
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
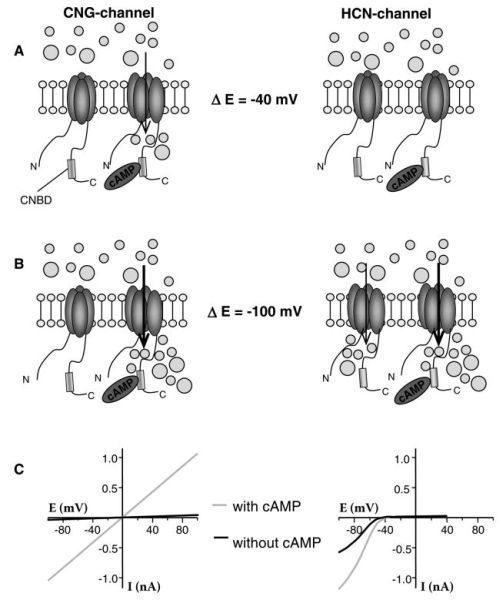
Functional cyclic nucleotide gated channels (CNG) and hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels (HCN) are oligomers composed by four subunits. The cyclic nucleotide binding domain (CNBD) is located close to the C-terminus of each subunit. (A) cAMP binding to the CNBD promotes opening of CNG but not HCN-channels at membrane potential > –40 mV. (B) cAMP binding to CNG-channels plus hyperpolarization of the cell induces a stronger inward cation current. HCN-channels are open during hyperpolarization, mid cAMP binding to the CNBD induces a faster opening of these channels. (C) Current-voltage relationship for CNG and HCN-channels in the presence (gray line) and absence (black line) of cAMP.

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.