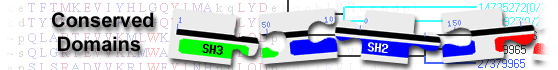protein DPCD isoform 6 [Homo sapiens]
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| DPCD super family | cl20800 | DPCD protein family; This protein is a found in eukaryotes and a mutation in this protein is ... |
6-50 | 3.67e-25 | ||
DPCD protein family; This protein is a found in eukaryotes and a mutation in this protein is thought to cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (PCD). This protein is 203 amino acids in length, 23 kDa in size and its function remains unknown. The gene that encodes this protein is a candidate gene for PCD and is expressed during ciliogenesis. PCD affects the airways and reproductive organs, and probing Northern blots show DPCD expression in humans is highest in the testes. Additionally, there is no indication of major splice variants. The actual alignment was detected with superfamily member pfam14913: Pssm-ID: 464369 Cd Length: 190 Bit Score: 91.16 E-value: 3.67e-25
|
||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| DPCD | pfam14913 | DPCD protein family; This protein is a found in eukaryotes and a mutation in this protein is ... |
6-50 | 3.67e-25 | ||
DPCD protein family; This protein is a found in eukaryotes and a mutation in this protein is thought to cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (PCD). This protein is 203 amino acids in length, 23 kDa in size and its function remains unknown. The gene that encodes this protein is a candidate gene for PCD and is expressed during ciliogenesis. PCD affects the airways and reproductive organs, and probing Northern blots show DPCD expression in humans is highest in the testes. Additionally, there is no indication of major splice variants. Pssm-ID: 464369 Cd Length: 190 Bit Score: 91.16 E-value: 3.67e-25
|
||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | ||
| DPCD | pfam14913 | DPCD protein family; This protein is a found in eukaryotes and a mutation in this protein is ... |
6-50 | 3.67e-25 | ||
DPCD protein family; This protein is a found in eukaryotes and a mutation in this protein is thought to cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (PCD). This protein is 203 amino acids in length, 23 kDa in size and its function remains unknown. The gene that encodes this protein is a candidate gene for PCD and is expressed during ciliogenesis. PCD affects the airways and reproductive organs, and probing Northern blots show DPCD expression in humans is highest in the testes. Additionally, there is no indication of major splice variants. Pssm-ID: 464369 Cd Length: 190 Bit Score: 91.16 E-value: 3.67e-25
|
||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|