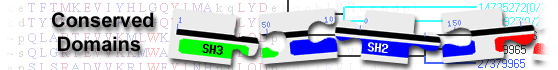alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase isoform a [Homo sapiens]
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| FUT8_N_cat | pfam19745 | Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase N- and catalytic domains; This entry represents the N-terminal ... |
68-498 | 0e+00 | |||||||
Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase N- and catalytic domains; This entry represents the N-terminal coiled-coil and the catalytic domains of the Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase (FUT8), an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a fucose residue in alpha 1-6 linkage to the N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residue in N-glycans. The catalytic domain comprises two structures, an open sheet alpha/beta structure, which contains five helices and three beta- strands at the N-terminal, and a Rossmann fold that contains five helices and five beta-strands at the C-terminal. The latter is conserved among the alpha1,2-, alpha1,6-, and protein O-fucosyltransferases and is similar to GT-B group glycosyltransferases. : Pssm-ID: 466170 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 431 Bit Score: 798.47 E-value: 0e+00
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Fut8 | cd11792 | Src homology 3 domain of Alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8); Fut8 catalyzes the alpha1, ... |
506-560 | 1.13e-29 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of Alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8); Fut8 catalyzes the alpha1,6-linkage of a fucose residue from a donor substrate to N-linked oligosaccharides on glycoproteins in a process called core fucosylation, which is crucial for growth factor receptor-mediated biological functions. Fut8-deficient mice show severe growth retardation, early death, and a pulmonary emphysema-like phenotype. Fut8 is also implicated to play roles in aging and cancer metastasis. It contains an N-terminal coiled-coil domain, a catalytic domain, and a C-terminal SH3 domain. The SH3 domain of Fut8 is located in the lumen and its role in glycosyl transfer is unclear. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. : Pssm-ID: 212726 Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 110.76 E-value: 1.13e-29
|
|||||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| FUT8_N_cat | pfam19745 | Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase N- and catalytic domains; This entry represents the N-terminal ... |
68-498 | 0e+00 | |||||||
Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase N- and catalytic domains; This entry represents the N-terminal coiled-coil and the catalytic domains of the Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase (FUT8), an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a fucose residue in alpha 1-6 linkage to the N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residue in N-glycans. The catalytic domain comprises two structures, an open sheet alpha/beta structure, which contains five helices and three beta- strands at the N-terminal, and a Rossmann fold that contains five helices and five beta-strands at the C-terminal. The latter is conserved among the alpha1,2-, alpha1,6-, and protein O-fucosyltransferases and is similar to GT-B group glycosyltransferases. Pssm-ID: 466170 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 431 Bit Score: 798.47 E-value: 0e+00
|
|||||||||||
| Fut8_like | cd11300 | Alpha 1-6-fucosyltransferase; Alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8) transfers a fucose moiety ... |
174-499 | 0e+00 | |||||||
Alpha 1-6-fucosyltransferase; Alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8) transfers a fucose moiety from GDP-fucose to the reducing terminal N-acetylglucosamine of the core structure of Asn-linked oligosaccharides, in a process termed core fucosylation. Core fucosylation is essential for the function of growth factor receptors. O-fucosyltransferase-like proteins are GDP-fucose dependent enzymes with similarities to the family 1 glycosyltransferases (GT1). They are soluble ER proteins that may be proteolytically cleaved from a membrane-associated preprotein, and are involved in the O-fucosylation of protein substrates, the core fucosylation of growth factor receptors, and other processes. Pssm-ID: 211386 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 328 Bit Score: 598.46 E-value: 0e+00
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Fut8 | cd11792 | Src homology 3 domain of Alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8); Fut8 catalyzes the alpha1, ... |
506-560 | 1.13e-29 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of Alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8); Fut8 catalyzes the alpha1,6-linkage of a fucose residue from a donor substrate to N-linked oligosaccharides on glycoproteins in a process called core fucosylation, which is crucial for growth factor receptor-mediated biological functions. Fut8-deficient mice show severe growth retardation, early death, and a pulmonary emphysema-like phenotype. Fut8 is also implicated to play roles in aging and cancer metastasis. It contains an N-terminal coiled-coil domain, a catalytic domain, and a C-terminal SH3 domain. The SH3 domain of Fut8 is located in the lumen and its role in glycosyl transfer is unclear. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212726 Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 110.76 E-value: 1.13e-29
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_9 | pfam14604 | Variant SH3 domain; |
509-559 | 8.92e-14 | |||||||
Variant SH3 domain; Pssm-ID: 434066 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 49 Bit Score: 65.72 E-value: 8.92e-14
|
|||||||||||
| SH3 | smart00326 | Src homology 3 domains; Src homology 3 (SH3) domains bind to target proteins through sequences ... |
508-559 | 2.65e-08 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domains; Src homology 3 (SH3) domains bind to target proteins through sequences containing proline and hydrophobic amino acids. Pro-containing polypeptides may bind to SH3 domains in 2 different binding orientations. Pssm-ID: 214620 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 56 Bit Score: 50.23 E-value: 2.65e-08
|
|||||||||||
| COG2433 | COG2433 | Possible nuclease of RNase H fold, RuvC/YqgF family [General function prediction only]; |
41-151 | 4.42e-04 | |||||||
Possible nuclease of RNase H fold, RuvC/YqgF family [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 441980 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 644 Bit Score: 43.31 E-value: 4.42e-04
|
|||||||||||
| PRK03918 | PRK03918 | DNA double-strand break repair ATPase Rad50; |
40-142 | 5.87e-03 | |||||||
DNA double-strand break repair ATPase Rad50; Pssm-ID: 235175 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 880 Bit Score: 39.66 E-value: 5.87e-03
|
|||||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| FUT8_N_cat | pfam19745 | Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase N- and catalytic domains; This entry represents the N-terminal ... |
68-498 | 0e+00 | |||||||
Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase N- and catalytic domains; This entry represents the N-terminal coiled-coil and the catalytic domains of the Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase (FUT8), an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a fucose residue in alpha 1-6 linkage to the N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residue in N-glycans. The catalytic domain comprises two structures, an open sheet alpha/beta structure, which contains five helices and three beta- strands at the N-terminal, and a Rossmann fold that contains five helices and five beta-strands at the C-terminal. The latter is conserved among the alpha1,2-, alpha1,6-, and protein O-fucosyltransferases and is similar to GT-B group glycosyltransferases. Pssm-ID: 466170 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 431 Bit Score: 798.47 E-value: 0e+00
|
|||||||||||
| Fut8_like | cd11300 | Alpha 1-6-fucosyltransferase; Alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8) transfers a fucose moiety ... |
174-499 | 0e+00 | |||||||
Alpha 1-6-fucosyltransferase; Alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8) transfers a fucose moiety from GDP-fucose to the reducing terminal N-acetylglucosamine of the core structure of Asn-linked oligosaccharides, in a process termed core fucosylation. Core fucosylation is essential for the function of growth factor receptors. O-fucosyltransferase-like proteins are GDP-fucose dependent enzymes with similarities to the family 1 glycosyltransferases (GT1). They are soluble ER proteins that may be proteolytically cleaved from a membrane-associated preprotein, and are involved in the O-fucosylation of protein substrates, the core fucosylation of growth factor receptors, and other processes. Pssm-ID: 211386 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 328 Bit Score: 598.46 E-value: 0e+00
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Fut8 | cd11792 | Src homology 3 domain of Alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8); Fut8 catalyzes the alpha1, ... |
506-560 | 1.13e-29 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of Alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8); Fut8 catalyzes the alpha1,6-linkage of a fucose residue from a donor substrate to N-linked oligosaccharides on glycoproteins in a process called core fucosylation, which is crucial for growth factor receptor-mediated biological functions. Fut8-deficient mice show severe growth retardation, early death, and a pulmonary emphysema-like phenotype. Fut8 is also implicated to play roles in aging and cancer metastasis. It contains an N-terminal coiled-coil domain, a catalytic domain, and a C-terminal SH3 domain. The SH3 domain of Fut8 is located in the lumen and its role in glycosyl transfer is unclear. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212726 Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 110.76 E-value: 1.13e-29
|
|||||||||||
| O-FucT_like | cd11296 | GDP-fucose protein O-fucosyltransferase and related proteins; O-fucosyltransferase-like ... |
325-473 | 1.98e-14 | |||||||
GDP-fucose protein O-fucosyltransferase and related proteins; O-fucosyltransferase-like proteins are GDP-fucose dependent enzymes with similarities to the family 1 glycosyltransferases (GT1). They are soluble ER proteins that may be proteolytically cleaved from a membrane-associated preprotein, and are involved in the O-fucosylation of protein substrates, the core fucosylation of growth factor receptors, and other processes. Pssm-ID: 211383 Cd Length: 206 Bit Score: 72.45 E-value: 1.98e-14
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_9 | pfam14604 | Variant SH3 domain; |
509-559 | 8.92e-14 | |||||||
Variant SH3 domain; Pssm-ID: 434066 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 49 Bit Score: 65.72 E-value: 8.92e-14
|
|||||||||||
| NodZ_like | cd11548 | Alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase similar to Bradyrhizobium NodZ; Bradyrhizobium NodZ is an alpha 1, ... |
329-475 | 6.74e-10 | |||||||
Alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase similar to Bradyrhizobium NodZ; Bradyrhizobium NodZ is an alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase involved in the biosynthesis of the nodulation factor, a lipo-chitooligosaccharide formed by three-to-six beta-1,4-linked N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (GlcNAc) residues and a fatty acid acyl group attached to the nitrogen atom at the non-reducing end. NodZ transfers L-fucose from the GDP-beta-L-fucose donor to the reducing residue of the chitin oligosaccharide backbone, before the attachment of a fatty acid group. O-fucosyltransferase-like proteins are GDP-fucose dependent enzymes with similarities to the family 1 glycosyltransferases (GT1). They are soluble ER proteins that may be proteolytically cleaved from a membrane-associated preprotein, and are involved in the O-fucosylation of protein substrates, the core fucosylation of growth factor receptors, and other processes. Pssm-ID: 211389 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 287 Bit Score: 60.46 E-value: 6.74e-10
|
|||||||||||
| SH3 | smart00326 | Src homology 3 domains; Src homology 3 (SH3) domains bind to target proteins through sequences ... |
508-559 | 2.65e-08 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domains; Src homology 3 (SH3) domains bind to target proteins through sequences containing proline and hydrophobic amino acids. Pro-containing polypeptides may bind to SH3 domains in 2 different binding orientations. Pssm-ID: 214620 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 56 Bit Score: 50.23 E-value: 2.65e-08
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_SH3RF2_3 | cd11784 | Third Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 2; SH3RF2 is also called ... |
508-558 | 4.83e-08 | |||||||
Third Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 2; SH3RF2 is also called POSHER (POSH-eliminating RING protein) or HEPP1 (heart protein phosphatase 1-binding protein). It acts as an anti-apoptotic regulator of the JNK pathway by binding to and promoting the degradation of SH3RF1 (or POSH), a scaffold protein that is required for pro-apoptotic JNK activation. It may also play a role in cardiac functions together with protein phosphatase 1. SH3RF2 contains an N-terminal RING finger domain and three SH3 domains. This model represents the third SH3 domain, located in the middle, of SH3RF2. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212718 Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 49.78 E-value: 4.83e-08
|
|||||||||||
| SH3 | cd00174 | Src Homology 3 domain superfamily; Src Homology 3 (SH3) domains are protein interaction ... |
508-555 | 1.18e-06 | |||||||
Src Homology 3 domain superfamily; Src Homology 3 (SH3) domains are protein interaction domains that bind proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. Thus, they are referred to as proline-recognition domains (PRDs). SH3 domains are less selective and show more diverse specificity compared to other PRDs. They have been shown to bind peptide sequences that lack the PxxP motif; examples include the PxxDY motif of Eps8 and the RKxxYxxY sequence in SKAP55. SH3 domain containing proteins play versatile and diverse roles in the cell, including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies, among others. Many members of this superfamily are adaptor proteins that associate with a number of protein partners, facilitating complex formation and signal transduction. Pssm-ID: 212690 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 51 Bit Score: 45.53 E-value: 1.18e-06
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_1 | pfam00018 | SH3 domain; SH3 (Src homology 3) domains are often indicative of a protein involved in signal ... |
508-555 | 1.72e-05 | |||||||
SH3 domain; SH3 (Src homology 3) domains are often indicative of a protein involved in signal transduction related to cytoskeletal organization. First described in the Src cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase. The structure is a partly opened beta barrel. Pssm-ID: 394975 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 47 Bit Score: 42.19 E-value: 1.72e-05
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_SH3RF_3 | cd11783 | Third Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 1 (SH3RF1), SH3RF3, and ... |
508-554 | 6.90e-05 | |||||||
Third Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 1 (SH3RF1), SH3RF3, and similar domains; SH3RF1 (or POSH) and SH3RF3 (or POSH2) are scaffold proteins that function as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases. They contain an N-terminal RING finger domain and four SH3 domains. This model represents the third SH3 domain, located in the middle of SH3RF1 and SH3RF3, and similar domains. SH3RF1 plays a role in calcium homeostasis through the control of the ubiquitin domain protein Herp. It may also have a role in regulating death receptor mediated and JNK mediated apoptosis. SH3RF3 interacts with p21-activated kinase 2 (PAK2) and GTP-loaded Rac1. It may play a role in regulating JNK mediated apoptosis in certain conditions. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212717 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 40.84 E-value: 6.90e-05
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Nostrin | cd11823 | Src homology 3 domain of Nitric Oxide Synthase TRaffic INducer; Nostrin is expressed in ... |
509-560 | 2.09e-04 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of Nitric Oxide Synthase TRaffic INducer; Nostrin is expressed in endothelial and epithelial cells and is involved in the regulation, trafficking and targeting of endothelial NOS (eNOS). It facilitates the endocytosis of eNOS by coordinating the functions of dynamin and the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP). Increased expression of Nostrin may be correlated to preeclampsia. Nostrin contains an N-terminal F-BAR domain and a C-terminal SH3 domain. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212757 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 53 Bit Score: 39.25 E-value: 2.09e-04
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_SH3RF3_3 | cd11925 | Third Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 3, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ... |
508-554 | 4.06e-04 | |||||||
Third Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 3, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase; SH3RF3 is also called POSH2 (Plenty of SH3s 2) or SH3MD4 (SH3 multiple domains protein 4). It is a scaffold protein with E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity. It was identified in the screen for interacting partners of p21-activated kinase 2 (PAK2). It may play a role in regulating JNK mediated apoptosis in certain conditions. It also interacts with GTP-loaded Rac1. SH3RF3 is highly homologous to SH3RF1; it also contains an N-terminal RING finger domain and four SH3 domains. This model represents the third SH3 domain, located in the middle, of SH3RF3. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212858 Cd Length: 57 Bit Score: 38.82 E-value: 4.06e-04
|
|||||||||||
| COG2433 | COG2433 | Possible nuclease of RNase H fold, RuvC/YqgF family [General function prediction only]; |
41-151 | 4.42e-04 | |||||||
Possible nuclease of RNase H fold, RuvC/YqgF family [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 441980 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 644 Bit Score: 43.31 E-value: 4.42e-04
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_UBASH3 | cd11791 | Src homology 3 domain of Ubiquitin-associated and SH3 domain-containing proteins, also called ... |
509-554 | 5.43e-04 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of Ubiquitin-associated and SH3 domain-containing proteins, also called TULA (T cell Ubiquitin LigAnd) family of proteins; UBASH3 or TULA proteins are also referred to as Suppressor of T cell receptor Signaling (STS) proteins. They contain an N-terminal UBA domain, a central SH3 domain, and a C-terminal histidine phosphatase domain. They bind c-Cbl through the SH3 domain and to ubiquitin via UBA. In some vertebrates, there are two TULA family proteins, called UBASH3A (also called TULA or STS-2) and UBASH3B (also called TULA-2 or STS-1), which show partly overlapping as well as distinct functions. UBASH3B is widely expressed while UBASH3A is only found in lymphoid cells. UBASH3A facilitates apoptosis induced in T cells through its interaction with the apoptosis-inducing factor AIF. UBASH3B is an active phosphatase while UBASH3A is not. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212725 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 59 Bit Score: 38.44 E-value: 5.43e-04
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_CIN85_2 | cd12055 | Second Src Homology 3 domain (SH3B) of Cbl-interacting protein of 85 kDa; CIN85, also called ... |
509-560 | 5.74e-04 | |||||||
Second Src Homology 3 domain (SH3B) of Cbl-interacting protein of 85 kDa; CIN85, also called SH3 domain-containing kinase-binding protein 1 (SH3KBP1) or CD2-binding protein 3 (CD2BP3) or Ruk, is an adaptor protein that is involved in the downregulation of receptor tyrosine kinases by facilitating endocytosis through interaction with endophilin-associated ubiquitin ligase Cbl proteins. It is also important in many other cellular processes including vesicle-mediated transport, cytoskeletal remodelling, apoptosis, cell adhesion and migration, and viral infection, among others. CIN85 exists as multiple variants from alternative splicing; the main variant contains three SH3 domains, a proline-rich region, and a C-terminal coiled-coil domain. All of these domains enable CIN85 to bind various protein partners and assemble complexes that have been implicated in many different functions. This alignment model represents the second SH3 domain (SH3B) of CIN85. SH3B has been shown to bind Cbl proline-rich peptides and ubiquitin. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212988 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 53 Bit Score: 38.05 E-value: 5.74e-04
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Intersectin_1 | cd11836 | First Src homology 3 domain (or SH3A) of Intersectin; Intersectins (ITSNs) are adaptor ... |
509-554 | 8.79e-04 | |||||||
First Src homology 3 domain (or SH3A) of Intersectin; Intersectins (ITSNs) are adaptor proteins that function in exo- and endocytosis, actin cytoskeletal reorganization, and signal transduction. They are essential for initiating clathrin-coated pit formation. They bind to many proteins through their multidomain structure and facilitate the assembly of multimeric complexes. Vertebrates contain two ITSN proteins, ITSN1 and ITSN2, which exist in alternatively spliced short and long isoforms. The short isoforms contain two Eps15 homology domains (EH1 and EH2), a coiled-coil region and five SH3 domains (SH3A-E), while the long isoforms, in addition, contain RhoGEF (also called Dbl-homologous or DH), Pleckstrin homology (PH) and C2 domains. ITSN1 and ITSN2 are both widely expressed, with variations depending on tissue type and stage of development. The first SH3 domain (or SH3A) of ITSN1 has been shown to bind many proteins including Sos1, dynamin1/2, CIN85, c-Cbl, PI3K-C2, SHIP2, N-WASP, and CdGAP, among others. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212770 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 37.72 E-value: 8.79e-04
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Shank | cd11832 | Src homology 3 domain of SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains (Shank) proteins; Shank ... |
508-556 | 8.80e-04 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains (Shank) proteins; Shank proteins carry scaffolding functions through multiple sites of protein-protein interaction in its domain architecture, including ankyrin (ANK) repeats, a long proline rich region, as well as SH3, PDZ, and SAM domains. They bind a variety of membrane and cytosolic proteins, and exist in alternatively spliced isoforms. They are highly enriched in postsynaptic density (PSD) where they interact with the cytoskeleton and with postsynaptic membrane receptors including NMDA and glutamate receptors. They are crucial in the construction and organization of the PSD and dendritic spines of excitatory synapses. There are three members of this family (Shank1, Shank2, Shank3) which show distinct and cell-type specific patterns of expression. Shank1 is brain-specific; Shank2 is found in neurons, glia, endocrine cells, liver, and kidney; Shank3 is widely expressed. The SH3 domain of Shank binds GRIP, a scaffold protein that binds AMPA receptors and Eph receptors/ligands. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212766 Cd Length: 50 Bit Score: 37.42 E-value: 8.80e-04
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_CIP4_Bzz1_like | cd11777 | Src Homology 3 domain of Cdc42-Interacting Protein 4, Bzz1 and similar domains; This subfamily ... |
509-559 | 1.12e-03 | |||||||
Src Homology 3 domain of Cdc42-Interacting Protein 4, Bzz1 and similar domains; This subfamily is composed of Cdc42-Interacting Protein 4 (CIP4) and similar proteins such as Formin Binding Protein 17 (FBP17) and FormiN Binding Protein 1-Like (FNBP1L), as well as yeast Bzz1 (or Bzz1p). CIP4 and FNBP1L are Cdc42 effectors that bind Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) and function in endocytosis. CIP4 and FBP17 bind to the Fas ligand and may be implicated in the inflammatory response. CIP4 may also play a role in phagocytosis. Bzz1 is also a WASP/Las17-interacting protein involved in endocytosis and trafficking to the vacuole. It physically interacts with type I myosins and functions in the early steps of endocytosis. Members of this subfamily contain an N-terminal F-BAR (FES-CIP4 Homology and Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs) domain as well as at least one C-terminal SH3 domain. Bzz1 contains a second SH3 domain at the C-terminus. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212711 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 37.20 E-value: 1.12e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_JIP1_like | cd11801 | Src homology 3 domain of JNK-interacting proteins 1 and 2, and similar domains; ... |
509-560 | 1.12e-03 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of JNK-interacting proteins 1 and 2, and similar domains; JNK-interacting proteins (JIPs) function as scaffolding proteins for c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathways. They bind to components of Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways such as JNK, MKK, and several MAP3Ks such as MLK and DLK. There are four JIPs (JIP1-4); all contain a JNK binding domain. JIP1 and JIP2 also contain SH3 and Phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domains. Both are highly expressed in the brain and pancreatic beta-cells. JIP1 functions as an adaptor linking motor to cargo during axonal transport and also is involved in regulating insulin secretion. JIP2 form complexes with fibroblast growth factor homologous factors (FHFs), which facilitates activation of the p38delta MAPK. The SH3 domain of JIP1 homodimerizes at the interface usually involved in proline-rich ligand recognition, despite the lack of this motif in the domain itself. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212735 Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 37.29 E-value: 1.12e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_ephexin1_like | cd11793 | Src homology 3 domain of ephexin-1-like SH3 domain containing Rho guanine nucleotide exchange ... |
508-560 | 1.12e-03 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of ephexin-1-like SH3 domain containing Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors; Members of this family contain RhoGEF (also called Dbl-homologous or DH), Pleckstrin Homology (PH), and C-terminal SH3 domains. They include the Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors ARHGEF5, ARHGEF16, ARHGEF19, ARHGEF26, ARHGEF27 (also called ephexin-1), and similar proteins, and are also called ephexins because they interact directly with ephrin A receptors. GEFs interact with Rho GTPases via their DH domains to catalyze nucleotide exchange by stabilizing the nucleotide-free GTPase intermediate. They play important roles in neuronal development. The SH3 domains of ARHGEFs play an autoinhibitory role through intramolecular interactions with a proline-rich region N-terminal to the DH domain. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212727 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 37.32 E-value: 1.12e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Sorbs1_3 | cd11916 | Third (or C-terminal) Src Homology 3 domain of Sorbin and SH3 domain containing 1 (Sorbs1), ... |
509-559 | 1.37e-03 | |||||||
Third (or C-terminal) Src Homology 3 domain of Sorbin and SH3 domain containing 1 (Sorbs1), also called ponsin; Sorbs1 is also called ponsin, SH3P12, or CAP (c-Cbl associated protein). It is an adaptor protein containing one sorbin homology (SoHo) and three SH3 domains. It binds Cbl and plays a major role in regulating the insulin signaling pathway by enhancing insulin-induced phosphorylation of Cbl. Sorbs1, like vinexin, localizes at cell-ECM and cell-cell adhesion sites where it binds vinculin, paxillin, and afadin. It may function in the control of cell motility. Other interaction partners of Sorbs1 include c-Abl, Sos, flotillin, Grb4, ataxin-7, filamin C, among others. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212849 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 59 Bit Score: 37.28 E-value: 1.37e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_SH3RF1_3 | cd11926 | Third Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 1, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ... |
508-554 | 1.64e-03 | |||||||
Third Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 1, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase; SH3RF1 is also called POSH (Plenty of SH3s) or SH3MD2 (SH3 multiple domains protein 2). It is a scaffold protein that acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. It plays a role in calcium homeostasis through the control of the ubiquitin domain protein Herp. It may also have a role in regulating death receptor mediated and JNK mediated apoptosis. SH3RF1 also enhances the ubiquitination of ROMK1 potassium channel resulting in its increased endocytosis. It contains an N-terminal RING finger domain and four SH3 domains. This model represents the third SH3 domain, located in the middle, of SH3RF1. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212859 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 36.87 E-value: 1.64e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_SH3RF_C | cd11785 | C-terminal (Fourth) Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 1 (SH3RF1), ... |
509-555 | 1.76e-03 | |||||||
C-terminal (Fourth) Src Homology 3 domain of SH3 domain containing ring finger 1 (SH3RF1), SH3RF3, and similar domains; SH3RF1 (or POSH) and SH3RF3 (or POSH2) are scaffold proteins that function as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases. They contain an N-terminal RING finger domain and four SH3 domains. This model represents the fourth SH3 domain, located at the C-terminus of SH3RF1 and SH3RF3, and similar domains. SH3RF1 plays a role in calcium homeostasis through the control of the ubiquitin domain protein Herp. It may also have a role in regulating death receptor mediated and JNK mediated apoptosis. SH3RF3 interacts with p21-activated kinase 2 (PAK2) and GTP-loaded Rac1. It may play a role in regulating JNK mediated apoptosis in certain conditions. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212719 Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 36.68 E-value: 1.76e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_BOI | cd11886 | Src Homology 3 domain of fungal BOI-like proteins; This subfamily includes the Saccharomyces ... |
508-554 | 1.99e-03 | |||||||
Src Homology 3 domain of fungal BOI-like proteins; This subfamily includes the Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins BOI1 and BOI2, and similar proteins. They contain an N-terminal SH3 domain, a Sterile alpha motif (SAM), and a Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain at the C-terminus. BOI1 and BOI2 interact with the SH3 domain of Bem1p, a protein involved in bud formation. They promote polarized cell growth and participates in the NoCut signaling pathway, which is involved in the control of cytokinesis. SH3 domains bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs; they play a role in the regulation of enzymes by intramolecular interactions, changing the subcellular localization of signal pathway components and mediate multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212819 Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 36.54 E-value: 1.99e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Cortactin_like | cd11819 | Src homology 3 domain of Cortactin and related proteins; This subfamily includes cortactin, ... |
508-555 | 2.17e-03 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of Cortactin and related proteins; This subfamily includes cortactin, Abp1 (actin-binding protein 1), hematopoietic lineage cell-specific protein 1 (HS1), and similar proteins. These proteins are involved in regulating actin dynamics through direct or indirect interaction with the Arp2/3 complex, which is required to initiate actin polymerization. They all contain at least one C-terminal SH3 domain. Cortactin and HS1 bind Arp2/3 and actin through an N-terminal region that contains an acidic domain and several copies of a repeat domain found in cortactin and HS1. Abp1 binds actin via an N-terminal actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF) homology domain. Yeast Abp1 binds Arp2/3 directly through two acidic domains. Mammalian Abp1 does not directly interact with Arp2/3; instead, it regulates actin dynamics indirectly by interacting with dynamin and WASP family proteins. The C-terminal region of these proteins acts as an adaptor or scaffold that can connect membrane trafficking and signaling proteins that bind the SH3 domain within the actin network. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212753 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 54 Bit Score: 36.52 E-value: 2.17e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_MyoIe_If_like | cd11827 | Src homology 3 domain of Myosins Ie, If, and similar proteins; Myosins Ie (MyoIe) and If ... |
509-555 | 2.24e-03 | |||||||
Src homology 3 domain of Myosins Ie, If, and similar proteins; Myosins Ie (MyoIe) and If (MyoIf) are nonmuscle, unconventional, long tailed, class I myosins containing an N-terminal motor domain and a myosin tail with TH1, TH2, and SH3 domains. MyoIe interacts with the endocytic proteins, dynamin and synaptojanin-1, through its SH3 domain; it may play a role in clathrin-dependent endocytosis. In the kidney, MyoIe is critical for podocyte function and normal glomerular filtration. Mutations in MyoIe is associated with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, a disease characterized by massive proteinuria and progression to end-stage kidney disease. MyoIf is predominantly expressed in the immune system; it plays a role in immune cell motility and innate immunity. Mutations in MyoIf may be associated with the loss of hearing. The MyoIf gene has also been found to be fused to the MLL (Mixed lineage leukemia) gene in infant acute myeloid leukemias (AML). SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212761 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 53 Bit Score: 36.24 E-value: 2.24e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_OSTF1 | cd11772 | Src Homology 3 domain of metazoan osteoclast stimulating factor 1; OSTF1, also named OSF or ... |
509-560 | 2.55e-03 | |||||||
Src Homology 3 domain of metazoan osteoclast stimulating factor 1; OSTF1, also named OSF or SH3P2, is a signaling protein containing SH3 and ankyrin-repeat domains. It acts through a Src-related pathway to enhance the formation of osteoclasts and bone resorption. It also acts as a negative regulator of cell motility. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212706 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 53 Bit Score: 36.12 E-value: 2.55e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Vinexin_3 | cd11918 | Third (or C-terminal) Src Homology 3 domain of Vinexin, also called Sorbin and SH3 domain ... |
509-554 | 2.65e-03 | |||||||
Third (or C-terminal) Src Homology 3 domain of Vinexin, also called Sorbin and SH3 domain containing 3 (Sorbs3); Vinexin is also called Sorbs3, SH3P3, and SH3-containing adapter molecule 1 (SCAM-1). It is an adaptor protein containing one sorbin homology (SoHo) and three SH3 domains. Vinexin was first identified as a vinculin binding protein; it is co-localized with vinculin at cell-ECM and cell-cell adhesion sites. There are several splice variants of vinexin: alpha, which contains the SoHo and three SH3 domains and displays tissue-specific expression; and beta, which contains only the three SH3 domains and is widely expressed. Vinexin alpha stimulates the accumulation of F-actin at focal contact sites. Vinexin also promotes keratinocyte migration and wound healing. The SH3 domains of vinexin have been reported to bind a number of ligands including vinculin, WAVE2, DLG5, Abl, and Cbl. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212851 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 58 Bit Score: 36.47 E-value: 2.65e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Sorbs_3 | cd11780 | Third (or C-terminal) Src Homology 3 domain of Sorbin and SH3 domain containing (Sorbs) ... |
509-554 | 5.08e-03 | |||||||
Third (or C-terminal) Src Homology 3 domain of Sorbin and SH3 domain containing (Sorbs) proteins and similar domains; This family, also called the vinexin family, is composed predominantly of adaptor proteins containing one sorbin homology (SoHo) and three SH3 domains. Members include the third SH3 domains of Sorbs1 (or ponsin), Sorbs2 (or ArgBP2), Vinexin (or Sorbs3), and similar domains. They are involved in the regulation of cytoskeletal organization, cell adhesion, and growth factor signaling. Members of this family bind multiple partners including signaling molecules like c-Abl, c-Arg, Sos, and c-Cbl, as well as cytoskeletal molecules such as vinculin and afadin. They may have overlapping functions. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212714 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 55 Bit Score: 35.35 E-value: 5.08e-03
|
|||||||||||
| PRK03918 | PRK03918 | DNA double-strand break repair ATPase Rad50; |
40-142 | 5.87e-03 | |||||||
DNA double-strand break repair ATPase Rad50; Pssm-ID: 235175 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 880 Bit Score: 39.66 E-value: 5.87e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_PIX | cd11877 | Src Homology 3 domain of Pak Interactive eXchange factors; PIX proteins are Rho guanine ... |
509-560 | 7.62e-03 | |||||||
Src Homology 3 domain of Pak Interactive eXchange factors; PIX proteins are Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), which activate small GTPases by exchanging bound GDP for free GTP. They act as GEFs for both Cdc42 and Rac 1, and have been implicated in cell motility, adhesion, neurite outgrowth, and cell polarity. Vertebrates contain two proteins from the PIX subfamily, alpha-PIX and beta-PIX. Alpha-PIX, also called ARHGEF6, is localized in dendritic spines where it regulates spine morphogenesis. Mutations in the ARHGEF6 gene cause X-linked intellectual disability in humans. Beta-PIX play roles in regulating neuroendocrine exocytosis, focal adhesion maturation, cell migration, synaptic vesicle localization, and insulin secretion. PIX proteins contain an N-terminal SH3 domain followed by RhoGEF (also called Dbl-homologous or DH) and Pleckstrin Homology (PH) domains, and a C-terminal leucine-zipper domain for dimerization. The SH3 domain of PIX binds to an atypical PxxxPR motif in p21-activated kinases (PAKs) with high affinity. The binding of PAKs to PIX facilitate the localization of PAKs to focal complexes and also localizes PAKs to PIX targets Cdc43 and Rac, leading to the activation of PAKs. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212810 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 53 Bit Score: 34.98 E-value: 7.62e-03
|
|||||||||||
| Fut1_Fut2_like | cd11301 | Alpha-1,2-fucosyltransferase; Alpha-1,2-fucosyltransferases (Fut1, Fut2) catalyze the transfer ... |
342-468 | 7.63e-03 | |||||||
Alpha-1,2-fucosyltransferase; Alpha-1,2-fucosyltransferases (Fut1, Fut2) catalyze the transfer of alpha-L-fucose to the terminal beta-D-galactose residue of glycoconjugates via an alpha-1,2-linkage, generating carbohydrate structures that exhibit H-antigenicity for blood-group carbohydrates. These structures also act as ligands for morphogenesis, the adhesion of microbes, and metastasizing cancer cells. Fut1 is responsible for producing the H antigen on red blood cells. Fut2 is expressed in epithelia of secretory tissues, and individuals termed "secretors" have at least one functional copy of the gene; they secrete H antigen which is further processed into A and/or B antigens depending on the ABO genotype. O-fucosyltransferase-like proteins are GDP-fucose dependent enzymes with similarities to the family 1 glycosyltransferases (GT1). They are soluble ER proteins that may be proteolytically cleaved from a membrane-associated preprotein, and are involved in the O-fucosylation of protein substrates, the core fucosylation of growth factor receptors, and other processes. Pssm-ID: 211387 Cd Length: 265 Bit Score: 38.60 E-value: 7.63e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_Sorbs2_3 | cd11917 | Third (or C-terminal) Src Homology 3 domain of Sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2 (Sorbs2), ... |
509-559 | 8.15e-03 | |||||||
Third (or C-terminal) Src Homology 3 domain of Sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2 (Sorbs2), also called Arg-binding protein 2 (ArgBP2); Sorbs2 or ArgBP2 is an adaptor protein containing one sorbin homology (SoHo) and three SH3 domains. It regulates actin-dependent processes including cell adhesion, morphology, and migration. It is expressed in many tissues and is abundant in the heart. Like vinexin, it is found in focal adhesion where it interacts with vinculin and afadin. It also localizes in epithelial cell stress fibers and in cardiac muscle cell Z-discs. Sorbs2 has been implicated to play roles in the signaling of c-Arg, Akt, and Pyk2. Other interaction partners of Sorbs2 include c-Abl, flotillin, spectrin, dynamin 1/2, synaptojanin, PTP-PEST, among others. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212850 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 61 Bit Score: 34.97 E-value: 8.15e-03
|
|||||||||||
| SH3_CD2AP-like_2 | cd11874 | Second Src Homology 3 domain (SH3B) of CD2-associated protein and similar proteins; This ... |
509-560 | 9.91e-03 | |||||||
Second Src Homology 3 domain (SH3B) of CD2-associated protein and similar proteins; This subfamily is composed of the second SH3 domain (SH3B) of CD2AP, CIN85 (Cbl-interacting protein of 85 kDa), and similar domains. CD2AP and CIN85 are adaptor proteins that bind to protein partners and assemble complexes that have been implicated in T cell activation, kidney function, and apoptosis of neuronal cells. They also associate with endocytic proteins, actin cytoskeleton components, and other adaptor proteins involved in receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling. CD2AP and the main isoform of CIN85 contain three SH3 domains, a proline-rich region, and a C-terminal coiled-coil domain. All of these domains enable CD2AP and CIN85 to bind various protein partners and assemble complexes that have been implicated in many different functions. SH3B of both proteins have been shown to bind to Cbl. In the case of CD2AP, its SH3B binds to Cbl at a site distinct from the c-Cbl/SH3A binding site. The CIN85 SH3B also binds ubiquitin. SH3 domains are protein interaction domains that bind to proline-rich ligands with moderate affinity and selectivity, preferentially to PxxP motifs. They play versatile and diverse roles in the cell including the regulation of enzymes, changing the subcellular localization of signaling pathway components, and mediating the formation of multiprotein complex assemblies. Pssm-ID: 212807 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 53 Bit Score: 34.62 E-value: 9.91e-03
|
|||||||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|