode expressed proteins. PLK5 functions in cell cycle arrest. Pssm-ID: 271001 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 258 Bit Score: 53.33 E-value: 1.75e-07
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek | cd08215 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase; ... |
36-260 | 1.96e-07 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The Nek family is composed of 11 different mammalian members (Nek1-11) with similarity to the catalytic domain of Aspergillus nidulans NIMA kinase, the founding member of the Nek family, which was identified in a screen for cell cycle mutants that were prevented from entering mitosis. Neks contain a conserved N-terminal catalytic domain and a more divergent C-terminal regulatory region of various sizes and structures. They are involved in the regulation of downstream processes following the activation of Cdc2, and many of their functions are cell cycle-related. They play critical roles in microtubule dynamics during ciliogenesis and mitosis. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270855 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 258 Bit Score: 52.85 E-value: 1.96e-07
|
|||||||||
| PTZ00267 | PTZ00267 | NIMA-related protein kinase; Provisional |
27-305 | 2.05e-07 | |||||
NIMA-related protein kinase; Provisional Pssm-ID: 140293 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 478 Bit Score: 54.25 E-value: 2.05e-07
|
|||||||||
| STKc_PLK2 | cd14188 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Polo-like kinase 2; STKs catalyze the ... |
69-260 | 2.99e-07 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Polo-like kinase 2; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. PLKs play important roles in cell cycle progression and in DNA damage responses. They regulate mitotic entry, mitotic exit, and cytokinesis. In general PLKs contain an N-terminal catalytic kinase domain and a C-terminal regulatory polo box domain (PBD), which is comprised by two bipartite polo-box motifs (or polo boxes) and is involved in protein interactions. There are five mammalian PLKs (PLK1-5) from distinct genes. PLK2, also called Snk (serum-inducible kinase), functions in G1 progression, S-phase arrest, and centriole duplication. Its gene is responsive to both growth factors and cellular stress, is a transcriptional target of p53, and activates a G2-M checkpoint. The PLK2 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 271090 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 255 Bit Score: 52.32 E-value: 2.99e-07
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Cdc7_like | cd06627 | Catalytic domain of Cell division control protein 7-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs ... |
69-218 | 9.83e-07 | |||||
Catalytic domain of Cell division control protein 7-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Members of this subfamily include Schizosaccharomyces pombe Cdc7, Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc15, Arabidopsis thaliana mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) epsilon, and related proteins. MAPKKKs phosphorylate and activate MAPK kinases, which in turn phosphorylate and activate MAPKs during signaling cascades that are important in mediating cellular responses to extracellular signals. Fission yeast Cdc7 is essential for cell division by playing a key role in the initiation of septum formation and cytokinesis. Budding yeast Cdc15 functions to coordinate mitotic exit with cytokinesis. Arabidopsis MAPKKK epsilon is required for pollen development in the plasma membrane. The Cdc7-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270797 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 254 Bit Score: 50.69 E-value: 9.83e-07
|
|||||||||
| STKc_STK36 | cd14002 | Catalytic domain of Serine/Threonine Kinase 36; STKs catalyze the transfer of the ... |
69-238 | 1.25e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of Serine/Threonine Kinase 36; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. STK36, also called Fused (or Fu) kinase, is involved in the Hedgehog signaling pathway. It is activated by the Smoothened (SMO) signal transducer, resulting in the stabilization of GLI transcription factors and the phosphorylation of SUFU to facilitate the nuclear accumulation of GLI. In Drosophila, Fused kinase is maternally required for proper segmentation during embryonic development and for the development of legs and wings during the larval stage. In mice, STK36 is not necessary for embryonic development, although mice deficient in STK36 display growth retardation postnatally. The STK36 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270904 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 253 Bit Score: 50.71 E-value: 1.25e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_CDKL2_3 | cd07846 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase Like 2 and 3; ... |
54-248 | 2.09e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase Like 2 and 3; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CDKL2, also called p56 KKIAMRE, is expressed in testis, kidney, lung, and brain. It functions mainly in mature neurons and plays an important role in learning and memory. Inactivation of CDKL3, also called NKIAMRE (NKIATRE in rat), by translocation is associated with mild mental retardation. It has been reported that CDKL3 is lost in leukemic cells having a chromosome arm 5q deletion, and may contribute to the transformed phenotype. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. The CDKL2/3 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270836 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 286 Bit Score: 50.11 E-value: 2.09e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_PAK | cd06614 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p21-activated kinase; STKs catalyze the ... |
69-222 | 4.66e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p21-activated kinase; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. PAKs are Rho family GTPase-regulated kinases that serve as important mediators in the function of Cdc42 (cell division cycle 42) and Rac. PAKs are implicated in the regulation of many cellular processes including growth factor receptor-mediated proliferation, cell polarity, cell motility, cell death and survival, and actin cytoskeleton organization. PAK deregulation is associated with tumor development. PAKs from higher eukaryotes are classified into two groups (I and II), according to their biochemical and structural features. Group I PAKs contain a PBD (p21-binding domain) overlapping with an AID (autoinhibitory domain), a C-terminal catalytic domain, SH3 binding sites and a non-classical SH3 binding site for PIX (PAK-interacting exchange factor). Group II PAKs contain a PBD and a catalytic domain, but lack other motifs found in group I PAKs. Since group II PAKs do not contain an obvious AID, they may be regulated differently from group I PAKs. Group I PAKs interact with the SH3 containing proteins Nck, Grb2 and PIX; no such binding has been demonstrated for group II PAKs. The PAK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270789 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 255 Bit Score: 48.75 E-value: 4.66e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek6 | cd08228 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase ... |
68-229 | 5.24e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase 6; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Nek6 is required for the transition from metaphase to anaphase. It also plays important roles in mitotic spindle formation and cytokinesis. Activated by Nek9 during mitosis, Nek6 phosphorylates Eg5, a kinesin that is important for spindle bipolarity. Nek6 localizes to spindle microtubules during metaphase and anaphase, and to the midbody during cytokinesis. It is one in a family of 11 different Neks (Nek1-11) that are involved in cell cycle control. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270865 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 268 Bit Score: 48.87 E-value: 5.24e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek9 | cd08221 | Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA) ... |
71-215 | 5.70e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase 9; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Nek9, also called Nercc1, is primarily a cytoplasmic protein but can also localize in the nucleus. It is involved in modulating chromosome alignment and splitting during mitosis. It interacts with the gamma-tubulin ring complex and the Ran GTPase, and is implicated in microtubule organization. Nek9 associates with FACT (FAcilitates Chromatin Transcription) and modulates interphase progression. It also interacts with Nek6, and Nek7, during mitosis, resulting in their activation. Nek9 is one in a family of 11 different Neks (Nek1-11) that are involved in cell cycle control. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270860 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 256 Bit Score: 48.58 E-value: 5.70e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_PknB_like | cd14014 | Catalytic domain of bacterial Serine/Threonine kinases, PknB and similar proteins; STKs ... |
59-239 | 6.24e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of bacterial Serine/Threonine kinases, PknB and similar proteins; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. This subfamily includes many bacterial eukaryotic-type STKs including Staphylococcus aureus PknB (also called PrkC or Stk1), Bacillus subtilis PrkC, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Pkn proteins (PknB, PknD, PknE, PknF, PknL, and PknH), among others. S. aureus PknB is the only eukaryotic-type STK present in this species, although many microorganisms encode for several such proteins. It is important for the survival and pathogenesis of S. aureus as it is involved in the regulation of purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis, cell wall metabolism, autolysis, virulence, and antibiotic resistance. M. tuberculosis PknB is essential for growth and it acts on diverse substrates including proteins involved in peptidoglycan synthesis, cell division, transcription, stress responses, and metabolic regulation. B. subtilis PrkC is located at the inner membrane of endospores and functions to trigger spore germination. Bacterial STKs in this subfamily show varied domain architectures. The well-characterized members such as S. aureus and M. tuberculosis PknB, and B. subtilis PrkC, contain an N-terminal cytosolic kinase domain, a transmembrane (TM) segment, and mutliple C-terminal extracellular PASTA domains. The PknB subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270916 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 260 Bit Score: 48.35 E-value: 6.24e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Byr2_like | cd06628 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, fungal Byr2-like Mitogen-Activated Protein ... |
69-238 | 6.47e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, fungal Byr2-like Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Members of this group include the MAPKKKs Schizosaccharomyces pombe Byr2, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Cryptococcus neoformans Ste11, and related proteins. They contain an N-terminal SAM (sterile alpha-motif) domain, which mediates protein-protein interaction, and a C-terminal catalytic domain. MAPKKKs phosphorylate and activate MAPK kinases, which in turn phosphorylate and activate MAPKs during signaling cascades that are important in mediating cellular responses to extracellular signals. Fission yeast Byr2 is regulated by Ras1. It responds to pheromone signaling and controls mating through the MAPK pathway. Budding yeast Ste11 functions in MAPK cascades that regulate mating, high osmolarity glycerol, and filamentous growth responses. The Byr2 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270798 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 267 Bit Score: 48.68 E-value: 6.47e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_PLK1 | cd14187 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Polo-like kinase 1; STKs catalyze the ... |
69-260 | 8.52e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Polo-like kinase 1; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. PLKs play important roles in cell cycle progression and in DNA damage responses. They regulate mitotic entry, mitotic exit, and cytokinesis. In general PLKs contain an N-terminal catalytic kinase domain and a C-terminal regulatory polo box domain (PBD), which is comprised by two bipartite polo-box motifs (or polo boxes) and is involved in protein interactions. There are five mammalian PLKs (PLK1-5) from distinct genes. PLK1 functions as a positive regulator of mitosis, meiosis, and cytokinesis. Its localization changes during mitotic progression; associating first with centrosomes in prophase, with kinetochores in prometaphase and metaphase, at the central spindle in anaphase, and in the midbody during telophase. It carries multiple functions throughout the cell cycle through interactions with differrent substrates at these specific subcellular locations. PLK1 is overexpressed in many human cancers and is associated with poor prognosis. The PLK1 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 271089 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 265 Bit Score: 48.01 E-value: 8.52e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_MAPKKK | cd06606 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase ... |
68-218 | 8.75e-06 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. MAPKKKs (MKKKs or MAP3Ks) are also called MAP/ERK kinase kinases (MEKKs) in some cases. They phosphorylate and activate MAPK kinases (MAPKKs or MKKs or MAP2Ks), which in turn phosphorylate and activate MAPKs during signaling cascades that are important in mediating cellular responses to extracellular signals. This subfamily is composed of the Apoptosis Signal-regulating Kinases ASK1 (or MAPKKK5) and ASK2 (or MAPKKK6), MEKK1, MEKK2, MEKK3, MEKK4, as well as plant and fungal MAPKKKs. Also included in this subfamily are the cell division control proteins Schizosaccharomyces pombe Cdc7 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc15. The MAPKKK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270783 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 258 Bit Score: 47.90 E-value: 8.75e-06
|
|||||||||
| STKc_HUNK | cd14070 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Hormonally up-regulated Neu-associated kinase ... |
39-221 | 1.25e-05 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Hormonally up-regulated Neu-associated kinase (also called MAK-V); STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. HUNK/MAK-V was identified from a mammary tumor in an MMTV-neu transgenic mouse. It is required for the metastasis of c-myc-induced mammary tumors, but is not necessary for c-myc-induced primary tumor formation or normal development. It is required for HER2/neu-induced tumor formation and maintenance of the cells' tumorigenic phenotype. It is over-expressed in aggressive subsets of ovary, colon, and breast carcinomas. HUNK interacts with synaptopodin, and may also play a role in synaptic plasticity. The HUNK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270972 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 262 Bit Score: 47.50 E-value: 1.25e-05
|
|||||||||
| PTZ00024 | PTZ00024 | cyclin-dependent protein kinase; Provisional |
66-295 | 1.60e-05 | |||||
cyclin-dependent protein kinase; Provisional Pssm-ID: 240233 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 335 Bit Score: 47.83 E-value: 1.60e-05
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek4 | cd08223 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase ... |
49-260 | 1.77e-05 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase 4; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Nek4 is highly abundant in the testis. Its specific function is unknown. Neks are involved in the regulation of downstream processes following the activation of Cdc2, and many of their functions are cell cycle-related. They play critical roles in microtubule dynamics during ciliogenesis and mitosis. Nek4 is one in a family of 11 different Neks (Nek1-11). The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270862 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 257 Bit Score: 47.05 E-value: 1.77e-05
|
|||||||||
| STKc_CNK2-like | cd08530 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CNK2 and similar ... |
73-259 | 2.45e-05 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CNK2 and similar proteins; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CNK2 has both cilliary and cell cycle functions. It influences flagellar length through promoting flagellar disassembly, and it regulates cell size, through influencing the size threshold at which cells commit to mitosis. This subfamily belongs to the (NIMA)-related kinase (Nek) family, which includes seven different Chlamydomonas Neks (CNKs 1-6 and Fa2). This subfamily includes CNK1, and -2. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270869 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 256 Bit Score: 46.62 E-value: 2.45e-05
|
|||||||||
| STKc_WNK4 | cd14033 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine protein kinase, With No Lysine (WNK) 4; STKs catalyze ... |
55-185 | 6.23e-05 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine protein kinase, With No Lysine (WNK) 4; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. WNK4 shows a restricted expression pattern and is usually found in epithelial cells. It is expressed in nephrons and in extrarenal tissues including intestine, eye, mammary glands, and prostate. WNK4 regulates a variety of ion transport proteins including apical or basolateral ion transporters, ion channels in the transcellular pathway, and claudins in the paracellular pathway. Mutations in WNK4 cause PseudoHypoAldosteronism type II (PHAII), characterized by hypertension and hyperkalemia. WNK4 inhibits the activity of the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC), which is responsible for about 15% of NaCl reabsorption in the kidney. It also inhibits the renal outer medullary potassium channel (ROMK) and decreases its surface expression. Hypertension and hyperkalemia in PHAII patients with WNK4 mutations may be partly due to increased NaCl reabsorption through NCC and impaired renal potassium secretion by ROMK, respectively. The WNK4 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270935 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 261 Bit Score: 45.38 E-value: 6.23e-05
|
|||||||||
| PK_Tyr_Ser-Thr | pfam07714 | Protein tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase; Protein phosphorylation, which plays a key role ... |
50-221 | 7.79e-05 | |||||
Protein tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase; Protein phosphorylation, which plays a key role in most cellular activities, is a reversible process mediated by protein kinases and phosphoprotein phosphatases. Protein kinases catalyze the transfer of the gamma phosphate from nucleotide triphosphates (often ATP) to one or more amino acid residues in a protein substrate side chain, resulting in a conformational change affecting protein function. Phosphoprotein phosphatases catalyze the reverse process. Protein kinases fall into three broad classes, characterized with respect to substrate specificity; Serine/threonine-protein kinases, tyrosine-protein kinases, and dual specificity protein kinases (e.g. MEK - phosphorylates both Thr and Tyr on target proteins). This entry represents the catalytic domain found in a number of serine/threonine- and tyrosine-protein kinases. It does not include the catalytic domain of dual specificity kinases. Pssm-ID: 462242 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 258 Bit Score: 45.18 E-value: 7.79e-05
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek2 | cd08217 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase ... |
69-229 | 7.89e-05 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase 2; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The Nek2 subfamily includes Aspergillus nidulans NIMA kinase, the founding member of the Nek family, which was identified in a screen for cell cycle mutants prevented from entering mitosis. NIMA is essential for mitotic entry and progression through mitosis, and its degradation is essential for mitotic exit. NIMA is involved in nuclear membrane fission. Vertebrate Nek2 is a cell cycle-regulated STK, localized in centrosomes and kinetochores, that regulates centrosome splitting at the G2/M phase. It also interacts with other mitotic kinases such as Polo-like kinase 1 and may play a role in spindle checkpoint. An increase in the expression of the human NEK2 gene is strongly associated with the progression of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Nek2 is one in a family of 11 different Neks (Nek1-11) that are involved in cell cycle control. It The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270857 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 265 Bit Score: 45.22 E-value: 7.89e-05
|
|||||||||
| STKc_CAMK | cd05117 | The catalytic domain of CAMK family Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of ... |
37-131 | 8.04e-05 | |||||
The catalytic domain of CAMK family Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CaMKs are multifunctional calcium and calmodulin (CaM) stimulated STKs involved in cell cycle regulation. There are several types of CaMKs including CaMKI, CaMKII, and CaMKIV. CaMKI proteins are monomeric and they play pivotal roles in the nervous system, including long-term potentiation, dendritic arborization, neurite outgrowth, and the formation of spines, synapses, and axons. CaMKII is a signaling molecule that translates upstream calcium and reactive oxygen species (ROS) signals into downstream responses that play important roles in synaptic function and cardiovascular physiology. CAMKIV is implicated in regulating several transcription factors like CREB, MEF2, and retinoid orphan receptors, as well as in T-cell development and signaling. The CAMK family also consists of other related kinases including the Phosphorylase kinase Gamma subunit (PhKG), the C-terminal kinase domains of Ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) and Mitogen and stress-activated kinase (MSK), Doublecortin-like kinase (DCKL), and the MAPK-activated protein kinases MK2, MK3, and MK5, among others. The CAMK family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270687 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 258 Bit Score: 45.16 E-value: 8.04e-05
|
|||||||||
| STKc_NIM1 | cd14075 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, NIM1; STKs catalyze the transfer of the ... |
71-223 | 1.39e-04 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, NIM1; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. NIM1 is a widely-expressed kinase belonging to the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) subfamily. Although present in most tissues, NIM1 kinase activity is only observed in the brain and testis. NIM1 is capable of autophosphorylating and activating itself, but may be present in other tissues in the inactive form. The physiological function of NIM1 has yet to be elucidated. The NIM1 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270977 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 255 Bit Score: 44.25 E-value: 1.39e-04
|
|||||||||
| STKc_WNK | cd13983 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine kinase, With No Lysine (WNK) kinase; STKs catalyze ... |
59-191 | 1.40e-04 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine kinase, With No Lysine (WNK) kinase; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. WNKs comprise a subfamily of STKs with an unusual placement of a catalytic lysine relative to all other protein kinases. They are critical in regulating ion balance and are thus, important components in the control of blood pressure. They are also involved in cell signaling, survival, proliferation, and organ development. WNKs are activated by hyperosmotic or low-chloride hypotonic stress and they function upstream of SPAK and OSR1 kinases, which regulate the activity of cation-chloride cotransporters through direct interaction and phosphorylation. There are four vertebrate WNKs which show varying expression patterns. WNK1 and WNK2 are widely expressed while WNK3 and WNK4 show a more restricted expression pattern. Because mutations in human WNK1 and WNK4 cause PseudoHypoAldosteronism type II (PHAII), characterized by hypertension (due to increased sodium reabsorption) and hyperkalemia (due to impaired renal potassium secretion), there are more studies conducted on these two proteins, compared to WNK2 and WNK3. The WNK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270885 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 258 Bit Score: 44.14 E-value: 1.40e-04
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Pho85 | cd07836 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Fungal Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase Pho85; ... |
37-220 | 1.90e-04 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Fungal Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase Pho85; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Pho85 is a multifunctional CDK in yeast. It is regulated by 10 different cyclins (Pcls) and plays a role in G1 progression, cell polarity, phosphate and glycogen metabolism, gene expression, and in signaling changes in the environment. It is not essential for yeast viability and is the functional homolog of mammalian CDK5, which plays a role in central nervous system development. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. The Pho85 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 143341 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 284 Bit Score: 44.01 E-value: 1.90e-04
|
|||||||||
| PKc_STE | cd05122 | Catalytic domain of STE family Protein Kinases; PKs catalyze the transfer of the ... |
34-221 | 2.40e-04 | |||||
Catalytic domain of STE family Protein Kinases; PKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine (ST) or tyrosine residues on protein substrates. This family is composed of STKs, and some dual-specificity PKs that phosphorylate both threonine and tyrosine residues of target proteins. Most members are kinases involved in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling cascades, acting as MAPK kinases (MAPKKs), MAPKK kinases (MAPKKKs), or MAPKKK kinases (MAP4Ks). The MAPK signaling pathways are important mediators of cellular responses to extracellular signals. The pathways involve a triple kinase core cascade comprising of the MAPK, which is phosphorylated and activated by a MAPKK, which itself is phosphorylated and activated by a MAPKKK. Each MAPK cascade is activated either by a small GTP-binding protein or by an adaptor protein, which transmits the signal either directly to a MAPKKK to start the triple kinase core cascade or indirectly through a mediator kinase, a MAP4K. Other STE family members include p21-activated kinases (PAKs) and class III myosins, among others. PAKs are Rho family GTPase-regulated kinases that serve as important mediators in the function of Cdc42 (cell division cycle 42) and Rac. Class III myosins are motor proteins containing an N-terminal kinase catalytic domain and a C-terminal actin-binding domain, which can phosphorylate several cytoskeletal proteins, conventional myosin regulatory light chains, as well as autophosphorylate the C-terminal motor domain. They play an important role in maintaining the structural integrity of photoreceptor cell microvilli. The STE family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270692 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 254 Bit Score: 43.73 E-value: 2.40e-04
|
|||||||||
| STKc_CaMK_like | cd14088 | Catalytic domain of an Uncharacterized group of Serine/Threonine kinases with similarity to ... |
59-221 | 2.52e-04 | |||||
Catalytic domain of an Uncharacterized group of Serine/Threonine kinases with similarity to Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. This subfamily is composed of uncharacterized STKs with similarity to CaMKs, which are multifunctional calcium and calmodulin (CaM) stimulated STKs involved in cell cycle regulation. The CaMK family includes CaMKI, CaMKII, CaMKIV, and CaMK kinase (CaMKK). CaMKs contain an N-terminal catalytic domain followed by a regulatory domain that harbors a CaM binding site. This uncharacterized subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270990 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 265 Bit Score: 43.48 E-value: 2.52e-04
|
|||||||||
| PTK_Jak2_rpt1 | cd05078 | Pseudokinase (repeat 1) domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinase, Janus kinase 2; Jak2 is widely ... |
99-218 | 6.47e-04 | |||||
Pseudokinase (repeat 1) domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinase, Janus kinase 2; Jak2 is widely expressed in many tissues. It is essential for the signaling of hormone-like cytokines such as growth hormone, erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, and prolactin, as well as some IFNs and cytokines that signal through the IL-3 and gp130 receptors. Disruption of Jak2 in mice results in an embryonic lethal phenotype with multiple defects including erythropoietic and cardiac abnormalities. It is the only Jak gene that results in a lethal phenotype when disrupted in mice. A mutation in the pseudokinase domain of Jak2, V617F, is present in many myeloproliferative diseases, including almost all patients with polycythemia vera, and 50% of patients with essential thrombocytosis and myelofibrosis. Jak2 is a cytoplasmic (or nonreceptor) PTK containing an N-terminal FERM domain, followed by a Src homology 2 (SH2) domain, a pseudokinase domain, and a C-terminal tyr kinase domain. The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to tyr kinases but lacks crucial residues for catalytic activity and ATP binding. Despite this, the presumed pseudokinase (repeat 1) domain of Jak2 exhibits dual-specificity kinase activity, phosphorylating two negative regulatory sites in Jak2: Ser523 and Tyr570. Inactivation of the repeat 1 domain increased Jak2 basal activity, suggesting that it modulates the kinase activity of the C-terminal catalytic (repeat 2) domain. The Jak2 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other kinases such as serine/threonine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270663 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 262 Bit Score: 42.24 E-value: 6.47e-04
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek3 | cd08219 | Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA) ... |
52-258 | 6.63e-04 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase 3; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Nek3 is primarily localized in the cytoplasm and shows no cell cycle-dependent changes in its activity. It is present in the axons of neurons and affects morphogenesis and polarity through its regulation of microtubule acetylation. Nek3 modulates the signaling of the prolactin receptor through its activation of Vav2 and contributes to prolactin-mediated motility of breast cancer cells. It is one in a family of 11 different Neks (Nek1-11) that are involved in cell cycle control. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 173759 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 255 Bit Score: 42.27 E-value: 6.63e-04
|
|||||||||
| STKc_MELK | cd14078 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Maternal Embryonic Leucine zipper Kinase; ... |
34-221 | 7.67e-04 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Maternal Embryonic Leucine zipper Kinase; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. MELK is a cell cycle dependent protein which functions in cytokinesis, cell cycle, apoptosis, cell proliferation, and mRNA processing. It is found upregulated in many types of cancer cells, playing an indispensable role in cancer cell survival. It makes an attractive target in the design of inhibitors for use in the treatment of a wide range of human cancer. The MELK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270980 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 257 Bit Score: 41.98 E-value: 7.67e-04
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek1 | cd08218 | Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA) ... |
69-215 | 8.70e-04 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase 1; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Nek1 is associated with centrosomes throughout the cell cycle. It is involved in the formation of primary cilium and in the maintenance of centrosomes. It cycles through the nucleus and may be capable of relaying signals between the cilium and the nucleus. Nek1 is implicated in the development of polycystic kidney disease, which is characterized by benign polycystic tumors formed by abnormal overgrowth of renal epithelial cells. It appears also to be involved in DNA damage response, and may be important for both correct DNA damage checkpoint activation and DNA repair. Nek1 is one in a family of 11 different Neks (Nek1-11) that are involved in cell cycle control. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270858 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 256 Bit Score: 41.72 E-value: 8.70e-04
|
|||||||||
| PTK_Jak_rpt1 | cd05037 | Pseudokinase (repeat 1) domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinases, Janus kinases; The Jak ... |
91-221 | 9.56e-04 | |||||
Pseudokinase (repeat 1) domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinases, Janus kinases; The Jak subfamily is composed of Jak1, Jak2, Jak3, TYK2, and similar proteins. They are cytoplasmic (or nonreceptor) PTKs containing an N-terminal FERM domain, followed by a Src homology 2 (SH2) domain, a pseudokinase domain, and a C-terminal catalytic tyr kinase domain. The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to tyr kinases but lacks crucial residues for catalytic activity and ATP binding. It modulates the kinase activity of the C-terminal catalytic domain. In the case of Jak2, the presumed pseudokinase (repeat 1) domain exhibits dual-specificity kinase activity, phosphorylating two negative regulatory sites in Jak2: Ser523 and Tyr570. Most Jaks are expressed in a wide variety of tissues, except for Jak3, which is expressed only in hematopoietic cells. Jaks are crucial for cytokine receptor signaling. They are activated by autophosphorylation upon cytokine-induced receptor aggregation, and subsequently trigger downstream signaling events such as the phosphorylation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs). Jaks are also involved in regulating the surface expression of some cytokine receptors. The Jak-STAT pathway is involved in many biological processes including hematopoiesis, immunoregulation, host defense, fertility, lactation, growth, and embryogenesis. The Jak subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other kinases such as serine/threonine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270633 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 259 Bit Score: 41.70 E-value: 9.56e-04
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Aurora-A | cd14116 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine kinase, Aurora-A kinase; STKs catalyze the transfer ... |
71-221 | 1.02e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine kinase, Aurora-A kinase; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Aurora kinases are key regulators of mitosis and are essential for the accurate and equal division of genomic material from parent to daughter cells. Vertebrates contain at least 2 Aurora kinases (A and B); mammals contains a third Aurora kinase gene (C). Aurora-A regulates cell cycle events from the late S-phase through the M-phase including centrosome maturation, mitotic entry, centrosome separation, spindle assembly, chromosome alignment, cytokinesis, and mitotic exit. Aurora-A activation depends on its autophosphorylation and binding to the microtubule-associated protein TPX2, which also localizes the kinase to spindle microtubules. Aurora-A is overexpressed in many cancer types such as prostate, ovarian, breast, bladder, gastric, and pancreatic. The Aurora subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 271018 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 258 Bit Score: 41.87 E-value: 1.02e-03
|
|||||||||
| PTKc_Aatyk3 | cd14206 | Catalytic domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinases, Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase 3; PTKs ... |
41-216 | 1.05e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinases, Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase 3; PTKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to tyrosine (tyr) residues in protein substrates. Aatyk3, also called lemur tyrosine kinase 3 (Lmtk3) is a receptor kinase containing a transmembrane segment and a long C-terminal cytoplasmic tail with a catalytic domain. The function of Aatyk3 is still unknown. The Aatyk3 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other kinases such as protein serine/threonine kinases, RIO kinases, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). Pssm-ID: 271108 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 276 Bit Score: 41.86 E-value: 1.05e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_CDKL1_4 | cd07847 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase Like 1 and 4; ... |
37-261 | 1.42e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase Like 1 and 4; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CDKL1, also called p42 KKIALRE, is a glial protein that is upregulated in gliosis. It is present in neuroblastoma and A431 human carcinoma cells, and may be implicated in neoplastic transformation. The function of CDKL4 is unknown. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. The CDKL1/4 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270837 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 286 Bit Score: 41.59 E-value: 1.42e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_Nek8 | cd08220 | Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA) ... |
56-215 | 1.60e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase 8; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Nek8 contains an N-terminal kinase catalytic domain and a C-terminal RCC1 (regulator of chromosome condensation) domain. A double point mutation in Nek8 causes cystic kidney disease in mice that genetically resembles human autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Nek8 is also associated with a rare form of juvenile renal cystic disease, nephronophthisis type 9. It has been suggested that a defect in the ciliary localization of Nek8 contributes to the development of cysts manifested by these diseases. Nek8 is one in a family of 11 different Neks (Nek1-11) that are involved in cell cycle control. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270859 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 256 Bit Score: 40.87 E-value: 1.60e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_PLK3 | cd14189 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Polo-like kinase 3; STKs catalyze the ... |
69-221 | 1.90e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Polo-like kinase 3; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. PLKs play important roles in cell cycle progression and in DNA damage responses. They regulate mitotic entry, mitotic exit, and cytokinesis. In general PLKs contain an N-terminal catalytic kinase domain and a C-terminal regulatory polo box domain (PBD), which is comprised by two bipartite polo-box motifs (or polo boxes) and is involved in protein interactions. There are five mammalian PLKs (PLK1-5) from distinct genes. PLK3, also called Prk or Fnk (FGF-inducible kinase), regulates angiogenesis and responses to DNA damage. Activated PLK3 mediates Chk2 phosphorylation by ATM and the resulting checkpoint activation. PLK3 phosphorylates DNA polymerase delta and may be involved in DNA repair. It also inhibits Cdc25c, thereby regulating the onset of mitosis. The PLK3 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 271091 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 255 Bit Score: 40.68 E-value: 1.90e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_SnRK3 | cd14663 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Sucrose nonfermenting 1-related protein ... |
39-221 | 1.91e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Sucrose nonfermenting 1-related protein kinase subfamily 3; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The SnRKs form three different subfamilies designated SnRK1-3. SnRK3 is represented in this cd. The SnRK3 group contains members also known as CBL-interacting protein kinase, salt overly sensitive 2, SOS3-interacting proteins and protein kinase S. These kinases interact with calcium-binding proteins such as SOS3, SCaBPs, and CBL proteins, and are involved in responses to salt stress and in sugar and ABA signaling. The SnRKs belong to a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 271133 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 256 Bit Score: 40.85 E-value: 1.91e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_WNK1 | cd14030 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine protein kinase, With No Lysine (WNK) 1; STKs catalyze ... |
54-185 | 2.36e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine protein kinase, With No Lysine (WNK) 1; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. WNK1 is widely expressed and is most abundant in the testis. In hyperosmotic or hypotonic low-chloride stress conditions, WNK1 is activated and it phosphorylates its substrates including SPAK and OSR1 kinases, which regulate the activity of cation-chloride cotransporters through direct interaction and phosphorylation. Mutations in WNK1 cause PseudoHypoAldosteronism type II (PHAII), characterized by hypertension and hyperkalemia. WNK1 negates WNK4-mediated inhibition of the sodium-chloride cotransporter NCC and activates the epithelial sodium channel ENaC by activating SGK1. WNK1 also decreases the surface expression of renal outer medullary potassium channel (ROMK) by stimulating their endocytosis. Hypertension and hyperkalemia in PHAII patients with WNK1 mutations may be due partly to increased activity of NCC and ENaC, and impaired renal potassium secretion by ROMK, respectively. In addition, WNK1 interacts with MEKK2/3 and acts as an activator of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 5. It also negatively regulates TGFbeta signaling. WNKs comprise a subfamily of STKs with an unusual placement of the catalytic lysine relative to all other protein kinases. The WNK1 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270932 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 289 Bit Score: 40.80 E-value: 2.36e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_CaMKI | cd14083 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine kinase, Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ... |
34-139 | 2.78e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine kinase, Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Type I; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CaMKs are multifunctional calcium and calmodulin (CaM) stimulated STKs involved in cell cycle regulation. There are several types of CaMKs including CaMKI, CaMKII, and CaMKIV. In vertebrates, there are four CaMKI proteins encoded by different genes (alpha, beta, gamma, and delta), each producing at least one variant. CaMKs contain an N-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain that harbors a CaM binding site. CaMKI proteins are monomeric and they play pivotal roles in the nervous system, including long-term potentiation, dendritic arborization, neurite outgrowth, and the formation of spines, synapses, and axons. In addition, they may be involved in osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. The CaMKI subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270985 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 259 Bit Score: 40.43 E-value: 2.78e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_GAK_like | cd13985 | Catalytic domain of cyclin G-Associated Kinase-like proteins; STKs catalyze the transfer of ... |
53-213 | 3.11e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of cyclin G-Associated Kinase-like proteins; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. This subfamily includes cyclin G-Associated Kinase (GAK), Drosophila melanogaster Numb-Associated Kinase (NAK)-like proteins, and similar protein kinases. GAK plays regulatory roles in clathrin-mediated membrane trafficking, the maintenance of centrosome integrity and chromosome congression, neural patterning, survival of neurons, and immune responses. NAK plays a role in asymmetric cell division through its association with Numb. It also regulates the localization of Dlg, a protein essential for septate junction formation. The GAK-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270887 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 272 Bit Score: 40.40 E-value: 3.11e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_WNK3 | cd14031 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine protein kinase, With No Lysine (WNK) 3; STKs catalyze ... |
56-185 | 3.26e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine protein kinase, With No Lysine (WNK) 3; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. WNK3 shows a restricted expression pattern; it is found at high levels in the pituary glands and is also expressed in the kidney and brain. It has been shown to regulate many ion transporters including members of the SLC12A family of cation-chloride cotransporters such as NCC and NKCC2, the renal potassium channel ROMK, and the epithelial calcium channels TRPV5 and TRPV6. WNK3 appears to sense low-chloride hypotonic stress and under these conditions, it activates SPAK, which directly interacts and phosphorylates cation-chloride cotransporters. WNK3 has also been shown to promote cell survival, possibly through interaction with procaspase-3 and HSP70. WNKs comprise a subfamily of STKs with an unusual placement of the catalytic lysine relative to all other protein kinases. The WNK3 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270933 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 275 Bit Score: 40.09 E-value: 3.26e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_SIK | cd14071 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Salt-Inducible kinases; STKs catalyze the ... |
34-221 | 3.57e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Salt-Inducible kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. SIKs are part of a complex network that regulates Na,K-ATPase to maintain sodium homeostasis and blood pressure. Vertebrates contain three forms of SIKs (SIK1-3) from three distinct genes, which display tissue-specific effects. SIK1, also called SNF1LK, controls steroidogenic enzyme production in adrenocortical cells. In the brain, both SIK1 and SIK2 regulate energy metabolism. SIK2, also called QIK or SNF1LK2, is involved in the regulation of gluconeogenesis in the liver and lipogenesis in adipose tissues, where it phosphorylates the insulin receptor substrate-1. In the liver, SIK3 (also called QSK) regulates cholesterol and bile acid metabolism. In addition, SIK2 plays an important role in the initiation of mitosis and regulates the localization of C-Nap1, a centrosome linker protein. The SIK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270973 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 253 Bit Score: 40.07 E-value: 3.57e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_AMPK-like | cd14003 | Catalytic domain of AMP-activated protein kinase-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze ... |
69-221 | 3.72e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of AMP-activated protein kinase-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The AMPK-like subfamily is composed of AMPK, MARK, BRSK, NUAK, MELK, SNRK, TSSK, and SIK, among others. LKB1 serves as a master upstream kinase that activates AMPK and most AMPK-like kinases. AMPK, also called SNF1 (sucrose non-fermenting1) in yeasts and SnRK1 (SNF1-related kinase1) in plants, is a heterotrimeric enzyme composed of a catalytic alpha subunit and two regulatory subunits, beta and gamma. It is a stress-activated kinase that serves as master regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism by monitoring carbon and energy supplies, via sensing the cell's AMP:ATP ratio. MARKs phosphorylate tau and related microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs), and regulates microtubule-based intracellular transport. They are involved in embryogenesis, epithelial cell polarization, cell signaling, and neuronal differentiation. BRSKs play important roles in establishing neuronal polarity. TSSK proteins are almost exclusively expressed postmeiotically in the testis and play important roles in spermatogenesis and/or spermiogenesis. The AMPK-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270905 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 252 Bit Score: 39.81 E-value: 3.72e-03
|
|||||||||
| PTKc_Aatyk | cd05042 | Catalytic domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinases, Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinases; PTKs ... |
41-221 | 6.16e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinases, Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinases; PTKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to tyrosine (tyr) residues in protein substrates. The Aatyk subfamily is also referred to as the lemur tyrosine kinase (Lmtk) subfamily. It consists of Aatyk1 (Lmtk1), Aatyk2 (Lmtk2, Brek), Aatyk3 (Lmtk3), and similar proteins. Aatyk proteins are mostly receptor PTKs (RTKs) containing a transmembrane segment and a long C-terminal cytoplasmic tail with a catalytic domain. Aatyk1 does not contain a transmembrane segment and is a cytoplasmic (or nonreceptor) kinase. Aatyk proteins are classified as PTKs based on overall sequence similarity and the phylogenetic tree. However, analysis of catalytic residues suggests that Aatyk proteins may be multispecific kinases, functioning also as serine/threonine kinases. They are involved in neural differentiation, nerve growth factor (NGF) signaling, apoptosis, and spermatogenesis. The Aatyk subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other kinases such as protein serine/threonine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270638 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 269 Bit Score: 39.49 E-value: 6.16e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_CDK_like | cd07829 | Catalytic domain of Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs ... |
69-220 | 6.22e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. CDKs are partly regulated by their subcellular localization, which defines substrate phosphorylation and the resulting specific function. CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, and CDK6 have well-defined functions in the cell cycle, such as the regulation of the early G1 phase by CDK4 or CDK6, the G1/S phase transition by CDK2, or the entry of mitosis by CDK1. They also exhibit overlapping cyclin specificity and functions in certain conditions. Knockout mice with a single CDK deleted remain viable with specific phenotypes, showing that some CDKs can compensate for each other. For example, CDK4 can compensate for the loss of CDK6, however, double knockout mice with both CDK4 and CDK6 deleted die in utero. CDK8 and CDK9 are mainly involved in transcription while CDK5 is implicated in neuronal function. CDK7 plays essential roles in both the cell cycle as a CDK-Activating Kinase (CAK) and in transcription as a component of the general transcription factor TFIIH. The CDK-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270823 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 282 Bit Score: 39.39 E-value: 6.22e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_FA2-like | cd08529 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii FA2 and similar ... |
71-260 | 6.51e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinases, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii FA2 and similar proteins; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii FA2 was discovered in a genetic screen for deflagellation-defective mutants. It is essential for basal-body/centriole-associated microtubule severing, and plays a role in cell cycle progression. No cellular function has yet been ascribed to CNK4. The Chlamydomonas reinhardtii FA2-like subfamily belongs to the (NIMA)-related kinase (Nek) family, which includes seven different Chlamydomonas Neks (CNKs 1-6 and Fa2). This subfamily contains FA2 and CNK4. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270868 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 256 Bit Score: 39.32 E-value: 6.51e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_MST3_like | cd06609 | Catalytic domain of Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs ... |
107-252 | 8.04e-03 | |||||
Catalytic domain of Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. This subfamily is composed of MST3, MST4, STK25, Schizosaccharomyces pombe Nak1 and Sid1, Saccharomyces cerevisiae sporulation-specific protein 1 (SPS1), and related proteins. Nak1 is required by fission yeast for polarizing the tips of actin cytoskeleton and is involved in cell growth, cell separation, cell morphology and cell-cycle progression. Sid1 is a component in the septation initiation network (SIN) signaling pathway, and plays a role in cytokinesis. SPS1 plays a role in regulating proteins required for spore wall formation. MST4 plays a role in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling during cytoskeletal rearrangement, morphogenesis, and apoptosis. MST3 phosphorylates the STK NDR and may play a role in cell cycle progression and cell morphology. STK25 may play a role in the regulation of cell migration and polarization. The MST3-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270786 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 274 Bit Score: 39.15 E-value: 8.04e-03
|
|||||||||
| STKc_MLCK-like | cd14006 | Catalytic kinase domain of Myosin Light Chain Kinase-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs ... |
50-211 | 9.08e-03 | |||||
Catalytic kinase domain of Myosin Light Chain Kinase-like Serine/Threonine Kinases; STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. This family is composed of MLCKs and related MLCK-like kinase domains from giant STKs such as titin, obscurin, SPEG, Unc-89, Trio, kalirin, and Twitchin. Also included in this family are Death-Associated Protein Kinases (DAPKs) and Death-associated protein kinase-Related Apoptosis-inducing protein Kinase (DRAKs). MLCK phosphorylates myosin regulatory light chain and controls the contraction of all muscle types. Titin, obscurin, Twitchin, and SPEG are muscle proteins involved in the contractile apparatus. The giant STKs are multidomain proteins containing immunoglobulin (Ig), fibronectin type III (FN3), SH3, RhoGEF, PH and kinase domains. Titin, obscurin, Twitchin, and SPEG contain many Ig domain repeats at the N-terminus, while Trio and Kalirin contain spectrin-like repeats. The MLCK-like family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Pssm-ID: 270908 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 247 Bit Score: 38.79 E-value: 9.08e-03
|
|||||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|