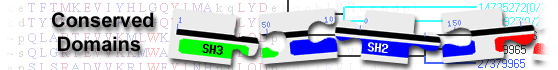tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 isoform a [Homo sapiens]
tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1( domain architecture ID 12068707)
tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1) removes a variety of covalent adducts from DNA through hydrolysis of a 3'-phosphodiester bond, giving rise to DNA with a free 3' phosphate; similar to Homo sapiens TDP1
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| Tyr-DNA_phospho | pfam06087 | Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Covalent intermediates between topoisomerase I and DNA can ... |
166-582 | 0e+00 | |||||||
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Covalent intermediates between topoisomerase I and DNA can become dead-end complexes that lead to cell death. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase can hydrolyse the bond between topoisomerase I and DNA. : Pssm-ID: 461824 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 442 Bit Score: 549.18 E-value: 0e+00
|
|||||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| Tyr-DNA_phospho | pfam06087 | Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Covalent intermediates between topoisomerase I and DNA can ... |
166-582 | 0e+00 | |||||||
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Covalent intermediates between topoisomerase I and DNA can become dead-end complexes that lead to cell death. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase can hydrolyse the bond between topoisomerase I and DNA. Pssm-ID: 461824 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 442 Bit Score: 549.18 E-value: 0e+00
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_mTdp1_2 | cd09195 | Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, ... |
352-545 | 5.53e-124 | |||||||
Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1, EC 3.1.4.-). Human Tdp1 (hTdp1) acts as an important DNA repair enzyme with a preference for single-stranded or blunt-ended duplex oligonucleotides. It can remove stalled topoisomerase I-DNA complexes by catalyzing the hydrolysis of a phosphodiester bond between a tyrosine side chain and a DNA 3'-phosphate. It is therefore a potential molecular target for new anti-cancer drugs. hTdp1 has been shown to associate with additional proteins, such as XRCC1, to form a multi-enzyme complex. These additional proteins may be involved in recognizing 3'-phoshotyrosyl DNA in vivo. hTdp1 is a monomeric protein containing two copies of a variant HKD motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), which consists of the highly conserved histidine and lysine residues, but lacks the aspartate residue that is well conserved in other phospholipase D (PLD, EC 3.1.4.4) enzymes. Like other PLD enzymes, hTdp1 may utilize a common two-step general acid/base catalytic mechanism, involving a DNA-enzyme intermediate to cleave phosphodiester bonds. A single active site involved in phosphatidyl group transfer would be formed by the two variant HKD motifs from the N- and C-terminal domains in a pseudodimeric way. Pssm-ID: 197291 Cd Length: 191 Bit Score: 363.54 E-value: 5.53e-124
|
|||||||||||
| PRK08084 | PRK08084 | DnaA inactivator Hda; |
429-491 | 4.95e-03 | |||||||
DnaA inactivator Hda; Pssm-ID: 181224 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 235 Bit Score: 38.89 E-value: 4.95e-03
|
|||||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| Tyr-DNA_phospho | pfam06087 | Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Covalent intermediates between topoisomerase I and DNA can ... |
166-582 | 0e+00 | |||||||
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Covalent intermediates between topoisomerase I and DNA can become dead-end complexes that lead to cell death. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase can hydrolyse the bond between topoisomerase I and DNA. Pssm-ID: 461824 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 442 Bit Score: 549.18 E-value: 0e+00
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_mTdp1_2 | cd09195 | Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, ... |
352-545 | 5.53e-124 | |||||||
Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1, EC 3.1.4.-). Human Tdp1 (hTdp1) acts as an important DNA repair enzyme with a preference for single-stranded or blunt-ended duplex oligonucleotides. It can remove stalled topoisomerase I-DNA complexes by catalyzing the hydrolysis of a phosphodiester bond between a tyrosine side chain and a DNA 3'-phosphate. It is therefore a potential molecular target for new anti-cancer drugs. hTdp1 has been shown to associate with additional proteins, such as XRCC1, to form a multi-enzyme complex. These additional proteins may be involved in recognizing 3'-phoshotyrosyl DNA in vivo. hTdp1 is a monomeric protein containing two copies of a variant HKD motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), which consists of the highly conserved histidine and lysine residues, but lacks the aspartate residue that is well conserved in other phospholipase D (PLD, EC 3.1.4.4) enzymes. Like other PLD enzymes, hTdp1 may utilize a common two-step general acid/base catalytic mechanism, involving a DNA-enzyme intermediate to cleave phosphodiester bonds. A single active site involved in phosphatidyl group transfer would be formed by the two variant HKD motifs from the N- and C-terminal domains in a pseudodimeric way. Pssm-ID: 197291 Cd Length: 191 Bit Score: 363.54 E-value: 5.53e-124
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_mTdp1_1 | cd09193 | Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, ... |
162-330 | 1.63e-94 | |||||||
Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of metazoan tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1, EC 3.1.4.-). Human Tdp1 (hTdp1) acts as an important DNA repair enzyme with a preference for single-stranded or blunt-ended duplex oligonucleotides. It can remove stalled topoisomerase I-DNA complexes by catalyzing the hydrolysis of a phosphodiester bond between a tyrosine side chain and a DNA 3'-phosphate. It is therefore a potential molecular target for new anti-cancer drugs. hTdp1 has been shown to associate with additional proteins, such as XRCC1, to form a multi-enzyme complex. These additional proteins may be involved in recognizing 3'-phoshotyrosyl DNA in vivo. hTdp1 is a monomeric protein containing two copies of a variant HKD motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), which consists of the highly conserved histidine and lysine residues, but lacks the aspartate residue that is well conserved in other phospholipase D (PLD, EC 3.1.4.4) enzymes. Like other PLD enzymes, hTdp1 may utilize a common two-step general acid/base catalytic mechanism, involving a DNA-enzyme intermediate to cleave phosphodiester bonds. A single active site involved in phosphatidyl group transfer would be formed by the two variant HKD motifs from the N- and C-terminal domains in a pseudodimeric way. Pssm-ID: 197289 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 169 Bit Score: 287.28 E-value: 1.63e-94
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_Tdp1_2 | cd09123 | Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of ... |
372-544 | 1.69e-65 | |||||||
Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1, EC 3.1.4.-), which exists in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes. Tdp1 acts as an important DNA repair enzyme that removes stalled topoisomerase I-DNA complexes by catalyzing the hydrolysis of a phosphodiester bond between a tyrosine side chain and a DNA 3'-phosphate. It is a monomeric protein that contains two copies of a variant HKD motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), which consists of the highly conserved histidine and lysine residues, but lacks the aspartate residue that is well conserved in other phospholipase D (PLD, EC 3.1.4.4) enzymes. Thus, this family represents a distinct class within the PLD superfamily. Like other PLD enzymes, Tdp1 may utilize a common two-step general acid/base catalytic mechanism, involving a DNA-enzyme intermediate to cleave phosphodiester bonds. A single active site involved in phosphatidyl group transfer would be formed by the two variant HKD motifs from the N- and C-terminal domains in a pseudodimeric way. Pssm-ID: 197222 Cd Length: 182 Bit Score: 212.21 E-value: 1.69e-65
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_Tdp1_1 | cd09122 | Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of ... |
183-327 | 1.27e-47 | |||||||
Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1, EC 3.1.4.-), which exists in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes. Tdp1 acts as an important DNA repair enzyme that removes stalled topoisomerase I-DNA complexes by catalyzing the hydrolysis of a phosphodiester bond between a tyrosine side chain and a DNA 3'-phosphate. It is a monomeric protein that contains two copies of a variant HKD motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), which consists of the highly conserved histidine and lysine residues, but lacks the aspartate residue that is well conserved in other phospholipase D (PLD, EC 3.1.4.4) enzymes. Thus, this family represents a distinct class within the PLD superfamily. Like other PLD enzymes, Tdp1 may utilize a common two-step general acid/base catalytic mechanism, involving a DNA-enzyme intermediate to cleave phosphodiester bonds. A single active site involved in phosphatidyl group transfer would be formed by the two variant HKD motifs from the N- and C-terminal domains in a pseudodimeric way. Pssm-ID: 197221 Cd Length: 145 Bit Score: 163.58 E-value: 1.27e-47
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_yTdp1_1 | cd09194 | Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of yeast tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 1, ... |
162-327 | 7.06e-35 | |||||||
Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of yeast tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 1, of yeast tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (yTdp1, EC 3.1.4.-). yTdp1 is involved in the repair of topoisomerase I DNA lesions by hydrolyzing the topoisomerase from the 3'-end of the DNA during double-strand break repair. Unlike human Tdp1 whose substrate-binding pocket can accommodate a fairly large topoisomerase I peptide fragment, yTdp1 has a preference for substrates containing one to four amino acid residues. The monomeric yTdp1 contains two copies of a variant HKD motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), which consists of the highly conserved histidine and lysine residues, but lacks the aspartate residue that is well conserved in other phospholipase D (PLD, EC 3.1.4.4) enzymes. Like other PLD enzymes, yTdp1 may utilize a common two-step general acid/base catalytic mechanism, involving a DNA-enzyme intermediate to cleave phosphodiester bonds. A single active site involved in phosphatidyl group transfer would be formed by the two variant HKD motifs from the N- and C-terminal domains in a pseudodimeric way. Pssm-ID: 197290 Cd Length: 166 Bit Score: 129.33 E-value: 7.06e-35
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_yTdp1_2 | cd09196 | Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of yeast tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 2, ... |
438-545 | 9.49e-22 | |||||||
Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of yeast tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase; Catalytic domain, repeat 2, of yeast tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (yTdp1, EC 3.1.4.-). yTdp1 is involved in the repair of topoisomerase I DNA lesions by hydrolyzing the topoisomerase from the 3'-end of the DNA during double-strand break repair. Unlike human Tdp1 whose substrate-binding pocket can accommodate a fairly large topoisomerase I peptide fragment, yTdp1 has a preference for substrates containing one to four amino acid residues. The monomeric yTdp1 contains two copies of a variant HKD motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), which consists of the highly conserved histidine and lysine residues, but lacks the aspartate residue that is well conserved in other phospholipase D (PLD, EC 3.1.4.4) enzymes. Like other PLD enzymes, yTdp1 may utilize a common two-step general acid/base catalytic mechanism, involving a DNA-enzyme intermediate to cleave phosphodiester bonds. A single active site involved in phosphatidyl group transfer would be formed by the two variant HKD motifs from the N- and C-terminal domains in a pseudodimeric way. Pssm-ID: 197292 Cd Length: 200 Bit Score: 93.59 E-value: 9.49e-22
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_SF | cd00138 | Catalytic domain of phospholipase D superfamily proteins; Catalytic domain of phospholipase D ... |
186-299 | 8.55e-05 | |||||||
Catalytic domain of phospholipase D superfamily proteins; Catalytic domain of phospholipase D (PLD) superfamily proteins. The PLD superfamily is composed of a large and diverse group of proteins including plant, mammalian and bacterial PLDs, bacterial cardiolipin (CL) synthases, bacterial phosphatidylserine synthases (PSS), eukaryotic phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP) synthase, eukaryotic tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (Tdp1), and some bacterial endonucleases (Nuc and BfiI), among others. PLD enzymes hydrolyze phospholipid phosphodiester bonds to yield phosphatidic acid and a free polar head group. They can also catalyze the transphosphatidylation of phospholipids to acceptor alcohols. The majority of members in this superfamily contain a short conserved sequence motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), called the HKD signature motif. There are varying expanded forms of this motif in different family members. Some members contain variant HKD motifs. Most PLD enzymes are monomeric proteins with two HKD motif-containing domains. Two HKD motifs from two domains form a single active site. Some PLD enzymes have only one copy of the HKD motif per subunit but form a functionally active dimer, which has a single active site at the dimer interface containing the two HKD motifs from both subunits. Different PLD enzymes may have evolved through domain fusion of a common catalytic core with separate substrate recognition domains. Despite their various catalytic functions and a very broad range of substrate specificities, the diverse group of PLD enzymes can bind to a phosphodiester moiety. Most of them are active as bi-lobed monomers or dimers, and may possess similar core structures for catalytic activity. They are generally thought to utilize a common two-step ping-pong catalytic mechanism, involving an enzyme-substrate intermediate, to cleave phosphodiester bonds. The two histidine residues from the two HKD motifs play key roles in the catalysis. Upon substrate binding, a histidine from one HKD motif could function as the nucleophile, attacking the phosphodiester bond to create a covalent phosphohistidine intermediate, while the other histidine residue from the second HKD motif could serve as a general acid, stabilizing the leaving group. Pssm-ID: 197200 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 119 Bit Score: 42.50 E-value: 8.55e-05
|
|||||||||||
| PRK08084 | PRK08084 | DnaA inactivator Hda; |
429-491 | 4.95e-03 | |||||||
DnaA inactivator Hda; Pssm-ID: 181224 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 235 Bit Score: 38.89 E-value: 4.95e-03
|
|||||||||||
| PLDc_SF | cd00138 | Catalytic domain of phospholipase D superfamily proteins; Catalytic domain of phospholipase D ... |
409-543 | 6.65e-03 | |||||||
Catalytic domain of phospholipase D superfamily proteins; Catalytic domain of phospholipase D (PLD) superfamily proteins. The PLD superfamily is composed of a large and diverse group of proteins including plant, mammalian and bacterial PLDs, bacterial cardiolipin (CL) synthases, bacterial phosphatidylserine synthases (PSS), eukaryotic phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP) synthase, eukaryotic tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (Tdp1), and some bacterial endonucleases (Nuc and BfiI), among others. PLD enzymes hydrolyze phospholipid phosphodiester bonds to yield phosphatidic acid and a free polar head group. They can also catalyze the transphosphatidylation of phospholipids to acceptor alcohols. The majority of members in this superfamily contain a short conserved sequence motif (H-x-K-x(4)-D, where x represents any amino acid residue), called the HKD signature motif. There are varying expanded forms of this motif in different family members. Some members contain variant HKD motifs. Most PLD enzymes are monomeric proteins with two HKD motif-containing domains. Two HKD motifs from two domains form a single active site. Some PLD enzymes have only one copy of the HKD motif per subunit but form a functionally active dimer, which has a single active site at the dimer interface containing the two HKD motifs from both subunits. Different PLD enzymes may have evolved through domain fusion of a common catalytic core with separate substrate recognition domains. Despite their various catalytic functions and a very broad range of substrate specificities, the diverse group of PLD enzymes can bind to a phosphodiester moiety. Most of them are active as bi-lobed monomers or dimers, and may possess similar core structures for catalytic activity. They are generally thought to utilize a common two-step ping-pong catalytic mechanism, involving an enzyme-substrate intermediate, to cleave phosphodiester bonds. The two histidine residues from the two HKD motifs play key roles in the catalysis. Upon substrate binding, a histidine from one HKD motif could function as the nucleophile, attacking the phosphodiester bond to create a covalent phosphohistidine intermediate, while the other histidine residue from the second HKD motif could serve as a general acid, stabilizing the leaving group. Pssm-ID: 197200 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 119 Bit Score: 37.11 E-value: 6.65e-03
|
|||||||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|