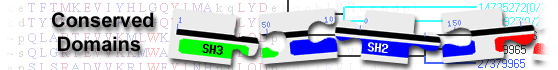hyaluronan-binding protein 2 isoform X3 [Mus musculus]
calcium-binding EGF-like domain-containing protein( domain architecture ID 10041892)
calcium-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain-containing protein may play a crucial role in numerous protein-protein interactions; similar to Homo sapiens Notch homolog 2 N-terminal-like proteins and protein delta homologs
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| EGF_CA | cd00054 | Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular ... |
67-103 | 3.79e-04 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular (mostly animal) proteins. Many of these proteins require calcium for their biological function and calcium-binding sites have been found to be located at the N-terminus of particular EGF-like domains; calcium-binding may be crucial for numerous protein-protein interactions. Six conserved core cysteines form three disulfide bridges as in non calcium-binding EGF domains, whose structures are very similar. EGF_CA can be found in tandem repeat arrangements. : Pssm-ID: 238011 Cd Length: 38 Bit Score: 36.85 E-value: 3.79e-04
|
||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| EGF_CA | cd00054 | Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular ... |
67-103 | 3.79e-04 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular (mostly animal) proteins. Many of these proteins require calcium for their biological function and calcium-binding sites have been found to be located at the N-terminus of particular EGF-like domains; calcium-binding may be crucial for numerous protein-protein interactions. Six conserved core cysteines form three disulfide bridges as in non calcium-binding EGF domains, whose structures are very similar. EGF_CA can be found in tandem repeat arrangements. Pssm-ID: 238011 Cd Length: 38 Bit Score: 36.85 E-value: 3.79e-04
|
||||||
| EGF | pfam00008 | EGF-like domain; There is no clear separation between noise and signal. pfam00053 is very ... |
71-101 | 6.50e-04 | ||
EGF-like domain; There is no clear separation between noise and signal. pfam00053 is very similar, but has 8 instead of 6 conserved cysteines. Includes some cytokine receptors. The EGF domain misses the N-terminus regions of the Ca2+ binding EGF domains (this is the main reason of discrepancy between swiss-prot domain start/end and Pfam). The family is hard to model due to many similar but different sub-types of EGF domains. Pfam certainly misses a number of EGF domains. Pssm-ID: 394967 Cd Length: 31 Bit Score: 35.82 E-value: 6.50e-04
|
||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| EGF_CA | cd00054 | Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular ... |
67-103 | 3.79e-04 | ||
Calcium-binding EGF-like domain, present in a large number of membrane-bound and extracellular (mostly animal) proteins. Many of these proteins require calcium for their biological function and calcium-binding sites have been found to be located at the N-terminus of particular EGF-like domains; calcium-binding may be crucial for numerous protein-protein interactions. Six conserved core cysteines form three disulfide bridges as in non calcium-binding EGF domains, whose structures are very similar. EGF_CA can be found in tandem repeat arrangements. Pssm-ID: 238011 Cd Length: 38 Bit Score: 36.85 E-value: 3.79e-04
|
||||||
| EGF | pfam00008 | EGF-like domain; There is no clear separation between noise and signal. pfam00053 is very ... |
71-101 | 6.50e-04 | ||
EGF-like domain; There is no clear separation between noise and signal. pfam00053 is very similar, but has 8 instead of 6 conserved cysteines. Includes some cytokine receptors. The EGF domain misses the N-terminus regions of the Ca2+ binding EGF domains (this is the main reason of discrepancy between swiss-prot domain start/end and Pfam). The family is hard to model due to many similar but different sub-types of EGF domains. Pfam certainly misses a number of EGF domains. Pssm-ID: 394967 Cd Length: 31 Bit Score: 35.82 E-value: 6.50e-04
|
||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|