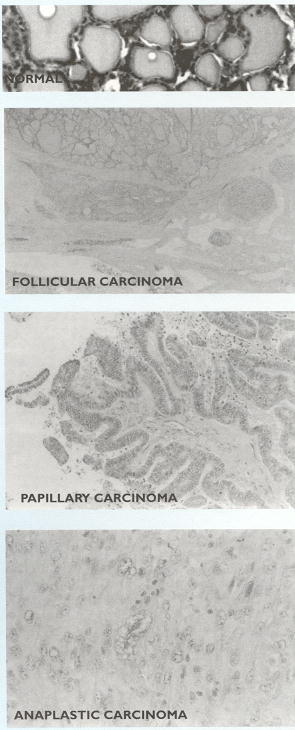
Box 3.31Classification of thyroid epithelial cell tumors
These are classified according to histological features
Primary
Secondary
TNM Grading
T — primary tumor
T0 — no palpable tumor
T1 — single tumor confined to the gland
T2 — multiple tumors confined to the gland
T3 — tumor extending beyond the gland
N — regional lymph nodes
M — distant metastases
M0 — none
M1 — distant metastases
Clinically, the dominant factor in governing prognosis in thyroid epithelial cell cancer is age. Others factors include size of primary tumor, degree of invasiveness, histological grade and the presence of metastases. Of these, all except histological grade are incorporated into the TNM classification.