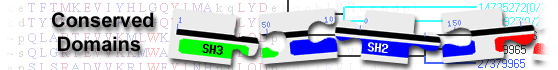UV radiation resistance-associated gene protein isoform X1 [Canis lupus familiaris]
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| VPS38 super family | cl39193 | Vacuolar protein sorting 38; The class III phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) known as Vps34 ... |
39-437 | 1.14e-09 | |||||||
Vacuolar protein sorting 38; The class III phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) known as Vps34 (vacuolar protein sorting 34, encoded by PIK3C3) regulate intracellular membrane trafficking in endocytic sorting, cytokinesis and autophagy. Vps34 forms complexes with other proteins: Vps15 (encoded by PIK3R4, known as p150 in mammalian cells), Vps30 (encoded by VPS30/ATG6 in yeast, equivalent to mammalian Beclin 1, encoded by BECN1) and either Vps38 (UVRAG) or Atg14 (ATG14L). This family includes members such as Vps38 found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Vps38 is characteriztic of complex II and essential for vacuolar protein sorting. In mammalian cells, complex II is also involved in autophagy, receptor degradation and cytokinesis as well as signaling, recycling and lysosomal tubulation. Independently from complex I and II, Beclin 1 and UVRAG also play separate roles in endosome function and neuron viability. In complex I, Vps38/UVRAG is substituted with Atg14/ATG14L. Although the N-terminal domains of Vps30, Vps38 and Atg14 differ, the overall similarity of their domain organizations suggests that these proteins may have evolved from a common ancestor. The actual alignment was detected with superfamily member pfam17649: Pssm-ID: 435943 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 425 Bit Score: 61.20 E-value: 1.14e-09
|
|||||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| VPS38 | pfam17649 | Vacuolar protein sorting 38; The class III phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) known as Vps34 ... |
39-437 | 1.14e-09 | |||||||
Vacuolar protein sorting 38; The class III phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) known as Vps34 (vacuolar protein sorting 34, encoded by PIK3C3) regulate intracellular membrane trafficking in endocytic sorting, cytokinesis and autophagy. Vps34 forms complexes with other proteins: Vps15 (encoded by PIK3R4, known as p150 in mammalian cells), Vps30 (encoded by VPS30/ATG6 in yeast, equivalent to mammalian Beclin 1, encoded by BECN1) and either Vps38 (UVRAG) or Atg14 (ATG14L). This family includes members such as Vps38 found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Vps38 is characteriztic of complex II and essential for vacuolar protein sorting. In mammalian cells, complex II is also involved in autophagy, receptor degradation and cytokinesis as well as signaling, recycling and lysosomal tubulation. Independently from complex I and II, Beclin 1 and UVRAG also play separate roles in endosome function and neuron viability. In complex I, Vps38/UVRAG is substituted with Atg14/ATG14L. Although the N-terminal domains of Vps30, Vps38 and Atg14 differ, the overall similarity of their domain organizations suggests that these proteins may have evolved from a common ancestor. Pssm-ID: 435943 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 425 Bit Score: 61.20 E-value: 1.14e-09
|
|||||||||||
| C2 | cd00030 | C2 domain; The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed ... |
44-118 | 1.17e-06 | |||||||
C2 domain; The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 175973 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 102 Bit Score: 47.45 E-value: 1.17e-06
|
|||||||||||
| C2 | smart00239 | Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, ... |
44-137 | 7.13e-06 | |||||||
Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, protein kinases C, and synaptotagmins (among others). Some do not appear to contain Ca2+-binding sites. Particular C2s appear to bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Unusual occurrence in perforin. Synaptotagmin and PLC C2s are permuted in sequence with respect to N- and C-terminal beta strands. SMART detects C2 domains using one or both of two profiles. Pssm-ID: 214577 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 101 Bit Score: 45.17 E-value: 7.13e-06
|
|||||||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||||||
| VPS38 | pfam17649 | Vacuolar protein sorting 38; The class III phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) known as Vps34 ... |
39-437 | 1.14e-09 | |||||||
Vacuolar protein sorting 38; The class III phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) known as Vps34 (vacuolar protein sorting 34, encoded by PIK3C3) regulate intracellular membrane trafficking in endocytic sorting, cytokinesis and autophagy. Vps34 forms complexes with other proteins: Vps15 (encoded by PIK3R4, known as p150 in mammalian cells), Vps30 (encoded by VPS30/ATG6 in yeast, equivalent to mammalian Beclin 1, encoded by BECN1) and either Vps38 (UVRAG) or Atg14 (ATG14L). This family includes members such as Vps38 found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Vps38 is characteriztic of complex II and essential for vacuolar protein sorting. In mammalian cells, complex II is also involved in autophagy, receptor degradation and cytokinesis as well as signaling, recycling and lysosomal tubulation. Independently from complex I and II, Beclin 1 and UVRAG also play separate roles in endosome function and neuron viability. In complex I, Vps38/UVRAG is substituted with Atg14/ATG14L. Although the N-terminal domains of Vps30, Vps38 and Atg14 differ, the overall similarity of their domain organizations suggests that these proteins may have evolved from a common ancestor. Pssm-ID: 435943 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 425 Bit Score: 61.20 E-value: 1.14e-09
|
|||||||||||
| ATG14 | pfam10186 | Vacuolar sorting 38 and autophagy-related subunit 14; The Atg14 or Apg14 proteins are ... |
184-449 | 4.72e-09 | |||||||
Vacuolar sorting 38 and autophagy-related subunit 14; The Atg14 or Apg14 proteins are hydrophilic proteins with a predicted molecular mass of 40.5 kDa, and have a coiled-coil motif at the N terminus region. Yeast cells with mutant Atg14 are defective not only in autophagy but also in sorting of carboxypeptidase Y (CPY), a vacuolar-soluble hydrolase, to the vacuole. Subcellular fractionation indicate that Apg14p and Apg6p are peripherally associated with a membrane structure(s). Apg14p was co-immunoprecipitated with Apg6p, suggesting that they form a stable protein complex. These results imply that Apg6/Vps30p has two distinct functions: in the autophagic process and in the vacuolar protein sorting pathway. Apg14p may be a component specifically required for the function of Apg6/Vps30p through the autophagic pathway. There are 17 auto-phagosomal component proteins which are categorized into six functional units, one of which is the AS-PI3K complex (Vps30/Atg6 and Atg14). The AS-PI3K complex and the Atg2-Atg18 complex are essential for nucleation, and the specific function of the AS-PI3K apparently is to produce phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) at the pre-autophagosomal structure (PAS). The localization of this complex at the PAS is controlled by Atg14. Autophagy mediates the cellular response to nutrient deprivation, protein aggregation, and pathogen invasion in humans, and malfunction of autophagy has been implicated in multiple human diseases including cancer. This effect seems to be mediated through direct interaction of the human Atg14 with Beclin 1 in the human phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase class III complex. Pssm-ID: 462986 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 347 Bit Score: 58.62 E-value: 4.72e-09
|
|||||||||||
| C2 | cd00030 | C2 domain; The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed ... |
44-118 | 1.17e-06 | |||||||
C2 domain; The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 175973 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 102 Bit Score: 47.45 E-value: 1.17e-06
|
|||||||||||
| C2 | smart00239 | Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, ... |
44-137 | 7.13e-06 | |||||||
Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (CalB); Ca2+-binding motif present in phospholipases, protein kinases C, and synaptotagmins (among others). Some do not appear to contain Ca2+-binding sites. Particular C2s appear to bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Unusual occurrence in perforin. Synaptotagmin and PLC C2s are permuted in sequence with respect to N- and C-terminal beta strands. SMART detects C2 domains using one or both of two profiles. Pssm-ID: 214577 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 101 Bit Score: 45.17 E-value: 7.13e-06
|
|||||||||||
| C2B_Copine | cd04047 | C2 domain second repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a ... |
48-95 | 3.80e-05 | |||||||
C2 domain second repeat in Copine; There are 2 copies of the C2 domain present in copine, a protein involved in membrane trafficking, protein-protein interactions, and perhaps even cell division and growth. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 176012 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 110 Bit Score: 43.32 E-value: 3.80e-05
|
|||||||||||
| C2D_Tricalbin-like | cd04040 | C2 domain fourth repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are ... |
48-123 | 4.27e-05 | |||||||
C2 domain fourth repeat present in Tricalbin-like proteins; 5 to 6 copies of the C2 domain are present in Tricalbin, a yeast homolog of Synaptotagmin, which is involved in membrane trafficking and sorting. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the fifth C2 repeat, C2E, and has a type-II topology. Pssm-ID: 176005 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 115 Bit Score: 43.33 E-value: 4.27e-05
|
|||||||||||
| C2 | pfam00168 | C2 domain; |
44-94 | 7.32e-04 | |||||||
C2 domain; Pssm-ID: 425499 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 104 Bit Score: 39.61 E-value: 7.32e-04
|
|||||||||||
| C2B_Synaptotagmin | cd00276 | C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmin; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking ... |
48-115 | 1.83e-03 | |||||||
C2 domain second repeat present in Synaptotagmin; Synaptotagmin is a membrane-trafficking protein characterized by a N-terminal transmembrane region, a linker, and 2 C-terminal C2 domains. There are several classes of Synaptotagmins. Previously all synaptotagmins were thought to be calcium sensors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion, but it has been shown that not all of them bind calcium. Of the 17 identified synaptotagmins only 8 bind calcium (1-3, 5-7, 9, 10). The function of the two C2 domains that bind calcium are: regulating the fusion step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis (C2A) and binding to phosphatidyl-inositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) in the absence of calcium ions and to phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) in their presence (C2B). C2B also regulates also the recycling step of synaptic vesicles. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. This cd contains the second C2 repeat, C2B, and has a type-I topology. Pssm-ID: 175975 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 134 Bit Score: 39.10 E-value: 1.83e-03
|
|||||||||||
| C2_KIAA0528-like | cd08688 | C2 domain found in the Human KIAA0528 cDNA clone; The members of this CD are named after the ... |
46-99 | 3.73e-03 | |||||||
C2 domain found in the Human KIAA0528 cDNA clone; The members of this CD are named after the Human KIAA0528 cDNA clone. All members here contain a single C2 repeat. No other information on this protein is currently known. The C2 domain was first identified in PKC. C2 domains fold into an 8-standed beta-sandwich that can adopt 2 structural arrangements: Type I and Type II, distinguished by a circular permutation involving their N- and C-terminal beta strands. Many C2 domains are Ca2+-dependent membrane-targeting modules that bind a wide variety of substances including bind phospholipids, inositol polyphosphates, and intracellular proteins. Most C2 domain proteins are either signal transduction enzymes that contain a single C2 domain, such as protein kinase C, or membrane trafficking proteins which contain at least two C2 domains, such as synaptotagmin 1. However, there are a few exceptions to this including RIM isoforms and some splice variants of piccolo/aczonin and intersectin which only have a single C2 domain. C2 domains with a calcium binding region have negatively charged residues, primarily aspartates, that serve as ligands for calcium ions. Pssm-ID: 176070 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 110 Bit Score: 37.67 E-value: 3.73e-03
|
|||||||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|