From: From RNA to Protein

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
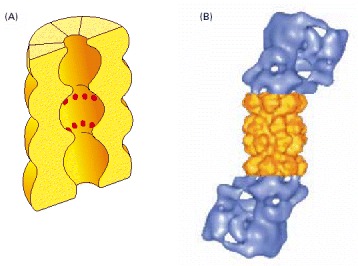
(A) A cut-away view of the structure of the central 20S cylinder, as determined by x-ray crystallography, with the active sites of the proteases indicated by red dots. (B) The structure of the entire proteasome, in which the central cylinder (yellow) is supplemented by a 19S cap (blue) at each end, whose structure has been determined by computer processing of electron microscope images. The complex cap structure selectively binds those proteins that have been marked for destruction; it then uses ATP hydrolysis to unfold their polypeptide chains and feed them into the inner chamber of the 20S cylinder for digestion to short peptides. (B, from W. Baumeister et al., Cell 92:367–380, 1998. © Elsevier.)
From: From RNA to Protein

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.