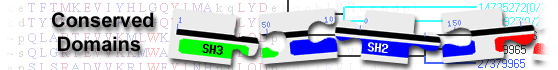Krueppel-like factor 6 [Acyrthosiphon pisum]
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| KLF6_7_N-like | cd21973 | N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins; This subfamily ... |
2-71 | 5.43e-40 | |||
N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins; This subfamily is composed of Kruppel-like factor or Krueppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins, including KLF Luna, a Drosophila KLF6/KLF7. KLF6 contributes to cell proliferation, differentiation, cell death and signal transduction. Hepatocyte expression of KLF6 regulates hepatic fatty acid and glucose metabolism via transcriptional activation of liver glucokinase and post-transcriptional regulation of the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARa). KLF7 is involved in regulation of the development and function of the nervous system and adipose tissue, type 2 diabetes, blood diseases, as well as pluripotent cell maintenance. KLF Luna is maternally required for synchronized nuclear and centrosome cycles in the preblastoderm embryo. KLF6 and KLF7 are transcriptional activators. They belong to a family of proteins, called the Specificity Protein (SP)/KLF family, characterized by a C-terminal DNA-binding domain of 81 amino acids consisting of three Kruppel-like C2H2 zinc fingers. These factors bind to a loose consensus motif, namely NNRCRCCYY (where N is any nucleotide; R is A/G, and Y is C/T), such as the recurring motifs in GC and GT boxes (5'-GGGGCGGGG-3' and 5-GGTGTGGGG-3') that are present in promoters and more distal regulatory elements of mammalian genes. Members of the KLF family can act as activators or repressors of transcription depending on cell and promoter context. KLFs regulate various cellular functions, such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as the development and homeostasis of several types of tissue. In addition to the C-terminal DNA-binding domain, each KLF also has a unique N-terminal activation/repression domain that confers specificity and allows it to bind specifically to a certain partner, leading to distinct activities in vivo. This model represents the related N-terminal domains of KLF6, KLF7, and similar proteins. : Pssm-ID: 409246 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 138 Bit Score: 137.79 E-value: 5.43e-40
|
|||||||
| COG5048 | COG5048 | FOG: Zn-finger [General function prediction only]; |
239-338 | 9.81e-07 | |||
FOG: Zn-finger [General function prediction only]; : Pssm-ID: 227381 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 467 Bit Score: 50.46 E-value: 9.81e-07
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| KLF6_7_N-like | cd21973 | N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins; This subfamily ... |
2-71 | 5.43e-40 | |||
N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins; This subfamily is composed of Kruppel-like factor or Krueppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins, including KLF Luna, a Drosophila KLF6/KLF7. KLF6 contributes to cell proliferation, differentiation, cell death and signal transduction. Hepatocyte expression of KLF6 regulates hepatic fatty acid and glucose metabolism via transcriptional activation of liver glucokinase and post-transcriptional regulation of the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARa). KLF7 is involved in regulation of the development and function of the nervous system and adipose tissue, type 2 diabetes, blood diseases, as well as pluripotent cell maintenance. KLF Luna is maternally required for synchronized nuclear and centrosome cycles in the preblastoderm embryo. KLF6 and KLF7 are transcriptional activators. They belong to a family of proteins, called the Specificity Protein (SP)/KLF family, characterized by a C-terminal DNA-binding domain of 81 amino acids consisting of three Kruppel-like C2H2 zinc fingers. These factors bind to a loose consensus motif, namely NNRCRCCYY (where N is any nucleotide; R is A/G, and Y is C/T), such as the recurring motifs in GC and GT boxes (5'-GGGGCGGGG-3' and 5-GGTGTGGGG-3') that are present in promoters and more distal regulatory elements of mammalian genes. Members of the KLF family can act as activators or repressors of transcription depending on cell and promoter context. KLFs regulate various cellular functions, such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as the development and homeostasis of several types of tissue. In addition to the C-terminal DNA-binding domain, each KLF also has a unique N-terminal activation/repression domain that confers specificity and allows it to bind specifically to a certain partner, leading to distinct activities in vivo. This model represents the related N-terminal domains of KLF6, KLF7, and similar proteins. Pssm-ID: 409246 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 138 Bit Score: 137.79 E-value: 5.43e-40
|
|||||||
| COG5048 | COG5048 | FOG: Zn-finger [General function prediction only]; |
239-338 | 9.81e-07 | |||
FOG: Zn-finger [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 227381 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 467 Bit Score: 50.46 E-value: 9.81e-07
|
|||||||
| zf-H2C2_2 | pfam13465 | Zinc-finger double domain; |
312-337 | 6.02e-04 | |||
Zinc-finger double domain; Pssm-ID: 463886 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 26 Bit Score: 36.58 E-value: 6.02e-04
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| KLF6_7_N-like | cd21973 | N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins; This subfamily ... |
2-71 | 5.43e-40 | |||
N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins; This subfamily is composed of Kruppel-like factor or Krueppel-like factor (KLF) 6, KLF7, and similar proteins, including KLF Luna, a Drosophila KLF6/KLF7. KLF6 contributes to cell proliferation, differentiation, cell death and signal transduction. Hepatocyte expression of KLF6 regulates hepatic fatty acid and glucose metabolism via transcriptional activation of liver glucokinase and post-transcriptional regulation of the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARa). KLF7 is involved in regulation of the development and function of the nervous system and adipose tissue, type 2 diabetes, blood diseases, as well as pluripotent cell maintenance. KLF Luna is maternally required for synchronized nuclear and centrosome cycles in the preblastoderm embryo. KLF6 and KLF7 are transcriptional activators. They belong to a family of proteins, called the Specificity Protein (SP)/KLF family, characterized by a C-terminal DNA-binding domain of 81 amino acids consisting of three Kruppel-like C2H2 zinc fingers. These factors bind to a loose consensus motif, namely NNRCRCCYY (where N is any nucleotide; R is A/G, and Y is C/T), such as the recurring motifs in GC and GT boxes (5'-GGGGCGGGG-3' and 5-GGTGTGGGG-3') that are present in promoters and more distal regulatory elements of mammalian genes. Members of the KLF family can act as activators or repressors of transcription depending on cell and promoter context. KLFs regulate various cellular functions, such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as the development and homeostasis of several types of tissue. In addition to the C-terminal DNA-binding domain, each KLF also has a unique N-terminal activation/repression domain that confers specificity and allows it to bind specifically to a certain partner, leading to distinct activities in vivo. This model represents the related N-terminal domains of KLF6, KLF7, and similar proteins. Pssm-ID: 409246 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 138 Bit Score: 137.79 E-value: 5.43e-40
|
|||||||
| KLF6_N | cd21586 | N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor 6; Kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6; also known as ... |
2-60 | 6.90e-23 | |||
N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor 6; Kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6; also known as Krueppel-like factor 6, BCD1, CBA1, COPEB, CPBP, GBF, PAC1, ST12, or ZF9) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the KLF6 gene. KLF6 contributes to cell proliferation, differentiation, cell death, and signal transduction. Hepatocyte expression of KLF6 regulates hepatic fatty acid and glucose metabolism via transcriptional activation of liver glucokinase and post-transcriptional regulation of the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARa). KLF6-expression contributes to hepatic insulin resistance and the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and NASH-cirrhosis. KLF6 also affects peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma)-signaling in NAFLD. KLF6 has also been identified as a tumor suppressor gene that is inactivated or downregulated in different cancers, including prostate, colon, and hepatocellular carcinomas. KLF6 transactivates genes controlling cell proliferation, including p21, E-cadherin, and pituary tumor-transforming gene 1 (PTTG1). KLF6 functions as a transcriptional activator. It belongs to a family of proteins, called the Specificity Protein (SP)/KLF family, characterized by a C-terminal DNA-binding domain of 81 amino acids consisting of three Kruppel-like C2H2 zinc fingers. These factors bind to a loose consensus motif, namely NNRCRCCYY (where N is any nucleotide; R is A/G, and Y is C/T), such as the recurring motifs in GC and GT boxes (5'-GGGGCGGGG-3' and 5-GGTGTGGGG-3') that are present in promoters and more distal regulatory elements of mammalian genes. Members of the KLF family can act as activators or repressors of transcription depending on cell and promoter context. KLFs regulate various cellular functions, such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as the development and homeostasis of several types of tissue. In addition to the C-terminal DNA-binding domain, each KLF also has a unique N-terminal activation/repression domain that confers specificity and allows it to bind specifically to a certain partner, leading to distinct activities in vivo. This model represents the N-terminal domain of KLF6. Pssm-ID: 409245 Cd Length: 198 Bit Score: 94.37 E-value: 6.90e-23
|
|||||||
| KLF7_N | cd21585 | N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor 7; Kruppel-like factor 7 (KLF7; also known as ... |
2-47 | 9.76e-22 | |||
N-terminal domain of Kruppel-like factor 7; Kruppel-like factor 7 (KLF7; also known as Krueppel-like factor 7, or ubiquitous Kruppel-like factor/UKLF) is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the KLF7 gene. KLF7 is involved in regulation of the development and function of the nervous system and adipose tissue, type 2 diabetes, blood diseases, as well as pluripotent cell maintenance. It functions as a transcriptional activator. It belongs to a family of proteins, called the Specificity Protein (SP)/KLF family, characterized by a C-terminal DNA-binding domain of 81 amino acids consisting of three Kruppel-like C2H2 zinc fingers. These factors bind to a loose consensus motif, namely NNRCRCCYY (where N is any nucleotide; R is A/G, and Y is C/T), such as the recurring motifs in GC and GT boxes (5'-GGGGCGGGG-3' and 5-GGTGTGGGG-3') that are present in promoters and more distal regulatory elements of mammalian genes. Members of the KLF family can act as activators or repressors of transcription depending on cell and promoter context. KLFs regulate various cellular functions, such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as the development and homeostasis of several types of tissue. In addition to the C-terminal DNA-binding domain, each KLF also has a unique N-terminal activation/repression domain that confers specificity and allows it to bind specifically to a certain partner, leading to distinct activities in vivo. This model represents the N-terminal domain of KLF7. Pssm-ID: 409244 Cd Length: 160 Bit Score: 90.25 E-value: 9.76e-22
|
|||||||
| COG5048 | COG5048 | FOG: Zn-finger [General function prediction only]; |
239-338 | 9.81e-07 | |||
FOG: Zn-finger [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 227381 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 467 Bit Score: 50.46 E-value: 9.81e-07
|
|||||||
| COG5048 | COG5048 | FOG: Zn-finger [General function prediction only]; |
252-331 | 7.46e-06 | |||
FOG: Zn-finger [General function prediction only]; Pssm-ID: 227381 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 467 Bit Score: 47.38 E-value: 7.46e-06
|
|||||||
| zf-H2C2_2 | pfam13465 | Zinc-finger double domain; |
312-337 | 6.02e-04 | |||
Zinc-finger double domain; Pssm-ID: 463886 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 26 Bit Score: 36.58 E-value: 6.02e-04
|
|||||||
| zf-C2H2_8 | pfam15909 | C2H2-type zinc ribbon; This family carries three zinc-fingers in tandem. |
268-348 | 1.53e-03 | |||
C2H2-type zinc ribbon; This family carries three zinc-fingers in tandem. Pssm-ID: 464935 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 98 Bit Score: 37.40 E-value: 1.53e-03
|
|||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|