From: Horizontal Gene Transfer in Prokaryotes: Quantification and Classification

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.

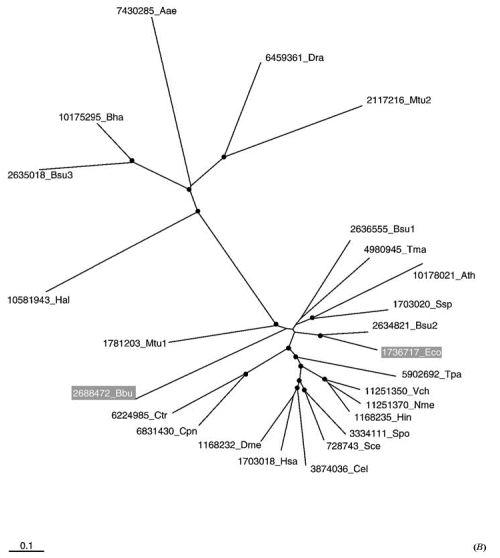
Phylogenetic trees illustrating xenologous gene displacement and acquisition of paralogous gene. (A) 3-Isopropylmalate dehydrogenase. (B) 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. The rootless neighbor-joining trees (94) were generated using the NEIGHBOR program of the PHYLIP package (28) from multiple alignments that were constructed using the CLUSTALW program (109). The black circles show the nodes with at least 60% bootstrap support (1000 replications). Proteins whose position in the tree is indicative of horizontal gene transfer (see text) are boxed in gray. Each protein is designated by its gene identification number in the nonredundant protein sequence database followed by the species name abbreviation: Aae, Aquifex aeolicus; Afu, Archaeoglobus fulgidus; Bbu, Borrelia burgdorferi; Bsu, Bacillus subtilis; Bha, Bacillus halodurans; Cje, Campylobacter jejuni; Cel, Caenorhabditis elegans; Cpn, Chlamydophila pneumoniae; Ctr, Chlamydia trachomatis; Dme, Drosophila melanogaster; Dra, Deinococcus radiodurans; Eco, Escherichia coli; Hal, Halobacterium sp. NRC-1; Hin, Haemophilus influenzae; Has, Homo sapiens; Mja, Methanococcus jannaschii; Mth, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum; Mtu, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Nme, Neisseria meningitidis; Pab, Pyrococcus abyssi; Pho, Pyrococcus horikoshii; Pse, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Sce, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Spo, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Ssp, Synechocystis sp.; Tma, Thermotoga maritima; Tpa, Treponema pallidum; Tth, Thermus thermophilus; Vch, Vibrio cholerae; Xfa, Xylella fastidiosa.
From: Horizontal Gene Transfer in Prokaryotes: Quantification and Classification

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.