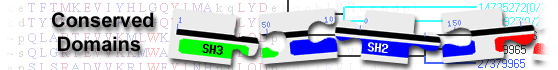pico, isoform A [Drosophila melanogaster]
RA_MRL_MIG10 and PH_APBB1IP domain-containing protein( domain architecture ID 13006522)
RA_MRL_MIG10 and PH_APBB1IP domain-containing protein
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| PH_APBB1IP | cd01259 | Amyloid beta (A4) Precursor protein-Binding, family B, member 1 Interacting Protein pleckstrin ... |
489-614 | 1.88e-52 | |||
Amyloid beta (A4) Precursor protein-Binding, family B, member 1 Interacting Protein pleckstrin homology (PH) domain; APBB1IP consists of a Ras-associated (RA) domain, a PH domain, a family-specific BPS region, and a C-terminal SH2 domain. Grb7, Grb10 and Grb14 are paralogs that are also present in this hierarchy. These adapter proteins bind a variety of receptor tyrosine kinases, including the insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) receptors. Grb10 and Grb14 are important tissue-specific negative regulators of insulin and IGF1 signaling based and may contribute to type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes in humans. RA-PH function as a single structural unit and is dimerized via a helical extension of the PH domain. The PH domain here are proposed to bind phosphoinositides non-cannonically ahd are unlikely to bind an activated GTPase. The tandem RA-PH domains are present in a second adapter-protein family, MRL proteins, Caenorhabditis elegans protein MIG-1012, the mammalian proteins RIAM and lamellipodin and the Drosophila melanogaster protein Pico12, all of which are Ena/VASP-binding proteins involved in actin-cytoskeleton rearrangement. PH domains have diverse functions, but in general are involved in targeting proteins to the appropriate cellular location or in the interaction with a binding partner. They share little sequence conservation, but all have a common fold, which is electrostatically polarized. Less than 10% of PH domains bind phosphoinositide phosphates (PIPs) with high affinity and specificity. PH domains are distinguished from other PIP-binding domains by their specific high-affinity binding to PIPs with two vicinal phosphate groups: PtdIns(3,4)P2, PtdIns(4,5)P2 or PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 which results in targeting some PH domain proteins to the plasma membrane. A few display strong specificity in lipid binding. Any specificity is usually determined by loop regions or insertions in the N-terminus of the domain, which are not conserved across all PH domains. PH domains are found in cellular signaling proteins such as serine/threonine kinase, tyrosine kinases, regulators of G-proteins, endocytotic GTPases, adaptors, as well as cytoskeletal associated molecules and in lipid associated enzymes. : Pssm-ID: 269961 Cd Length: 124 Bit Score: 179.74 E-value: 1.88e-52
|
|||||||
| RA_MRL_MIG10 | cd16138 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Caenorhabditis elegans abnormal cell migration protein 10 ... |
366-451 | 5.86e-51 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Caenorhabditis elegans abnormal cell migration protein 10 (MIG-10) and similar proteins; MIG-10 is lamellipodin (Lpd) found in C. elegans. It stabilizes invading cell adhesion to basement membrane and is a negative transcriptional target of Evi-1 proto-oncogene, EGL-43, in C. elegans. It also shows netrin-independent functions and is a transcriptional target of FOS-1A, a transcription factor that promotes basement membrane breaching, during anchor cell invasion in C. elegans. MIG-10 is a member of MRL (Mig10/RIAM/Lpd) family of proteins that is involved in antero-posterior migration of embryonic neurons CAN (canalassociated neurons), ALM (anterior lateral microtubule cells) and HSN (hermaphrodite-specific neurons). MRL proteins share a common structural architecture, including a central structural unit consisting of an RA domain and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, an upstream coiled-coil region, and a number of polyproline motifs. RA domain-containing proteins function by interacting with Ras proteins directly or indirectly and are involved in several different functions ranging from tumor suppression to being oncoproteins. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. RA and PH form a tandem domain pair (RA-PH), and serve tightly coordinated functions in both Ras GTPase signaling via the RA domain and membrane translocalization via the PH domain. : Pssm-ID: 340555 Cd Length: 86 Bit Score: 173.79 E-value: 5.86e-51
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| PH_APBB1IP | cd01259 | Amyloid beta (A4) Precursor protein-Binding, family B, member 1 Interacting Protein pleckstrin ... |
489-614 | 1.88e-52 | |||
Amyloid beta (A4) Precursor protein-Binding, family B, member 1 Interacting Protein pleckstrin homology (PH) domain; APBB1IP consists of a Ras-associated (RA) domain, a PH domain, a family-specific BPS region, and a C-terminal SH2 domain. Grb7, Grb10 and Grb14 are paralogs that are also present in this hierarchy. These adapter proteins bind a variety of receptor tyrosine kinases, including the insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) receptors. Grb10 and Grb14 are important tissue-specific negative regulators of insulin and IGF1 signaling based and may contribute to type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes in humans. RA-PH function as a single structural unit and is dimerized via a helical extension of the PH domain. The PH domain here are proposed to bind phosphoinositides non-cannonically ahd are unlikely to bind an activated GTPase. The tandem RA-PH domains are present in a second adapter-protein family, MRL proteins, Caenorhabditis elegans protein MIG-1012, the mammalian proteins RIAM and lamellipodin and the Drosophila melanogaster protein Pico12, all of which are Ena/VASP-binding proteins involved in actin-cytoskeleton rearrangement. PH domains have diverse functions, but in general are involved in targeting proteins to the appropriate cellular location or in the interaction with a binding partner. They share little sequence conservation, but all have a common fold, which is electrostatically polarized. Less than 10% of PH domains bind phosphoinositide phosphates (PIPs) with high affinity and specificity. PH domains are distinguished from other PIP-binding domains by their specific high-affinity binding to PIPs with two vicinal phosphate groups: PtdIns(3,4)P2, PtdIns(4,5)P2 or PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 which results in targeting some PH domain proteins to the plasma membrane. A few display strong specificity in lipid binding. Any specificity is usually determined by loop regions or insertions in the N-terminus of the domain, which are not conserved across all PH domains. PH domains are found in cellular signaling proteins such as serine/threonine kinase, tyrosine kinases, regulators of G-proteins, endocytotic GTPases, adaptors, as well as cytoskeletal associated molecules and in lipid associated enzymes. Pssm-ID: 269961 Cd Length: 124 Bit Score: 179.74 E-value: 1.88e-52
|
|||||||
| RA_MRL_MIG10 | cd16138 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Caenorhabditis elegans abnormal cell migration protein 10 ... |
366-451 | 5.86e-51 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Caenorhabditis elegans abnormal cell migration protein 10 (MIG-10) and similar proteins; MIG-10 is lamellipodin (Lpd) found in C. elegans. It stabilizes invading cell adhesion to basement membrane and is a negative transcriptional target of Evi-1 proto-oncogene, EGL-43, in C. elegans. It also shows netrin-independent functions and is a transcriptional target of FOS-1A, a transcription factor that promotes basement membrane breaching, during anchor cell invasion in C. elegans. MIG-10 is a member of MRL (Mig10/RIAM/Lpd) family of proteins that is involved in antero-posterior migration of embryonic neurons CAN (canalassociated neurons), ALM (anterior lateral microtubule cells) and HSN (hermaphrodite-specific neurons). MRL proteins share a common structural architecture, including a central structural unit consisting of an RA domain and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, an upstream coiled-coil region, and a number of polyproline motifs. RA domain-containing proteins function by interacting with Ras proteins directly or indirectly and are involved in several different functions ranging from tumor suppression to being oncoproteins. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. RA and PH form a tandem domain pair (RA-PH), and serve tightly coordinated functions in both Ras GTPase signaling via the RA domain and membrane translocalization via the PH domain. Pssm-ID: 340555 Cd Length: 86 Bit Score: 173.79 E-value: 5.86e-51
|
|||||||
| RA | pfam00788 | Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain; RasGTP effectors (in cases of AF6, canoe and RalGDS); ... |
367-452 | 1.02e-15 | |||
Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain; RasGTP effectors (in cases of AF6, canoe and RalGDS); putative RasGTP effectors in other cases. Recent evidence (not yet in MEDLINE) shows that some RA domains do NOT bind RasGTP. Predicted structure similar to that determined, and that of the RasGTP-binding domain of Raf kinase. Pssm-ID: 425871 Cd Length: 93 Bit Score: 73.52 E-value: 1.02e-15
|
|||||||
| PH | smart00233 | Pleckstrin homology domain; Domain commonly found in eukaryotic signalling proteins. The ... |
494-601 | 1.09e-07 | |||
Pleckstrin homology domain; Domain commonly found in eukaryotic signalling proteins. The domain family possesses multiple functions including the abilities to bind inositol phosphates, and various proteins. PH domains have been found to possess inserted domains (such as in PLC gamma, syntrophins) and to be inserted within other domains. Mutations in Brutons tyrosine kinase (Btk) within its PH domain cause X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA) in patients. Point mutations cluster into the positively charged end of the molecule around the predicted binding site for phosphatidylinositol lipids. Pssm-ID: 214574 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 102 Bit Score: 51.01 E-value: 1.09e-07
|
|||||||
| RA | smart00314 | Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain; RasGTP effectors (in cases of AF6, canoe and RalGDS); ... |
372-451 | 8.06e-07 | |||
Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain; RasGTP effectors (in cases of AF6, canoe and RalGDS); putative RasGTP effectors in other cases. Kalhammer et al. have shown that not all RA domains bind RasGTP. Predicted structure similar to that determined, and that of the RasGTP-binding domain of Raf kinase. Predicted RA domains in PLC210 and nore1 found to bind RasGTP. Included outliers (Grb7, Grb14, adenylyl cyclases etc.) Pssm-ID: 214612 Cd Length: 90 Bit Score: 48.06 E-value: 8.06e-07
|
|||||||
| PH | pfam00169 | PH domain; PH stands for pleckstrin homology. |
494-605 | 1.52e-04 | |||
PH domain; PH stands for pleckstrin homology. Pssm-ID: 459697 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 105 Bit Score: 42.16 E-value: 1.52e-04
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| PH_APBB1IP | cd01259 | Amyloid beta (A4) Precursor protein-Binding, family B, member 1 Interacting Protein pleckstrin ... |
489-614 | 1.88e-52 | |||
Amyloid beta (A4) Precursor protein-Binding, family B, member 1 Interacting Protein pleckstrin homology (PH) domain; APBB1IP consists of a Ras-associated (RA) domain, a PH domain, a family-specific BPS region, and a C-terminal SH2 domain. Grb7, Grb10 and Grb14 are paralogs that are also present in this hierarchy. These adapter proteins bind a variety of receptor tyrosine kinases, including the insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) receptors. Grb10 and Grb14 are important tissue-specific negative regulators of insulin and IGF1 signaling based and may contribute to type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes in humans. RA-PH function as a single structural unit and is dimerized via a helical extension of the PH domain. The PH domain here are proposed to bind phosphoinositides non-cannonically ahd are unlikely to bind an activated GTPase. The tandem RA-PH domains are present in a second adapter-protein family, MRL proteins, Caenorhabditis elegans protein MIG-1012, the mammalian proteins RIAM and lamellipodin and the Drosophila melanogaster protein Pico12, all of which are Ena/VASP-binding proteins involved in actin-cytoskeleton rearrangement. PH domains have diverse functions, but in general are involved in targeting proteins to the appropriate cellular location or in the interaction with a binding partner. They share little sequence conservation, but all have a common fold, which is electrostatically polarized. Less than 10% of PH domains bind phosphoinositide phosphates (PIPs) with high affinity and specificity. PH domains are distinguished from other PIP-binding domains by their specific high-affinity binding to PIPs with two vicinal phosphate groups: PtdIns(3,4)P2, PtdIns(4,5)P2 or PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 which results in targeting some PH domain proteins to the plasma membrane. A few display strong specificity in lipid binding. Any specificity is usually determined by loop regions or insertions in the N-terminus of the domain, which are not conserved across all PH domains. PH domains are found in cellular signaling proteins such as serine/threonine kinase, tyrosine kinases, regulators of G-proteins, endocytotic GTPases, adaptors, as well as cytoskeletal associated molecules and in lipid associated enzymes. Pssm-ID: 269961 Cd Length: 124 Bit Score: 179.74 E-value: 1.88e-52
|
|||||||
| RA_MRL_MIG10 | cd16138 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Caenorhabditis elegans abnormal cell migration protein 10 ... |
366-451 | 5.86e-51 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Caenorhabditis elegans abnormal cell migration protein 10 (MIG-10) and similar proteins; MIG-10 is lamellipodin (Lpd) found in C. elegans. It stabilizes invading cell adhesion to basement membrane and is a negative transcriptional target of Evi-1 proto-oncogene, EGL-43, in C. elegans. It also shows netrin-independent functions and is a transcriptional target of FOS-1A, a transcription factor that promotes basement membrane breaching, during anchor cell invasion in C. elegans. MIG-10 is a member of MRL (Mig10/RIAM/Lpd) family of proteins that is involved in antero-posterior migration of embryonic neurons CAN (canalassociated neurons), ALM (anterior lateral microtubule cells) and HSN (hermaphrodite-specific neurons). MRL proteins share a common structural architecture, including a central structural unit consisting of an RA domain and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, an upstream coiled-coil region, and a number of polyproline motifs. RA domain-containing proteins function by interacting with Ras proteins directly or indirectly and are involved in several different functions ranging from tumor suppression to being oncoproteins. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. RA and PH form a tandem domain pair (RA-PH), and serve tightly coordinated functions in both Ras GTPase signaling via the RA domain and membrane translocalization via the PH domain. Pssm-ID: 340555 Cd Length: 86 Bit Score: 173.79 E-value: 5.86e-51
|
|||||||
| RA_MRL | cd01787 | Ras-associating (RA) domain of Mig10/RIAM/Lpd (MRL) family; MRL proteins share a common ... |
367-451 | 7.68e-34 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain of Mig10/RIAM/Lpd (MRL) family; MRL proteins share a common structural architecture, including a central structural unit consisting of a Ras-associating (RA) domain and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, an upstream coiled-coil region, and a number of polyproline motifs. RA domain-containing proteins function by interacting with Ras proteins directly or indirectly and are involved in several different functions ranging from tumor suppression to being oncoproteins. Ras proteins are small GTPases that are involved in cellular signal transduction. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. RA and PH form a tandem domain pair (RA-PH), and serve tightly coordinated functions in both Ras GTPase signaling via the RA domain and membrane translocalization via the PH domain. MRL proteins have distinct functions in cell migration and adhesion, signaling, and in cell growth. Pssm-ID: 340485 Cd Length: 85 Bit Score: 124.84 E-value: 7.68e-34
|
|||||||
| RA_MRL_like | cd17112 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Mig10/RIAM/Lpd (MRL) family and growth factor ... |
370-449 | 5.13e-23 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Mig10/RIAM/Lpd (MRL) family and growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 7/10/14; MRL proteins share a common structural architecture, including a central structural unit consisting of a Ras-associating (RA) domain and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, an upstream coiled-coil region, and a number of polyproline motifs. RA domain-containing proteins function by interacting with Ras proteins directly or indirectly and are involved in several different functions ranging from tumor suppression to being oncoproteins. Ras proteins are small GTPases that are involved in cellular signal transduction. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like (Ubl) fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. RA and PH form a tandem domain pair (RA-PH), and serve tightly coordinated functions in both Ras GTPase signaling via the RA domain and membrane translocalization via the PH domain. MRL proteins have distinct functions in cell migration and adhesion, signaling, and in cell growth. Grb7/10/14 are multi-domain cytoplasmic adaptor proteins that are recruited to activated receptor tyrosine kinases. Grb7 and its related family members Grb10 and Grb14 share a conserved domain architecture that includes an amino-terminal proline-rich region, a central segment termed the GM region (for Grb and Mig) which includes the RA, PIR, and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains, and a carboxyl-terminal SH2 domain. The tandem RA and PH domains of Grb7/10/14 are also found in a second adaptor family, Rap1-interacting adaptor molecule (RIAM) and lamellipodin, which is involved in actin-cytoskeleton rearrangement. Grb7/10/14 family proteins are phosphorylated on serine/threonine as well as tyrosine residues and are mainly localized to the cytoplasm. Pssm-ID: 340632 Cd Length: 81 Bit Score: 93.89 E-value: 5.13e-23
|
|||||||
| RA_MRL_Lpd | cd16136 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in the adapter protein lamellipodin (Lpd); Lpd, also termed ... |
365-453 | 1.20e-22 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in the adapter protein lamellipodin (Lpd); Lpd, also termed Ras-associated and pleckstrin homology domains-containing protein 1 (RAPH1), or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 chromosomal region candidate gene 18 protein, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 chromosomal region candidate gene 9 protein, or proline-rich EVH1 ligand 2 (PREL-2), or protein RMO1, is a member of MRL (Mig10/RIAM/Lpd) family proteins that regulates cell migration and promote lamellipodia protrusion in fibroblast by interacting with Ena/VASP proteins. MRL proteins share a common structural architecture, including a central structural unit consisting of an RA domain and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, an upstream coiled-coil region, and a number of polyproline motifs. Lpd also contains a helical region at the amino terminus for talin binding. RA domain-containing proteins function by interacting with Ras proteins directly or indirectly and are involved in several different functions ranging from tumor suppression to being oncoproteins. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. RA and PH domain in Lpd form a tandem domain pair (RA-PH), and serve tightly coordinated functions in both Ras GTPase signaling via the RA domain and membrane translocalization via the PH domain. Lpd also exhibits other unique enzymatic functions including its catalytic activity of butyrylcholinesterase, a potent therapeutic treatment targeting cocaine abuse. Pssm-ID: 340553 Cd Length: 90 Bit Score: 93.23 E-value: 1.20e-22
|
|||||||
| RA_MRL_RIAM | cd16137 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Rap1-GTP-interacting adapter molecule (RIAM); RIAM, also ... |
366-453 | 1.58e-17 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in Rap1-GTP-interacting adapter molecule (RIAM); RIAM, also termed amyloid beta A4 precursor protein-binding family B member 1-interacting protein, or APBB1-interacting protein 1, or proline-rich EVH1 ligand 1 (PREL-1), or proline-rich protein 73, or retinoic acid-responsive proline-rich protein 1 (RARP-1), is a member of MRL (Mig10/RIAM/Lpd) family proteins that regulates cell migration and promote lamellipodia protrusion in fibroblast by interacting with Ena/VASP proteins. RIAM regulates cell migration and mediates Rap1-induced cell adhesion. MRL proteins share a common structural architecture, including a central structural unit consisting of an RA domain and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, an upstream coiled-coil region, and a number of polyproline motifs. RA domain-containing proteins function by interacting with Ras proteins directly or indirectly and are involved in several different functions ranging from tumor suppression to being oncoproteins. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. RIAM also contains a helical region at the amino terminus for talin binding. RA and PH form a tandem domain pair (RA-PH), and serve tightly coordinated functions in both Ras GTPase signaling via the RA domain and membrane translocalization via the PH domain. Pssm-ID: 340554 Cd Length: 89 Bit Score: 78.76 E-value: 1.58e-17
|
|||||||
| RA | pfam00788 | Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain; RasGTP effectors (in cases of AF6, canoe and RalGDS); ... |
367-452 | 1.02e-15 | |||
Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain; RasGTP effectors (in cases of AF6, canoe and RalGDS); putative RasGTP effectors in other cases. Recent evidence (not yet in MEDLINE) shows that some RA domains do NOT bind RasGTP. Predicted structure similar to that determined, and that of the RasGTP-binding domain of Raf kinase. Pssm-ID: 425871 Cd Length: 93 Bit Score: 73.52 E-value: 1.02e-15
|
|||||||
| RA_GRB7_10_14 | cd16124 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 7/10/14; The ... |
370-449 | 1.98e-14 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 7/10/14; The RA domain is highly conserved among the members of the Grb proteins family which includes Grb7, Grb10 and Grb14. Grb7/10/14 are multi-domain cytoplasmic adaptor proteins that are recruited to activated receptor tyrosine kinases. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. Grb7 and its related family members Grb10 and Grb14 share a conserved domain architecture that includes an amino-terminal proline-rich region, a central segment termed the GM region (for Grb and Mig) which includes the RA, PIR, and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains, and a carboxyl-terminal SH2 domain. The tandem RA and PH domains of Grb7/10/14 are also found in a second adaptor family, Rap1-interacting adaptor molecule (RIAM) and lamellipodin, which is involved in actin-cytoskeleton rearrangement. Grb7/10/14 family proteins are phosphorylated on serine/threonine as well as tyrosine residues and are mainly localized to the cytoplasm. Pssm-ID: 340541 Cd Length: 85 Bit Score: 69.58 E-value: 1.98e-14
|
|||||||
| RA_GRB7 | cd16140 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 7; GRB7, also ... |
370-449 | 6.86e-13 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 7; GRB7, also termed B47, or epidermal growth factor receptor GRB-7, or GRB7 adapter protein, is a signal-transducing cytoplasmic adaptor protein that is co-opted by numerous tyrosine kinases involved in various cellular signaling and functions. Grb7 and its related family members Grb10 and Grb14 share a conserved domain architecture that includes an amino-terminal proline-rich region, a central segment termed the GM region (for Grb and Mig) which includes the RA, PIR, and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains, and a carboxyl-terminal SH2 domain. The tandem RA and PH domains of Grb7/10/14 are also found in a second adaptor family, Rap1-interacting adaptor molecule (RIAM) and lamellipodin, which is involved in actin-cytoskeleton rearrangement. Grb7/10/14 family proteins are phosphorylated on serine/threonine as well as tyrosine residues and are mainly localized to the cytoplasm. Grb7 could interact with activated N-Ras in transfected cells. Pssm-ID: 340557 Cd Length: 88 Bit Score: 65.25 E-value: 6.86e-13
|
|||||||
| RA_GRB14 | cd16139 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 14; Grb14, a ... |
370-449 | 5.24e-12 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 14; Grb14, a member of cytoplasmic adaptor proteins, is a tissue-specific negative regulator of insulin signaling. RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub). Ubi is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair in eukaryotes. A novel function of Grb14 RA domain is to interact with the nucleotide binding pocket of a cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha subunit (CNGA1) and inhibits its activity. Grb7 and its related family members Grb10 and Grb14 share a conserved domain architecture that includes an amino-terminal proline-rich region, a central segment termed the GM region (for Grb and Mig) which includes the RA, PIR, and PH domains, and a carboxyl-terminal SH2 domain. Grb7/10/14 family proteins are phosphorylated on serine/threonine as well as tyrosine residues and are mainly localized to the cytoplasm. Pssm-ID: 340556 Cd Length: 85 Bit Score: 62.93 E-value: 5.24e-12
|
|||||||
| RA_GRB10 | cd16141 | Ras-associating (RA) domain found in growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 10; GRB10, ... |
370-457 | 4.60e-10 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain found in growth factor receptor-bound (Grb) protein 10; GRB10, also termed insulin receptor-binding protein Grb-IR, is a multi-domain cytoplasmic adaptor protein that binds to the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) and inhibits insulin signaling. Grb10 and its related family members Grb7 and Grb14 share a conserved domain architecture that includes an amino-terminal proline-rich region, a central segment termed the GM region (for Grb and Mig) which includes the RA, PIR, and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains, and a carboxyl-terminal SH2 domain. The tandem RA and PH domains of Grb7/10/14 are also found in a second adaptor family, Rap1-interacting adaptor molecule (RIAM) and lamellipodin, which is involved in actin-cytoskeleton rearrangement. Grb7/10/14 family proteins are phosphorylated on serine/threonine as well as tyrosine residues and are mainly localized to the cytoplasm. Grb14 binds to both GTPase-defective mutant Rab5 as well as CNGA1, whereas Grb10 binds only to GTP-bound form of active Rab5. Pssm-ID: 340558 Cd Length: 92 Bit Score: 57.57 E-value: 4.60e-10
|
|||||||
| PH | smart00233 | Pleckstrin homology domain; Domain commonly found in eukaryotic signalling proteins. The ... |
494-601 | 1.09e-07 | |||
Pleckstrin homology domain; Domain commonly found in eukaryotic signalling proteins. The domain family possesses multiple functions including the abilities to bind inositol phosphates, and various proteins. PH domains have been found to possess inserted domains (such as in PLC gamma, syntrophins) and to be inserted within other domains. Mutations in Brutons tyrosine kinase (Btk) within its PH domain cause X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA) in patients. Point mutations cluster into the positively charged end of the molecule around the predicted binding site for phosphatidylinositol lipids. Pssm-ID: 214574 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 102 Bit Score: 51.01 E-value: 1.09e-07
|
|||||||
| RA | smart00314 | Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain; RasGTP effectors (in cases of AF6, canoe and RalGDS); ... |
372-451 | 8.06e-07 | |||
Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain; RasGTP effectors (in cases of AF6, canoe and RalGDS); putative RasGTP effectors in other cases. Kalhammer et al. have shown that not all RA domains bind RasGTP. Predicted structure similar to that determined, and that of the RasGTP-binding domain of Raf kinase. Predicted RA domains in PLC210 and nore1 found to bind RasGTP. Included outliers (Grb7, Grb14, adenylyl cyclases etc.) Pssm-ID: 214612 Cd Length: 90 Bit Score: 48.06 E-value: 8.06e-07
|
|||||||
| RA | cd17043 | Ras-associating (RA) domain, structurally similar to a beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold; RA ... |
367-450 | 5.79e-06 | |||
Ras-associating (RA) domain, structurally similar to a beta-grasp ubiquitin-like fold; RA domain-containing proteins function by interacting with Ras proteins directly or indirectly and are involved in various functions ranging from tumor suppression to being oncoproteins. Ras proteins are small GTPases that are involved in cellular signal transduction. The RA domain has the beta-grasp ubiquitin-like (Ubl) fold with low sequence similarity to ubiquitin (Ub); Ub is a protein modifier in eukaryotes that is involved in various cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA repair. RA-containing proteins include RalGDS, AF6, RIN, RASSF1, SNX27, CYR1, STE50, and phospholipase C epsilon. Pssm-ID: 340563 Cd Length: 87 Bit Score: 45.77 E-value: 5.79e-06
|
|||||||
| PH | cd00821 | Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain; PH domains have diverse functions, but in general are ... |
496-600 | 2.70e-05 | |||
Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain; PH domains have diverse functions, but in general are involved in targeting proteins to the appropriate cellular location or in the interaction with a binding partner. They share little sequence conservation, but all have a common fold, which is electrostatically polarized. Less than 10% of PH domains bind phosphoinositide phosphates (PIPs) with high affinity and specificity. PH domains are distinguished from other PIP-binding domains by their specific high-affinity binding to PIPs with two vicinal phosphate groups: PtdIns(3,4)P2, PtdIns(4,5)P2 or PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 which results in targeting some PH domain proteins to the plasma membrane. A few display strong specificity in lipid binding. Any specificity is usually determined by loop regions or insertions in the N-terminus of the domain, which are not conserved across all PH domains. PH domains are found in cellular signaling proteins such as serine/threonine kinase, tyrosine kinases, regulators of G-proteins, endocytotic GTPases, adaptors, as well as cytoskeletal associated molecules and in lipid associated enzymes. Pssm-ID: 275388 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 92 Bit Score: 44.07 E-value: 2.70e-05
|
|||||||
| PH | pfam00169 | PH domain; PH stands for pleckstrin homology. |
494-605 | 1.52e-04 | |||
PH domain; PH stands for pleckstrin homology. Pssm-ID: 459697 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 105 Bit Score: 42.16 E-value: 1.52e-04
|
|||||||
| FERM_F1_DdMyo7_like | cd17208 | FERM (Four.1 protein, Ezrin, Radixin, Moesin) domain, F1 sub-domain, found in Dictyostelium ... |
366-437 | 3.02e-03 | |||
FERM (Four.1 protein, Ezrin, Radixin, Moesin) domain, F1 sub-domain, found in Dictyostelium discoideum Myosin-VIIa (DdMyo7) and similar proteins; DdMyo7, also termed Myosin-I heavy chain, or class VII unconventional myosin, or M7, plays a role in adhesion in Dictyostelium where it is a component of a complex of proteins that serve to link membrane receptors to the underlying actin cytoskeleton. It interacts with talinA, an actin-binding protein with a known role in cell-substrate adhesion. DdMyo7 is required for phagocytosis. It is also essential for the extension of filopodia, plasma membrane protrusions filled with parallel bundles of F-actin. Members in this family contain a myosin motor domain, two MyTH4 domains, two FERM (Band 4.1, ezrin, radixin, moesin) domains, and two Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains. Some family members contain an extra SH3 domain. Each FERM domain is made up of three sub-domains, F1, F2, and F3. This family corresponds to the F1 sub-domain, which is also called the N-terminal ubiquitin-like structural domain of the FERM domain (FERM_N). Pssm-ID: 340728 Cd Length: 98 Bit Score: 38.39 E-value: 3.02e-03
|
|||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|