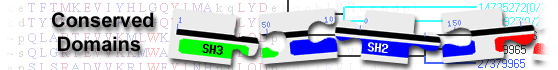copine-1 isoform a [Homo sapiens]
copine family protein( domain architecture ID 10134306)
copine family protein similar to copines, a class of C2 domain-containing, calcium-dependent, phospholipid-binding proteins
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||
| vWA_copine_like | cd01459 | VWA Copine: Copines are phospholipid-binding proteins originally identified in paramecium. ... |
251-509 | 4.71e-122 | |||||
VWA Copine: Copines are phospholipid-binding proteins originally identified in paramecium. They are found in human and orthologues have been found in C. elegans and Arabidopsis Thaliana. None have been found in D. Melanogaster or S. Cereviciae. Phylogenetic distribution suggests that copines have been lost in some eukaryotes. No functional properties have been assigned to the VWA domains present in copines. The members of this subgroup contain a functional MIDAS motif based on their preferential binding to magnesium and manganese. However, the MIDAS motif is not totally conserved, in most cases the MIDAS consists of the sequence DxTxS instead of the motif DxSxS that is found in most cases. The C2 domains present in copines mediate phospholipid binding. : Pssm-ID: 238736 Cd Length: 254 Bit Score: 358.61 E-value: 4.71e-122
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Copine | cd04048 | C2 domain first repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a ... |
6-124 | 5.44e-57 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a protein involved in membrane trafficking, protein-protein interactions, and perhaps even cell division and growth. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-I topology. : Pssm-ID: 176013 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 120 Bit Score: 186.24 E-value: 5.44e-57
|
|||||||||
| C2B_Copine | cd04047 | C2 domain second repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a ... |
138-245 | 4.73e-54 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a protein involved in membrane trafficking, protein-protein interactions, and perhaps even cell division and growth. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. : Pssm-ID: 176012 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 110 Bit Score: 178.14 E-value: 4.73e-54
|
|||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||
| vWA_copine_like | cd01459 | VWA Copine: Copines are phospholipid-binding proteins originally identified in paramecium. ... |
251-509 | 4.71e-122 | |||||
VWA Copine: Copines are phospholipid-binding proteins originally identified in paramecium. They are found in human and orthologues have been found in C. elegans and Arabidopsis Thaliana. None have been found in D. Melanogaster or S. Cereviciae. Phylogenetic distribution suggests that copines have been lost in some eukaryotes. No functional properties have been assigned to the VWA domains present in copines. The members of this subgroup contain a functional MIDAS motif based on their preferential binding to magnesium and manganese. However, the MIDAS motif is not totally conserved, in most cases the MIDAS consists of the sequence DxTxS instead of the motif DxSxS that is found in most cases. The C2 domains present in copines mediate phospholipid binding. Pssm-ID: 238736 Cd Length: 254 Bit Score: 358.61 E-value: 4.71e-122
|
|||||||||
| Copine | pfam07002 | Copine; This family represents a conserved region approximately 220 residues long within ... |
304-517 | 1.76e-108 | |||||
Copine; This family represents a conserved region approximately 220 residues long within eukaryotic copines. Copines are Ca(2+)-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins that are thought to be involved in membrane-trafficking, and may also be involved in cell division and growth. Pssm-ID: 462064 Cd Length: 214 Bit Score: 322.36 E-value: 1.76e-108
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Copine | cd04048 | C2 domain first repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a ... |
6-124 | 5.44e-57 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a protein involved in membrane trafficking, protein-protein interactions, and perhaps even cell division and growth. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176013 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 120 Bit Score: 186.24 E-value: 5.44e-57
|
|||||||||
| C2B_Copine | cd04047 | C2 domain second repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a ... |
138-245 | 4.73e-54 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a protein involved in membrane trafficking, protein-protein interactions, and perhaps even cell division and growth. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176012 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 110 Bit Score: 178.14 E-value: 4.73e-54
|
|||||||||
| C2 | pfam00168 | C2 domain; |
144-234 | 1.26e-18 | |||||
C2 domain; Pssm-ID: 425499 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 104 Bit Score: 81.21 E-value: 1.26e-18
|
|||||||||
| C2 | smart00239 | Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, ... |
144-235 | 1.86e-17 | |||||
Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, protein kinases C, and synaptotagmins (among others). Some do not appear to contain Ca2+-binding sites. Particular C2s appear to bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Unusual occurrence in perforin. Synaptotagmin and PLC C2s are permuted in sequence with respect to N- and C-terminal beta strands. SMART detects C2 domains using one or both of two profiles. Pssm-ID: 214577 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 101 Bit Score: 77.91 E-value: 1.86e-17
|
|||||||||
| C2 | pfam00168 | C2 domain; |
12-116 | 2.23e-14 | |||||
C2 domain; Pssm-ID: 425499 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 104 Bit Score: 69.27 E-value: 2.23e-14
|
|||||||||
| C2 | smart00239 | Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, ... |
12-108 | 2.16e-12 | |||||
Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, protein kinases C, and synaptotagmins (among others). Some do not appear to contain Ca2+-binding sites. Particular C2s appear to bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Unusual occurrence in perforin. Synaptotagmin and PLC C2s are permuted in sequence with respect to N- and C-terminal beta strands. SMART detects C2 domains using one or both of two profiles. Pssm-ID: 214577 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 101 Bit Score: 63.28 E-value: 2.16e-12
|
|||||||||
| VWA | smart00327 | von Willebrand factor (vWF) type A domain; VWA domains in extracellular eukaryotic proteins ... |
285-484 | 2.58e-09 | |||||
von Willebrand factor (vWF) type A domain; VWA domains in extracellular eukaryotic proteins mediate adhesion via metal ion-dependent adhesion sites (MIDAS). Intracellular VWA domains and homologues in prokaryotes have recently been identified. The proposed VWA domains in integrin beta subunits have recently been substantiated using sequence-based methods. Pssm-ID: 214621 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 175 Bit Score: 56.69 E-value: 2.58e-09
|
|||||||||
| COG5038 | COG5038 | Ca2+-dependent lipid-binding protein, contains C2 domain [General function prediction only]; |
63-235 | 7.85e-08 | |||||
Ca2+-dependent lipid-binding protein, contains C2 domain [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 227371 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 1227 Bit Score: 55.54 E-value: 7.85e-08
|
|||||||||
| TerY | COG4245 | Uncharacterized conserved protein YegL, contains vWA domain of TerY type [Function unknown]; |
369-475 | 9.45e-03 | |||||
Uncharacterized conserved protein YegL, contains vWA domain of TerY type [Function unknown]; Pssm-ID: 443387 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 196 Bit Score: 37.60 E-value: 9.45e-03
|
|||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||
| vWA_copine_like | cd01459 | VWA Copine: Copines are phospholipid-binding proteins originally identified in paramecium. ... |
251-509 | 4.71e-122 | |||||
VWA Copine: Copines are phospholipid-binding proteins originally identified in paramecium. They are found in human and orthologues have been found in C. elegans and Arabidopsis Thaliana. None have been found in D. Melanogaster or S. Cereviciae. Phylogenetic distribution suggests that copines have been lost in some eukaryotes. No functional properties have been assigned to the VWA domains present in copines. The members of this subgroup contain a functional MIDAS motif based on their preferential binding to magnesium and manganese. However, the MIDAS motif is not totally conserved, in most cases the MIDAS consists of the sequence DxTxS instead of the motif DxSxS that is found in most cases. The C2 domains present in copines mediate phospholipid binding. Pssm-ID: 238736 Cd Length: 254 Bit Score: 358.61 E-value: 4.71e-122
|
|||||||||
| Copine | pfam07002 | Copine; This family represents a conserved region approximately 220 residues long within ... |
304-517 | 1.76e-108 | |||||
Copine; This family represents a conserved region approximately 220 residues long within eukaryotic copines. Copines are Ca(2+)-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins that are thought to be involved in membrane-trafficking, and may also be involved in cell division and growth. Pssm-ID: 462064 Cd Length: 214 Bit Score: 322.36 E-value: 1.76e-108
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Copine | cd04048 | C2 domain first repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a ... |
6-124 | 5.44e-57 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a protein involved in membrane trafficking, protein-protein interactions, and perhaps even cell division and growth. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176013 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 120 Bit Score: 186.24 E-value: 5.44e-57
|
|||||||||
| C2B_Copine | cd04047 | C2 domain second repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a ... |
138-245 | 4.73e-54 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a protein involved in membrane trafficking, protein-protein interactions, and perhaps even cell division and growth. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176012 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 110 Bit Score: 178.14 E-value: 4.73e-54
|
|||||||||
| C2 | pfam00168 | C2 domain; |
144-234 | 1.26e-18 | |||||
C2 domain; Pssm-ID: 425499 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 104 Bit Score: 81.21 E-value: 1.26e-18
|
|||||||||
| C2 | smart00239 | Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, ... |
144-235 | 1.86e-17 | |||||
Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, protein kinases C, and synaptotagmins (among others). Some do not appear to contain Ca2+-binding sites. Particular C2s appear to bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Unusual occurrence in perforin. Synaptotagmin and PLC C2s are permuted in sequence with respect to N- and C-terminal beta strands. SMART detects C2 domains using one or both of two profiles. Pssm-ID: 214577 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 101 Bit Score: 77.91 E-value: 1.86e-17
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Copine | cd04048 | C2 domain first repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a ... |
140-238 | 1.79e-15 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a protein involved in membrane trafficking, protein-protein interactions, and perhaps even cell division and growth. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176013 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 120 Bit Score: 72.60 E-value: 1.79e-15
|
|||||||||
| C2 | cd00030 | C2 domain; The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed ... |
144-246 | 3.84e-15 | |||||
C2 domain; The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 175973 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 102 Bit Score: 71.33 E-value: 3.84e-15
|
|||||||||
| C2 | pfam00168 | C2 domain; |
12-116 | 2.23e-14 | |||||
C2 domain; Pssm-ID: 425499 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 104 Bit Score: 69.27 E-value: 2.23e-14
|
|||||||||
| C2 | smart00239 | Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, ... |
12-108 | 2.16e-12 | |||||
Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, protein kinases C, and synaptotagmins (among others). Some do not appear to contain Ca2+-binding sites. Particular C2s appear to bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Unusual occurrence in perforin. Synaptotagmin and PLC C2s are permuted in sequence with respect to N- and C-terminal beta strands. SMART detects C2 domains using one or both of two profiles. Pssm-ID: 214577 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 101 Bit Score: 63.28 E-value: 2.16e-12
|
|||||||||
| C2D_Tricalbin-like | cd04040 | C2 domain fourth repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are ... |
144-243 | 7.26e-12 | |||||
C2 domain fourth repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are present in Tricalbin, a yeast homolog of Synaptotagmin, which is involved in membrane trafficking and sorting. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the fifth C2 repeat, C2E, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176005 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 115 Bit Score: 62.20 E-value: 7.26e-12
|
|||||||||
| C2A_MCTP_PRT | cd04042 | C2 domain first repeat found in Multiple C2 domain and Transmembrane region Proteins (MCTP); ... |
145-234 | 1.11e-11 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat found in Multiple C2 domain and Transmembrane region Proteins (MCTP); MCTPs are involved in Ca2+ signaling at the membrane. MCTP is composed of a variable N-terminal sequence, three C2 domains, two transmembrane regions (TMRs), and a short C-terminal sequence. It is one of four protein classes that are anchored to membranes via a transmembrane region; the others being synaptotagmins, extended synaptotagmins, and ferlins. MCTPs are the only membrane-bound C2 domain proteins that contain two functional TMRs. MCTPs are unique in that they bind Ca2+ but not phospholipids. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176007 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 121 Bit Score: 61.91 E-value: 1.11e-11
|
|||||||||
| C2 | cd00030 | C2 domain; The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed ... |
12-114 | 5.46e-10 | |||||
C2 domain; The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 175973 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 102 Bit Score: 56.69 E-value: 5.46e-10
|
|||||||||
| VWA | smart00327 | von Willebrand factor (vWF) type A domain; VWA domains in extracellular eukaryotic proteins ... |
285-484 | 2.58e-09 | |||||
von Willebrand factor (vWF) type A domain; VWA domains in extracellular eukaryotic proteins mediate adhesion via metal ion-dependent adhesion sites (MIDAS). Intracellular VWA domains and homologues in prokaryotes have recently been identified. The proposed VWA domains in integrin beta subunits have recently been substantiated using sequence-based methods. Pssm-ID: 214621 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 175 Bit Score: 56.69 E-value: 2.58e-09
|
|||||||||
| C2A_C2C_Synaptotagmin_like | cd08391 | C2 domain first and third repeat in Synaptotagmin-like proteins; Synaptotagmin is a ... |
144-232 | 1.73e-08 | |||||
C2 domain first and third repeat in Synaptotagmin-like proteins; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains either the first or third repeat in Synaptotagmin-like proteins with a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176037 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 121 Bit Score: 52.68 E-value: 1.73e-08
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Ferlin | cd08373 | C2 domain first repeat in Ferlin; Ferlins are involved in vesicle fusion events. Ferlins and ... |
143-234 | 6.29e-08 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat in Ferlin; Ferlins are involved in vesicle fusion events. Ferlins and other proteins, such as Synaptotagmins, are implicated in facilitating the fusion process when cell membranes fuse together. There are six known human Ferlins: Dysferlin (Fer1L1), Otoferlin (Fer1L2), Myoferlin (Fer1L3), Fer1L4, Fer1L5, and Fer1L6. Defects in these genes can lead to a wide range of diseases including muscular dystrophy (dysferlin), deafness (otoferlin), and infertility (fer-1, fertilization factor-1). Structurally they have 6 tandem C2 domains, designated as (C2A-C2F) and a single C-terminal transmembrane domain, though there is a new study that disputes this and claims that there are actually 7 tandem C2 domains with another C2 domain inserted between C2D and C2E. In a subset of them (Dysferlin, Myoferlin, and Fer1) there is an additional conserved domain called DysF. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176019 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 127 Bit Score: 51.49 E-value: 6.29e-08
|
|||||||||
| COG5038 | COG5038 | Ca2+-dependent lipid-binding protein, contains C2 domain [General function prediction only]; |
63-235 | 7.85e-08 | |||||
Ca2+-dependent lipid-binding protein, contains C2 domain [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 227371 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 1227 Bit Score: 55.54 E-value: 7.85e-08
|
|||||||||
| C2B_RasA1_RasA4 | cd04025 | C2 domain second repeat present in RasA1 and RasA4; RasA1 and RasA4 are GAP1s (GTPase ... |
144-265 | 2.47e-07 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat present in RasA1 and RasA4; RasA1 and RasA4 are GAP1s (GTPase activating protein 1s ), Ras-specific GAP members, which suppresses Ras function by enhancing the GTPase activity of Ras proteins resulting in the inactive GDP-bound form of Ras. In this way it can control cellular proliferation and differentiation. Both proteins contain two C2 domains, a Ras-GAP domain, a plextrin homology (PH)-like domain, and a Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) zinc binding domain. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 175991 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 123 Bit Score: 49.41 E-value: 2.47e-07
|
|||||||||
| C2C_Tricalbin-like | cd04045 | C2 domain third repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are ... |
145-234 | 2.65e-07 | |||||
C2 domain third repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are present in Tricalbin, a yeast homolog of Synaptotagmin, which is involved in membrane trafficking and sorting. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the third C2 repeat, C2C, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176010 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 120 Bit Score: 49.51 E-value: 2.65e-07
|
|||||||||
| C2B_MCTP_PRT | cd08376 | C2 domain second repeat found in Multiple C2 domain and Transmembrane region Proteins (MCTP); ... |
139-234 | 6.80e-07 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat found in Multiple C2 domain and Transmembrane region Proteins (MCTP); MCTPs are involved in Ca2+ signaling at the membrane. MCTP is composed of a variable N-terminal sequence, three C2 domains, two transmembrane regions (TMRs), and a short C-terminal sequence. It is one of four protein classes that are anchored to membranes via a transmembrane region; the others being synaptotagmins, extended synaptotagmins, and ferlins. MCTPs are the only membrane-bound C2 domain proteins that contain two functional TMRs. MCTPs are unique in that they bind Ca2+ but not phospholipids. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176022 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 116 Bit Score: 48.02 E-value: 6.80e-07
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Synaptotagmin-like | cd04024 | C2 domain first repeat present in Synaptotagmin-like proteins; Synaptotagmin is a ... |
144-238 | 1.22e-06 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat present in Synaptotagmin-like proteins; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 175990 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 128 Bit Score: 47.80 E-value: 1.22e-06
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Synaptotagmin-7 | cd08386 | C2A domain first repeat present in Synaptotagmin 7; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking ... |
124-234 | 1.29e-06 | |||||
C2A domain first repeat present in Synaptotagmin 7; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Synaptotagmin 7, a member of class 2 synaptotagmins, is located in presynaptic plasma membranes in neurons, dense-core vesicles in endocrine cells, and lysosomes in fibroblasts. It has been shown to play a role in regulation of Ca2+-dependent lysosomal exocytosis in fibroblasts and may also function as a vesicular Ca2+-sensor. It is distinguished from the other synaptotagmins by having over 12 splice forms. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176032 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 125 Bit Score: 47.71 E-value: 1.29e-06
|
|||||||||
| C2D_Tricalbin-like | cd04040 | C2 domain fourth repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are ... |
12-127 | 1.67e-06 | |||||
C2 domain fourth repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are present in Tricalbin, a yeast homolog of Synaptotagmin, which is involved in membrane trafficking and sorting. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the fifth C2 repeat, C2E, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176005 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 115 Bit Score: 46.79 E-value: 1.67e-06
|
|||||||||
| C2B_Synaptotagmin-3-5-6-9-10 | cd08403 | C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmins 3, 5, 6, 9, and 10; Synaptotagmin is a ... |
122-225 | 2.21e-06 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmins 3, 5, 6, 9, and 10; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Synaptotagmin 3, a member of class 3 synaptotagmins, is located in the brain and localized to the active zone and plasma membrane. It functions as a Ca2+ sensor for fast exocytosis. It, along with synaptotagmins 5,6, and 10, has disulfide bonds at its N-terminus. Synaptotagmin 9, a class 5 synaptotagmins, is located in the brain and localized to the synaptic vesicles. It is thought to be a Ca2+-sensor for dense-core vesicle exocytosis. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176048 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 134 Bit Score: 47.12 E-value: 2.21e-06
|
|||||||||
| C2B_Synaptotagmin-7 | cd08405 | C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmin 7; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking ... |
137-225 | 2.25e-06 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmin 7; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Synaptotagmin 7, a member of class 2 synaptotagmins, is located in presynaptic plasma membranes in neurons, dense-core vesicles in endocrine cells, and lysosomes in fibroblasts. It has been shown to play a role in regulation of Ca2+-dependent lysosomal exocytosis in fibroblasts and may also function as a vesicular Ca2+-sensor. It is distinguished from the other synaptotagmins by having over 12 splice forms. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176050 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 136 Bit Score: 47.03 E-value: 2.25e-06
|
|||||||||
| C2_PKC_alpha_gamma | cd04026 | C2 domain in Protein Kinase C (PKC) alpha and gamma; A single C2 domain is found in PKC alpha ... |
124-240 | 2.77e-06 | |||||
C2 domain in Protein Kinase C (PKC) alpha and gamma; A single C2 domain is found in PKC alpha and gamma. The PKC family of serine/threonine kinases regulates apoptosis, proliferation, migration, motility, chemo-resistance, and differentiation. There are 3 groups: group 1(alpha, betaI, beta II, gamma) which require phospholipids and calcium, group 2 (delta, epsilon, theta, eta) which do not require calcium for activation, and group 3 (xi, iota/lambda) which are atypical and can be activated in the absence of diacylglycerol and calcium. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Members here have a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 175992 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 131 Bit Score: 46.87 E-value: 2.77e-06
|
|||||||||
| C2B_Synaptotagmin-1 | cd08402 | C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmin 1; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking ... |
144-225 | 2.26e-05 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmin 1; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Synaptotagmin 1, a member of the class 1 synaptotagmins, is located in the brain and endocranium and localized to the synaptic vesicles and secretory granules. It functions as a Ca2+ sensor for fast exocytosis. It, like synaptotagmin-2, has an N-glycosylated N-terminus. Synaptotagmin 4, a member of class 4 synaptotagmins, is located in the brain. It functions are unknown. It, like synaptotagmin-11, has an Asp to Ser substitution in its C2A domain. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176047 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 136 Bit Score: 44.31 E-value: 2.26e-05
|
|||||||||
| vWA-TerF-like | pfam10138 | vWA found in TerF C terminus; vWA domain fused to TerD domain typified by the TerF protein. ... |
387-517 | 9.41e-05 | |||||
vWA found in TerF C terminus; vWA domain fused to TerD domain typified by the TerF protein. Some times found as solos. Pssm-ID: 401947 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 200 Bit Score: 43.43 E-value: 9.41e-05
|
|||||||||
| C2A_fungal | cd04041 | C2 domain first repeat; fungal group; C2 domains were first identified in Protein Kinase C ... |
146-234 | 1.03e-04 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat; fungal group; C2 domains were first identified in Protein Kinase C (PKC). C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 176006 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 111 Bit Score: 41.86 E-value: 1.03e-04
|
|||||||||
| C2_KIAA0528-like | cd08688 | C2 domain found in the Human KIAA0528 cDNA clone; The members of this CD are named after the ... |
144-226 | 2.92e-04 | |||||
C2 domain found in the Human KIAA0528 cDNA clone; The members of this CD are named after the Human KIAA0528 cDNA clone. All members here contain a single C2 repeat. No other information on this protein is currently known. The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 176070 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 110 Bit Score: 40.37 E-value: 2.92e-04
|
|||||||||
| C2_Calpain | cd04046 | C2 domain present in Calpain proteins; A single C2 domain is found in calpains (EC 3.4.22.52, ... |
4-130 | 3.70e-04 | |||||
C2 domain present in Calpain proteins; A single C2 domain is found in calpains (EC 3.4.22.52, EC 3.4.22.53), calcium-dependent, non-lysosomal cysteine proteases. Caplains are classified as belonging to Clan CA by MEROPS and include six families: C1, C2, C10, C12, C28, and C47. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 176011 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 126 Bit Score: 40.34 E-value: 3.70e-04
|
|||||||||
| C2B_Synaptotagmin | cd00276 | C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmin; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking ... |
122-225 | 1.03e-03 | |||||
C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmin; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. There are several classes of Synaptotagmins. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 175975 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 134 Bit Score: 39.49 E-value: 1.03e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2_PSD | cd04039 | C2 domain present in Phosphatidylserine decarboxylase (PSD); PSD is involved in the ... |
138-234 | 1.21e-03 | |||||
C2 domain present in Phosphatidylserine decarboxylase (PSD); PSD is involved in the biosynthesis of aminophospholipid by converting phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) to phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn). There is a single C2 domain present and it is thought to confer PtdSer binding motif that is common to PKC and synaptotagmin. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 176004 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 108 Bit Score: 38.77 E-value: 1.21e-03
|
|||||||||
| COG5038 | COG5038 | Ca2+-dependent lipid-binding protein, contains C2 domain [General function prediction only]; |
146-238 | 1.58e-03 | |||||
Ca2+-dependent lipid-binding protein, contains C2 domain [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 227371 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 1227 Bit Score: 41.28 E-value: 1.58e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Synaptotagmin-8 | cd08387 | C2A domain first repeat present in Synaptotagmin 8; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking ... |
144-234 | 2.33e-03 | |||||
C2A domain first repeat present in Synaptotagmin 8; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176033 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 124 Bit Score: 38.15 E-value: 2.33e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2A_C2C_Synaptotagmin_like | cd08391 | C2 domain first and third repeat in Synaptotagmin-like proteins; Synaptotagmin is a ... |
12-117 | 2.43e-03 | |||||
C2 domain first and third repeat in Synaptotagmin-like proteins; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains either the first or third repeat in Synaptotagmin-like proteins with a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176037 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 121 Bit Score: 38.04 E-value: 2.43e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2C_KIAA1228 | cd04030 | C2 domain third repeat present in uncharacterized human KIAA1228-like proteins; KIAA proteins ... |
121-196 | 2.47e-03 | |||||
C2 domain third repeat present in uncharacterized human KIAA1228-like proteins; KIAA proteins are uncharacterized human proteins. They were compiled by the Kazusa mammalian cDNA project which identified more than 2000 human genes. They are identified by 4 digit codes that precede the KIAA designation. Many KIAA genes are still functionally uncharacterized including KIAA1228. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the third C2 repeat, C2C, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 175996 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 127 Bit Score: 38.02 E-value: 2.47e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2_NEDD4_NEDD4L | cd04033 | C2 domain present in the Human neural precursor cell-expressed, developmentally down-regulated ... |
144-189 | 2.98e-03 | |||||
C2 domain present in the Human neural precursor cell-expressed, developmentally down-regulated 4 (NEDD4) and NEDD4-like (NEDD4L/NEDD42); Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 are two of the nine members of the Human Nedd4 family. All vertebrates appear to have both Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 genes. They are thought to participate in the regulation of epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) activity. They also have identical specificity for ubiquitin conjugating enzymes (E2). Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 are composed of a C2 domain, 2-4 WW domains, and a ubiquitin ligase Hect domain. Their WW domains can bind PPxY (PY) or LPSY motifs, and in vitro studies suggest that WW3 and WW4 of both proteins bind PY motifs in the key substrates, with WW3 generally exhibiting higher affinity. Most Nedd4 family members, especially Nedd4-2, also have multiple splice variants, which might play different roles in regulating their substrates. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 175999 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 133 Bit Score: 38.10 E-value: 2.98e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Synaptotagmin-1-5-6-9-10 | cd08385 | C2A domain first repeat present in Synaptotagmins 1, 5, 6, 9, and 10; Synaptotagmin is a ... |
144-225 | 3.05e-03 | |||||
C2A domain first repeat present in Synaptotagmins 1, 5, 6, 9, and 10; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. Synaptotagmin 1, a member of class 1 synaptotagmins, is located in the brain and endocranium and localized to the synaptic vesicles and secretory granules. It functions as a Ca2+ sensor for fast exocytosis as do synaptotagmins 5, 6, and 10. It is distinguished from the other synaptotagmins by having an N-glycosylated N-terminus. Synaptotagmins 5, 6, and 10, members of class 3 synaptotagmins, are located primarily in the brain and localized to the active zone and plasma membrane. They is distinguished from the other synaptotagmins by having disulfide bonds at its N-terminus. Synaptotagmin 6 also regulates the acrosome reaction, a unique Ca2+-regulated exocytosis, in sperm. Synaptotagmin 9, a class 5 synaptotagmins, is located in the brain and localized to the synaptic vesicles. It is thought to be a Ca2+-sensor for dense-core vesicle exocytosis. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176031 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 124 Bit Score: 38.01 E-value: 3.05e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2A_Tricalbin-like | cd04044 | C2 domain first repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are ... |
146-239 | 3.29e-03 | |||||
C2 domain first repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are present in Tricalbin, a yeast homolog of Synaptotagmin, which is involved in membrane trafficking and sorting. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the first C2 repeat, C2A, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176009 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 124 Bit Score: 37.53 E-value: 3.29e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2_ArfGAP | cd04038 | C2 domain present in Arf GTPase Activating Proteins (GAP); ArfGAP is a GTPase activating ... |
148-225 | 4.26e-03 | |||||
C2 domain present in Arf GTPase Activating Proteins (GAP); ArfGAP is a GTPase activating protein which regulates the ADP ribosylation factor Arf, a member of the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins. The GTP-bound form of Arf is involved in Golgi morphology and is involved in recruiting coat proteins. ArfGAP is responsible for the GDP-bound form of Arf which is necessary for uncoating the membrane and allowing the Golgi to fuse with an acceptor compartment. These proteins contain an N-terminal ArfGAP domain containing the characteristic zinc finger motif (Cys-x2-Cys-x(16,17)-x2-Cys) and C-terminal C2 domain. C2 domains were first identified in Protein Kinase C (PKC). C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 176003 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 145 Bit Score: 37.69 E-value: 4.26e-03
|
|||||||||
| VWA | pfam00092 | von Willebrand factor type A domain; |
383-469 | 4.42e-03 | |||||
von Willebrand factor type A domain; Pssm-ID: 459670 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 174 Bit Score: 38.41 E-value: 4.42e-03
|
|||||||||
| C2E_Ferlin | cd04037 | C2 domain fifth repeat in Ferlin; Ferlins are involved in vesicle fusion events. Ferlins and ... |
144-226 | 5.24e-03 | |||||
C2 domain fifth repeat in Ferlin; Ferlins are involved in vesicle fusion events. Ferlins and other proteins, such as Synaptotagmins, are implicated in facilitating the fusion process when cell membranes fuse together. There are six known human Ferlins: Dysferlin (Fer1L1), Otoferlin (Fer1L2), Myoferlin (Fer1L3), Fer1L4, Fer1L5, and Fer1L6. Defects in these genes can lead to a wide range of diseases including muscular dystrophy (dysferlin), deafness (otoferlin), and infertility (fer-1, fertilization factor-1). Structurally they have 6 tandem C2 domains, designated as (C2A-C2F) and a single C-terminal transmembrane domain, though there is a new study that disputes this and claims that there are actually 7 tandem C2 domains with another C2 domain inserted between C2D and C2E. In a subset of them (Dysferlin, Myoferlin, and Fer1) there is an additional conserved domain called DysF. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the fifth C2 repeat, C2E, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176002 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 124 Bit Score: 37.14 E-value: 5.24e-03
|
|||||||||
| vWFA | cd00198 | Von Willebrand factor type A (vWA) domain was originally found in the blood coagulation ... |
382-469 | 8.16e-03 | |||||
Von Willebrand factor type A (vWA) domain was originally found in the blood coagulation protein von Willebrand factor (vWF). Typically, the vWA domain is made up of approximately 200 amino acid residues folded into a classic a/b para-rossmann type of fold. The vWA domain, since its discovery, has drawn great interest because of its widespread occurrence and its involvement in a wide variety of important cellular functions. These include basal membrane formation, cell migration, cell differentiation, adhesion, haemostasis, signaling, chromosomal stability, malignant transformation and in immune defenses In integrins these domains form heterodimers while in vWF it forms multimers. There are different interaction surfaces of this domain as seen by the various molecules it complexes with. Ligand binding in most cases is mediated by the presence of a metal ion dependent adhesion site termed as the MIDAS motif that is a characteristic feature of most, if not all A domains. Pssm-ID: 238119 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 161 Bit Score: 37.16 E-value: 8.16e-03
|
|||||||||
| TerY | COG4245 | Uncharacterized conserved protein YegL, contains vWA domain of TerY type [Function unknown]; |
369-475 | 9.45e-03 | |||||
Uncharacterized conserved protein YegL, contains vWA domain of TerY type [Function unknown]; Pssm-ID: 443387 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 196 Bit Score: 37.60 E-value: 9.45e-03
|
|||||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|